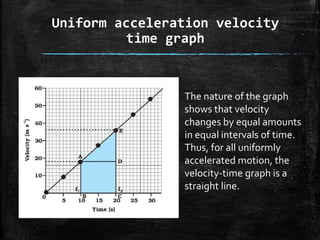
1. A velocity-time graph represents the variation of an object's velocity over time as it moves in a straight line, with time on the x-axis and velocity on the y-axis.
2. For uniform motion, the graph is a straight line parallel to the x-axis, while for uniform acceleration the graph is a straight line. Non-uniform acceleration can produce graphs of varying shapes.
3. The three laws of motion relate displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time: v = u + at, s = ut + 1/2at2, and 2as = v2 - u2. These equations can be derived and used to analyze motion graphsically.