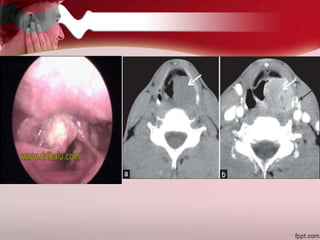
Ear pain, or otalgia, can originate from diseases within the ear itself or from diseases in surrounding areas that cause referred pain. Referred otalgia is a common presentation and can be caused by conditions of the teeth, jaw, throat, neck muscles, or cancers of the throat or neck. A thorough history, physical exam, and diagnostic tests are needed to identify the underlying source of the ear pain.