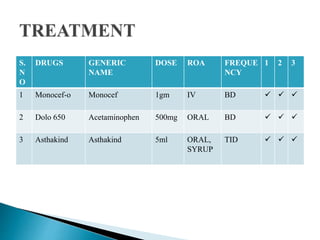
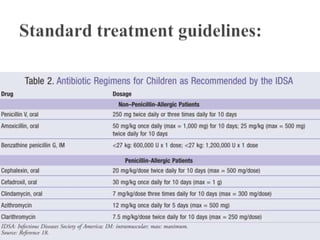
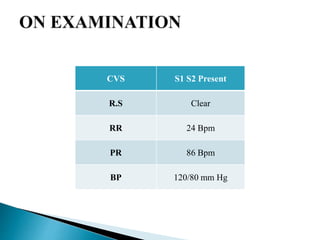
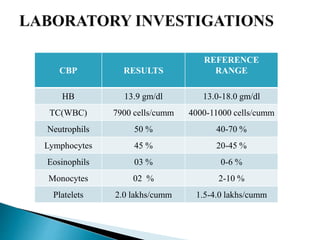
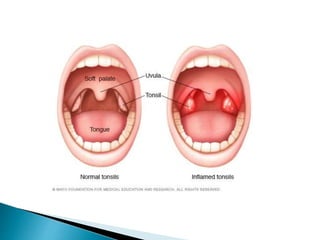
A 9-year-old female patient is diagnosed with chronic tonsillitis, presenting with progressive difficulty and pain while swallowing, unrelieved by medication. Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by inflammation of the tonsils and can lead to complications if untreated, including breathing difficulties and risk of rheumatic fever. Treatment options include antibiotics for bacterial infections and tonsillectomy for recurrent or severe cases.









![A polymicrobial bacterial population is observed in most cases of
chronic tonsillitis, with alpha- and beta-hemolytic streptococcal species, S
aureus, H influenzae, and Bacteroides species having been identified.
A study that was based on bacteriology of the tonsillar surface and core in
30 children undergoing tonsillectomy suggested that antibiotics prescribed
6 months before surgery did not alter the tonsillar bacteriology at the time
of tonsillectomy. [4] A relationship between tonsillar size and chronic
bacterial tonsillitis is believed to exist.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronictonsillitis-200628134754/85/Chronic-tonsillitis-14-320.jpg)