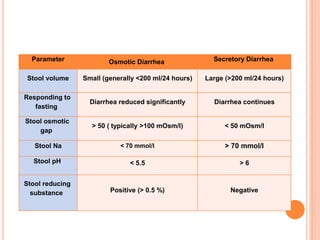
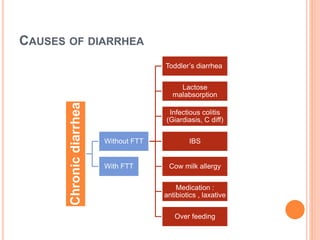
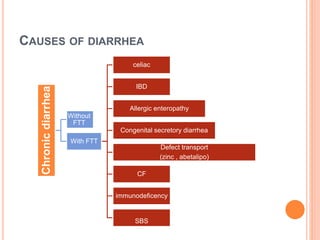
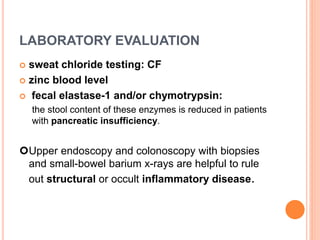
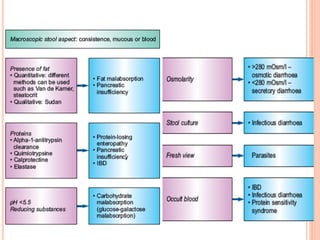
This document discusses the approach to chronic diarrhea in children. It defines chronic diarrhea and outlines its pathophysiology and types. A wide range of potential causes are described. The clinical approach involves a detailed history, laboratory evaluation including celiac serology, and consideration of functional diarrhea in young children. Management focuses on hydration, nutrition, and treating any underlying disease. Probiotics may help in some cases while antidiarrheal medications can improve symptoms but have side effects.