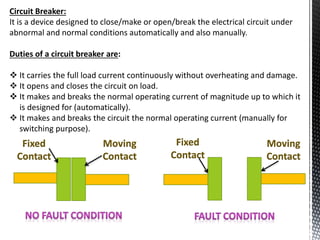
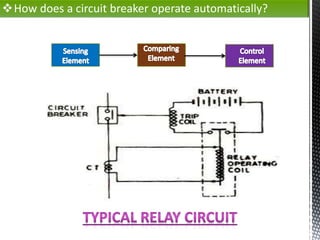
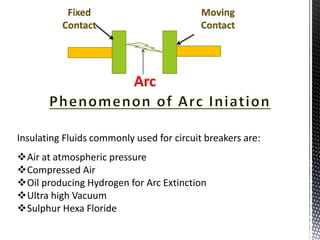
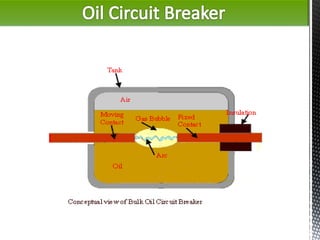
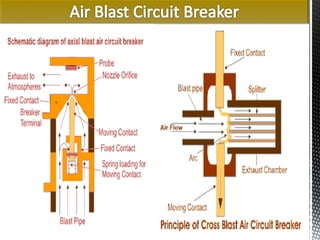
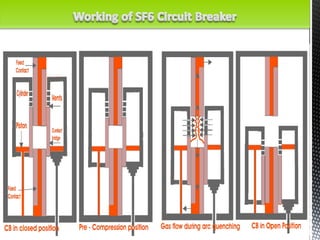
The document discusses circuit breakers, which are devices that automatically or manually open and close electrical circuits under varying conditions. It outlines their functions, operation mechanisms, types (such as oil, air blast, SF6, and vacuum circuit breakers), and the pros and cons of each type. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of choosing the right circuit breaker for specific voltage levels to protect electrical equipment from faults.