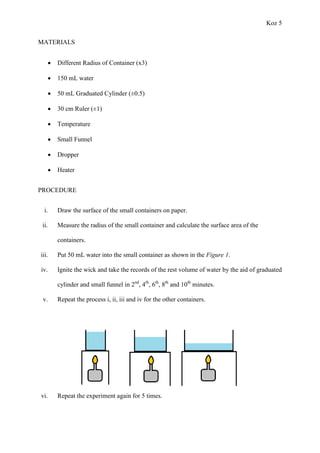
The document describes an experiment that investigated how surface area affects evaporation rate. Three containers with different surface areas (150 cm^2, 384 cm^2, 864 cm^2) were filled with 50 mL of water and the volume remaining was measured every 2 minutes for 10 minutes. The results showed that as surface area increased, the evaporation rate also increased - containers with larger surface areas had lower volumes remaining after each time interval. This supports the hypothesis that increasing surface area increases evaporation rate by providing more surface for water molecules to transition from liquid to gas.