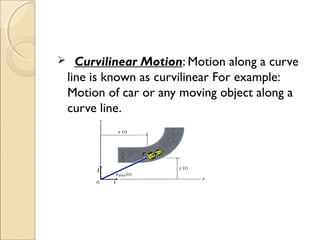
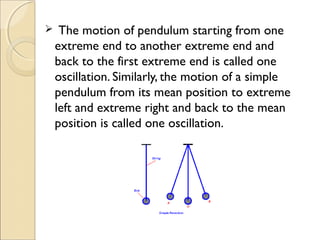
This document discusses different types of motion including rectilinear, curvilinear, and circular motion. It defines key concepts related to motion such as time period, speed, and periodic motion. Rectilinear motion refers to motion along a straight line, while curvilinear motion is along a curved line. Circular motion occurs along a circle. Time period is the time taken to complete one oscillation, and periodic motion repeats at fixed time intervals. Speed is the distance covered per unit of time and can be uniform or non-uniform. Common units of speed include meters/second and kilometers/hour.