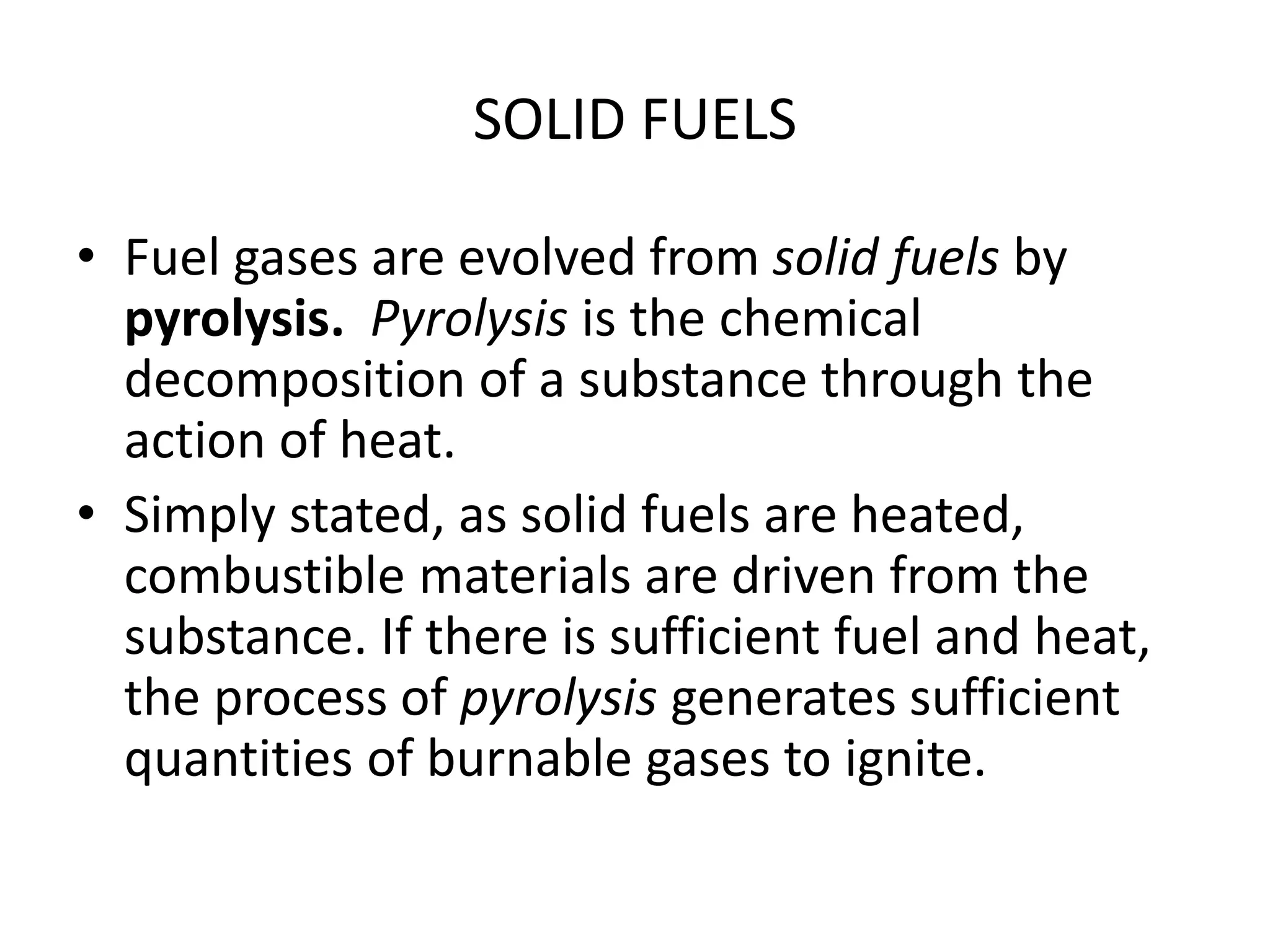
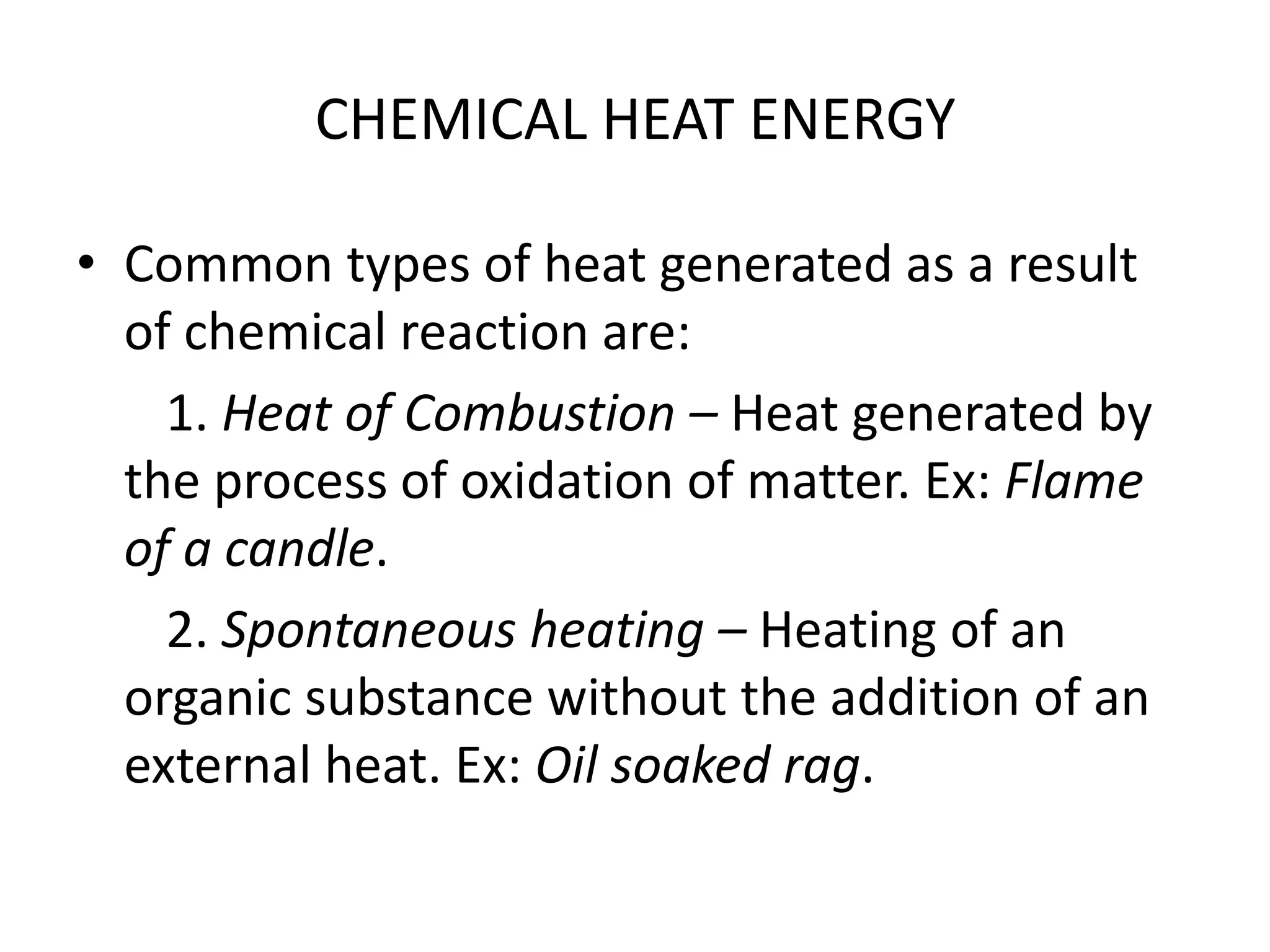
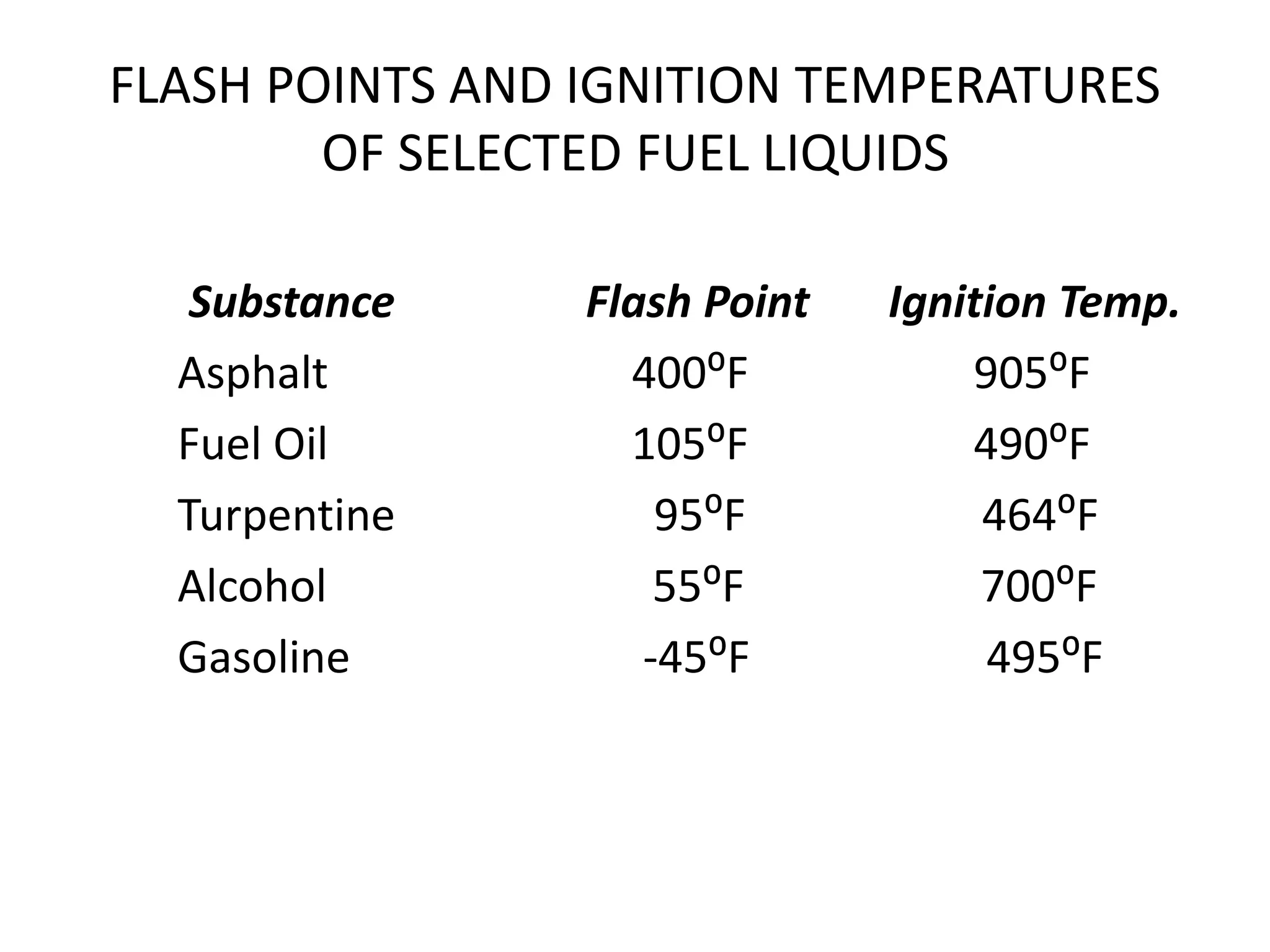
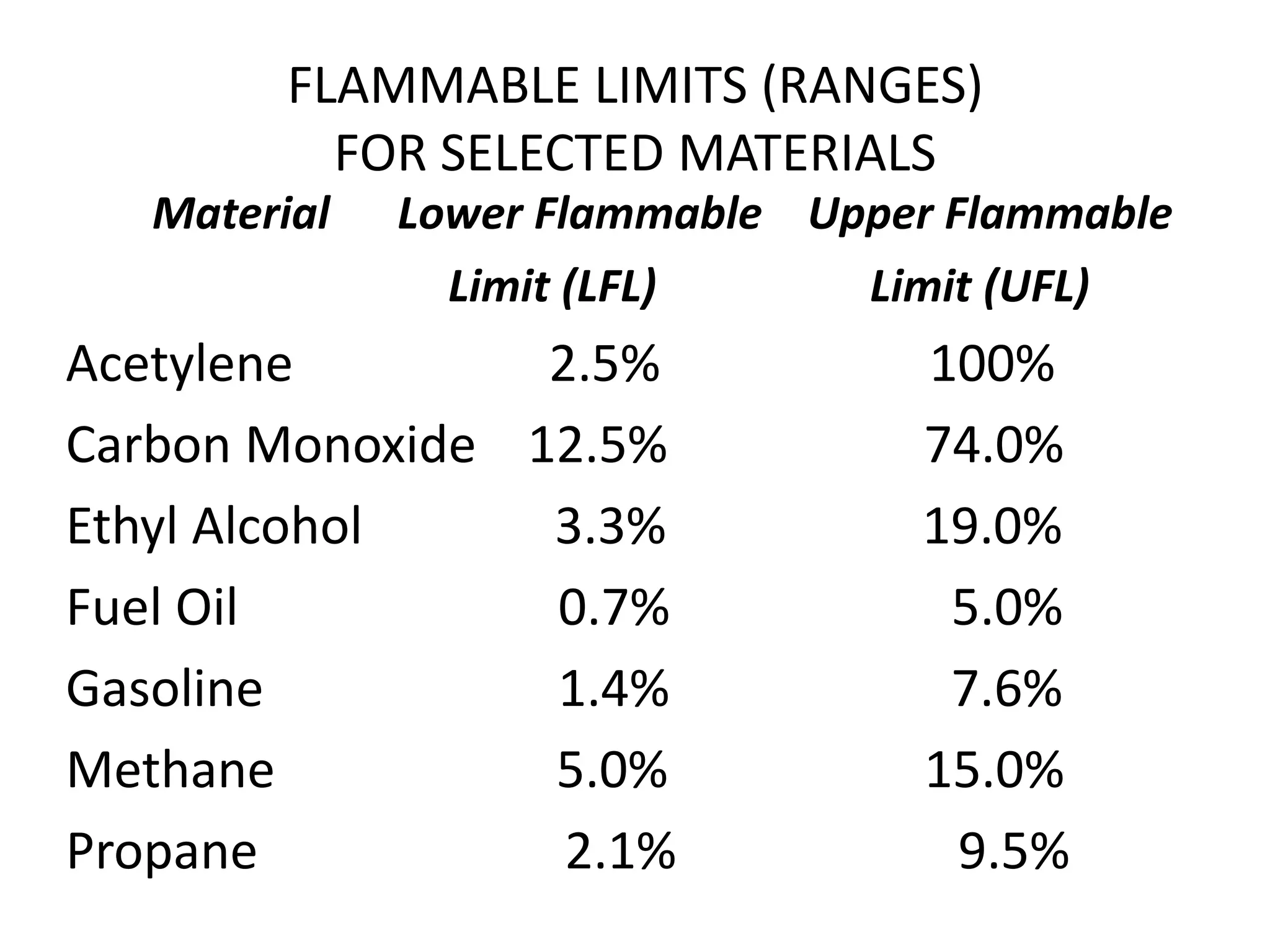
This document defines key terms related to fire chemistry and behavior. It explains that the three necessary elements for a fire are heat, fuel, and an oxidizing agent (usually oxygen from air). Fires start when these elements come together in the proper proportions. Fuels must be in gaseous form to burn, requiring solids and liquids to undergo pyrolysis or vaporization first when heated. Heat is then transferred between objects via conduction, convection or radiation to allow the fire to spread.