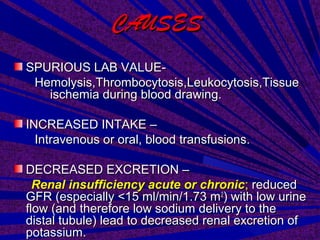
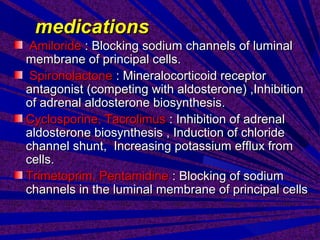
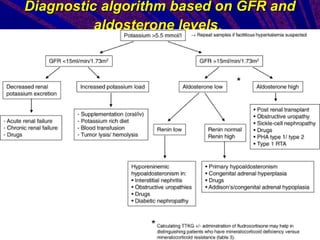
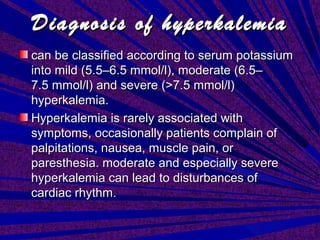
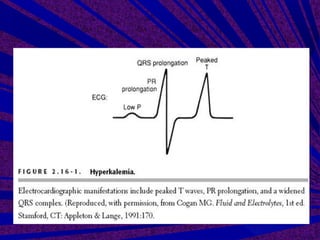
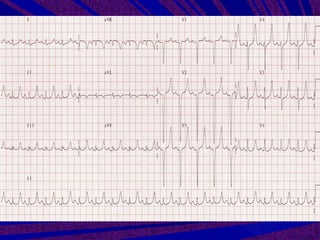
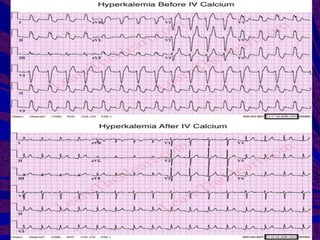
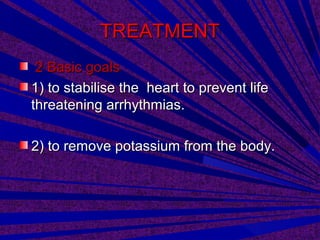
This document discusses hyperkalemia, or high levels of potassium in the blood. It covers the normal physiology of potassium balance in the body, including intake through foods, absorption in the intestines, and excretion primarily through the kidneys under regulation of the hormone aldosterone. Causes of hyperkalemia include reduced kidney function, medications that interfere with potassium excretion, and conditions that cause a shift of potassium out of cells. The document provides details on evaluating, diagnosing, and classifying different severities of hyperkalemia based on serum potassium levels.