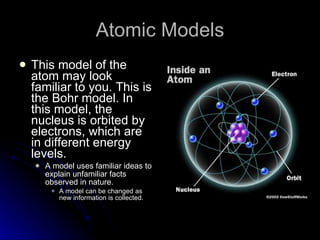
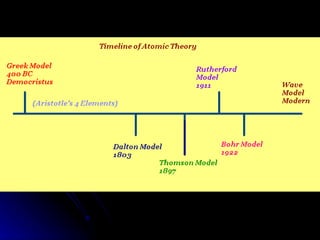
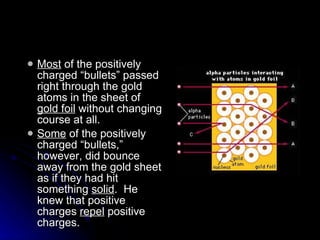
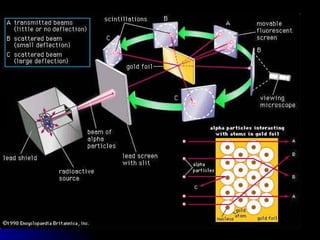
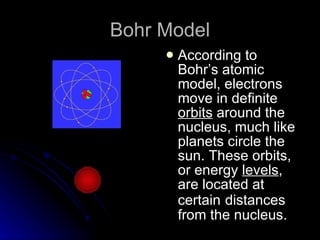
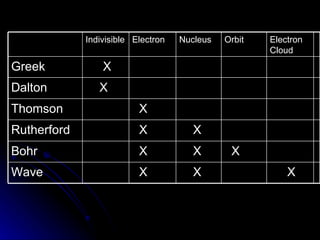
The document traces the development of atomic theory over time from ancient Greek philosophers to modern models. It describes Democritus' idea that matter is made of indivisible particles called "atomos", Dalton's model of atoms as indivisible spheres, Thomson's "plum pudding" model with electrons scattered in a positively charged substance, Rutherford's gold foil experiment showing atoms are mostly empty space with a dense nucleus, Bohr's model of electrons in specific energy levels orbiting the nucleus like planets, and the modern wave model where electrons exist as probability clouds rather than definite orbits.