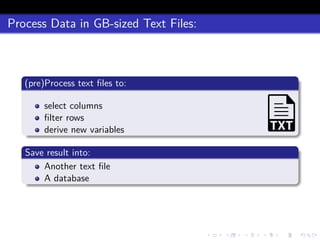
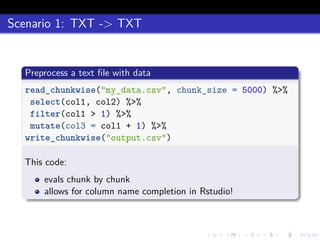
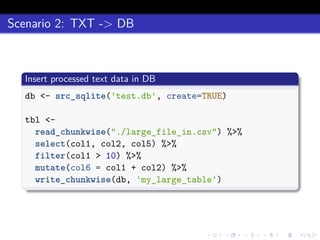
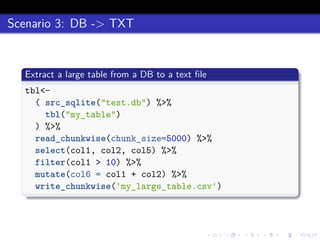
This document discusses processing large datasets stored in text files using chunked, an R package that allows working with data in chunks to overcome memory limitations. It presents chunked as Option 4 for working with large data, describing how it reads and writes data chunk-by-chunk using lazy processing. Scenarios demonstrated include preprocessing a text file and writing output (TXT->TXT), importing data into a database (TXT->DB), and extracting from a database to a text file (DB->TXT). While many dplyr verbs work chunkwise, it notes summarize, group_by, arrange, right_join, and full_join currently do not.