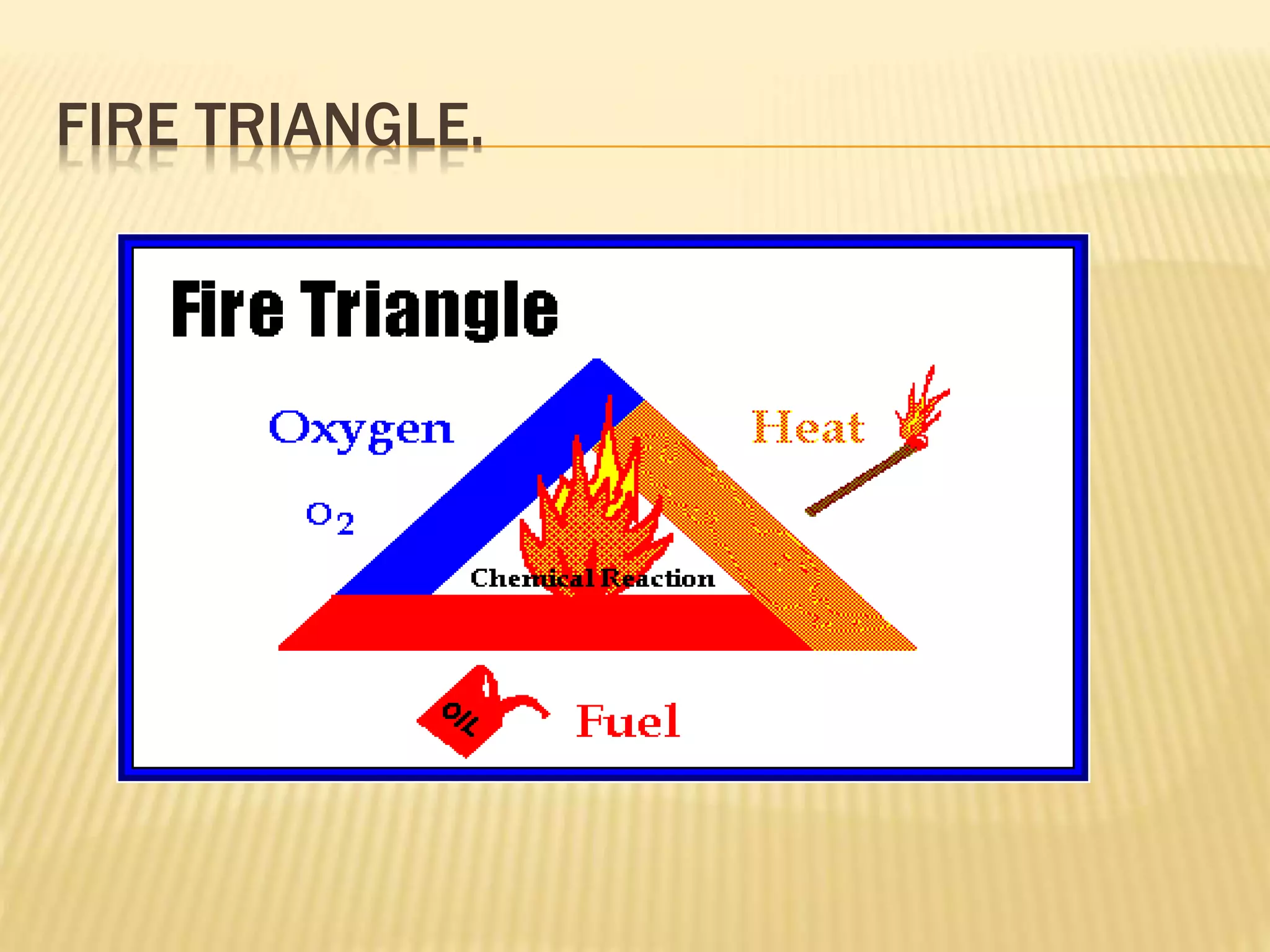
This document discusses arson, including its definition, investigation, causes, and laws around it. Arson is the deliberate act of burning property and is difficult to solve due to planning by the perpetrator. A fire investigator's role is to analyze evidence from the scene to determine if the fire was accidental or intentional. There are various motives for arson such as vandalism, crime concealment, and profit. Laws define degrees of arson based on the property burned. Fire investigations aim to determine the cause to prevent future fires and identify those responsible.