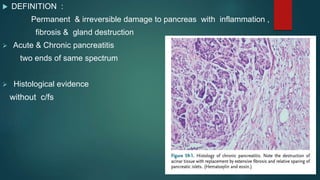
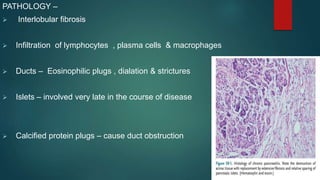
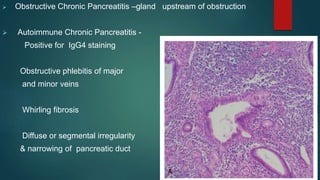
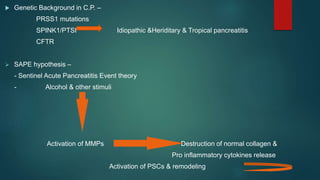
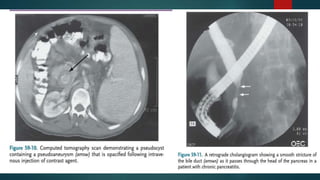
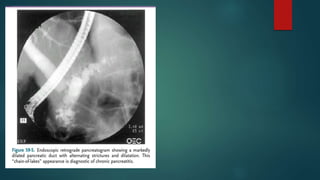
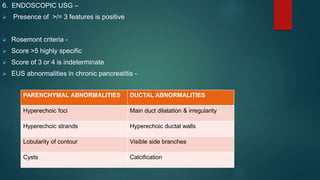
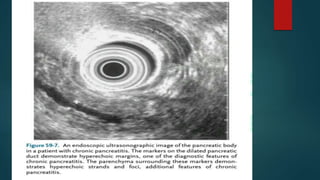
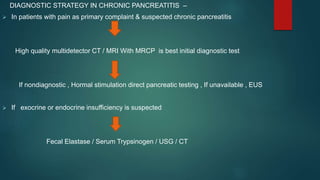
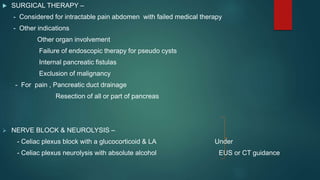
This document provides an overview of chronic pancreatitis, including its definition, epidemiology, pathology, etiology, clinical features, complications, diagnosis, and treatment. Key points include: chronic pancreatitis results from permanent pancreatic damage and inflammation; common causes include alcohol abuse and genetic factors; complications involve pain, diabetes, maldigestion; diagnosis utilizes tests of pancreatic structure and function; treatment focuses on pain management, enzyme supplementation, and addressing underlying causes such as alcohol cessation.