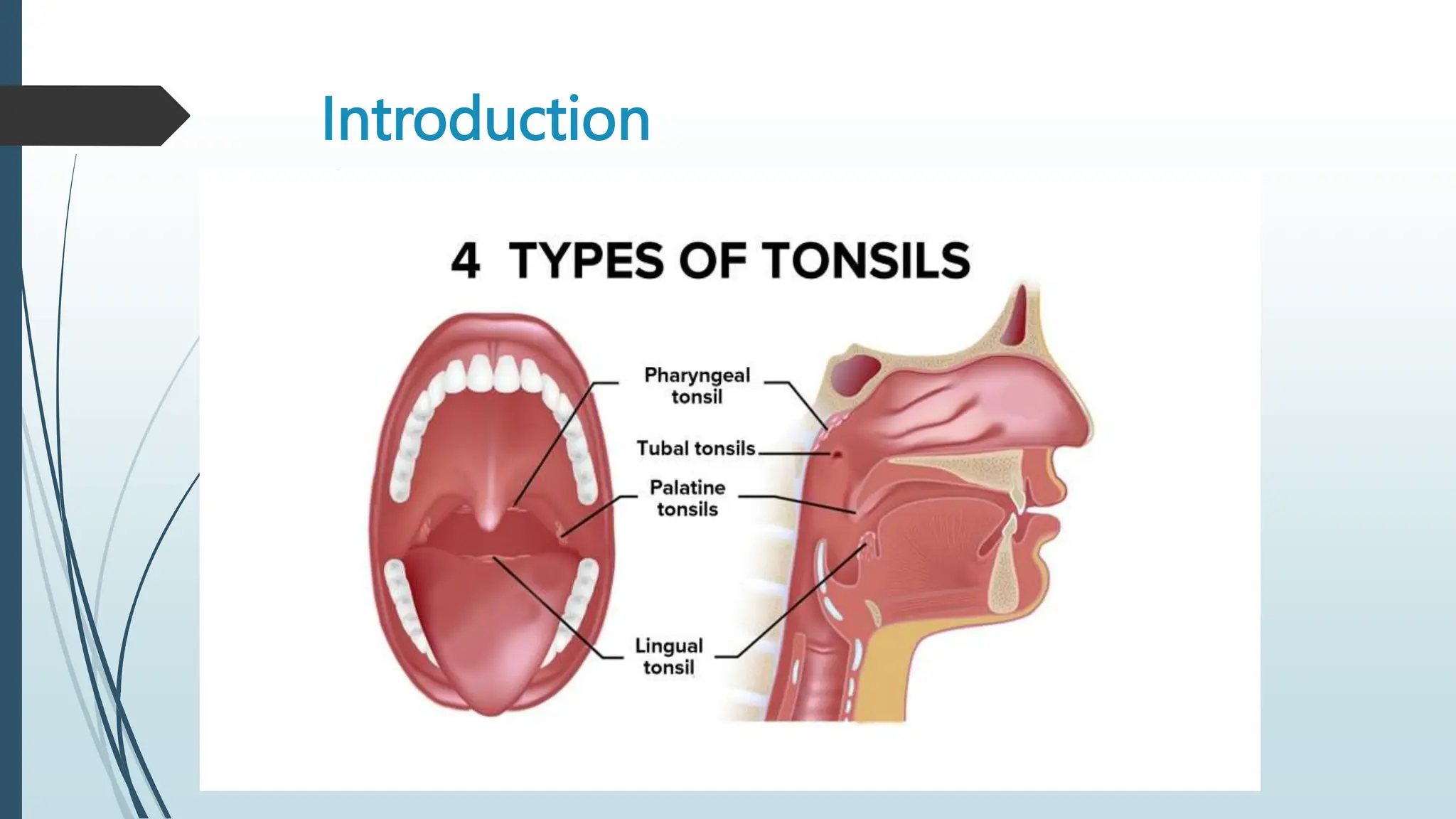
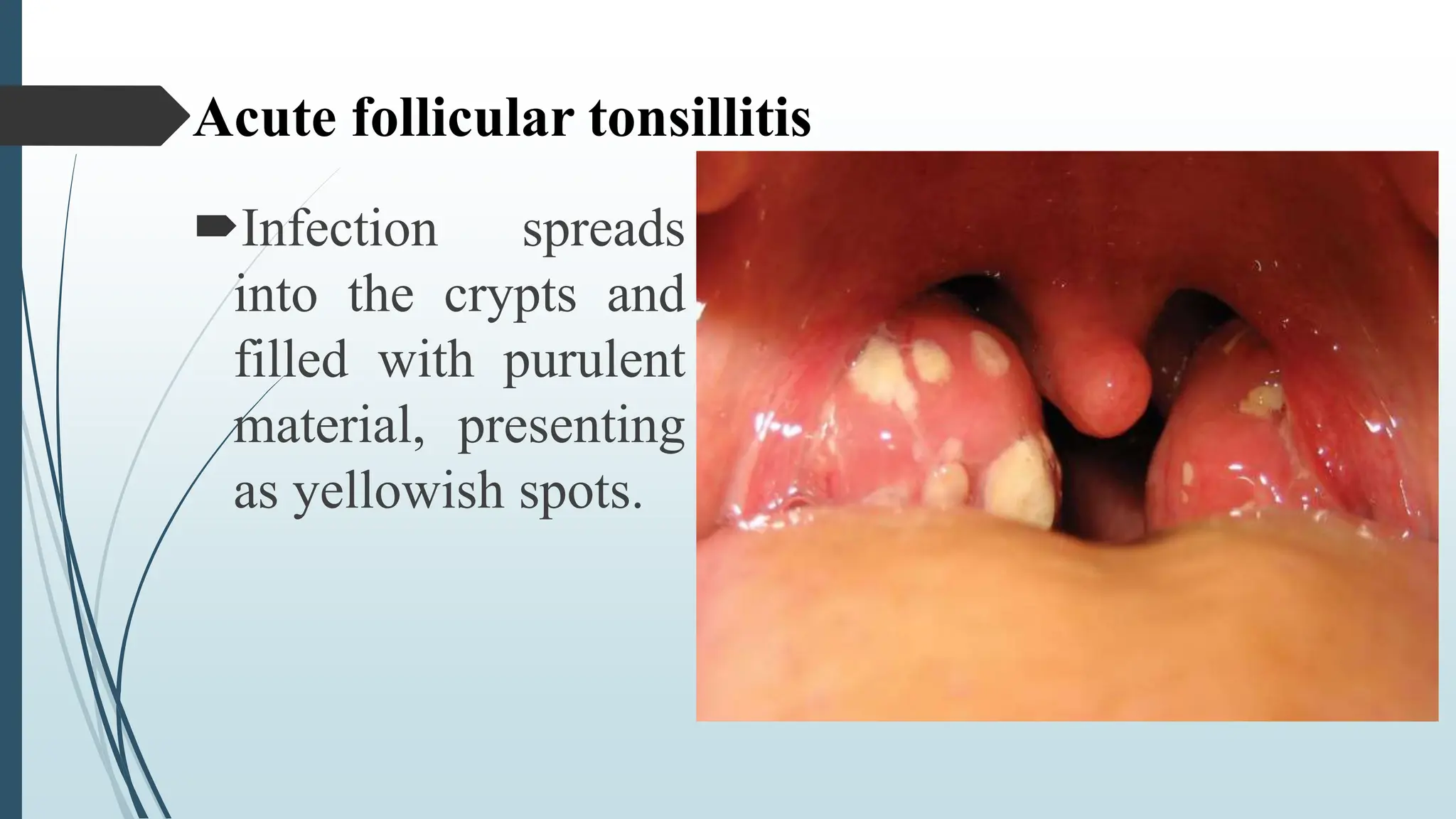
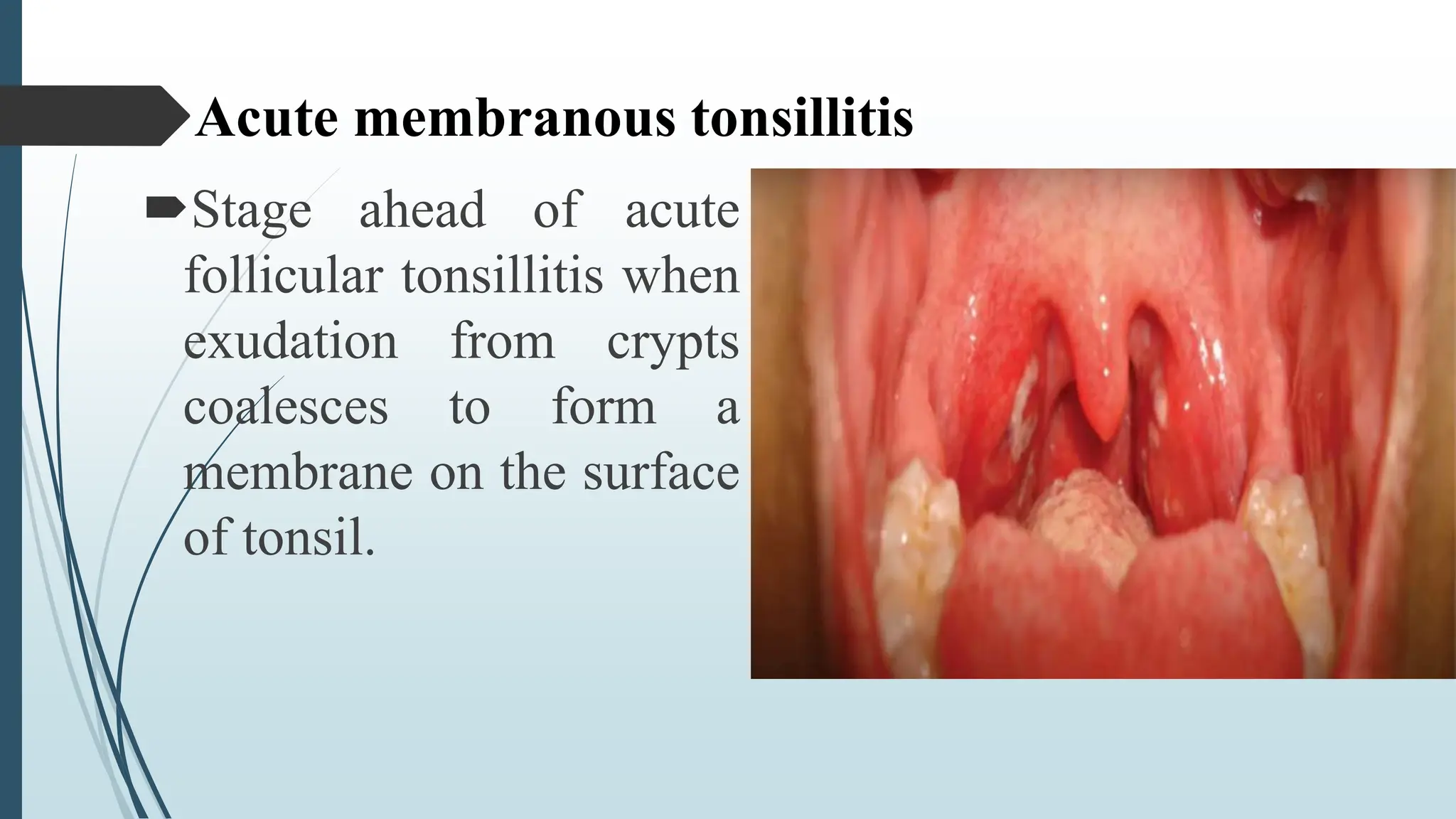
This document provides information about tonsillitis, including its definition, incidence, causes, risk factors, types, symptoms, treatment and complications. Tonsillitis is the inflammation and infection of the tonsils, most commonly caused by viruses or streptococcus bacteria. It occurs most in children ages 5-9 years old. Types of tonsillitis include acute, subacute, and chronic. Symptoms include sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and fever. Treatment involves antibiotics, pain medication, warm salt water gargles, and tonsillectomy for recurrent cases. Complications include peritonsillar abscess, cervical abscess or rheumatic fever if left untreated. With proper treatment, children usually recover fully from tons