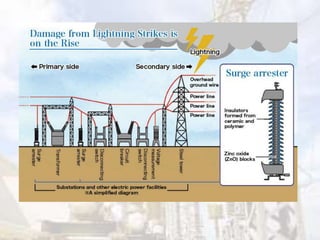
Surge arrestors are protective devices that limit voltage spikes and surges from damaging electrical equipment. They work by diverting excess current during events like lightning strikes or power faults to ground. When voltage increases, the resistor inside the arrestor decreases in resistance, allowing extra current to drain out and prevent voltage from increasing in protected equipment. Surge arrestors are installed at substations and near transformers to shield sensitive equipment from voltage transients. They parallel arrangement allows surges to be discharged without propagating through the system.