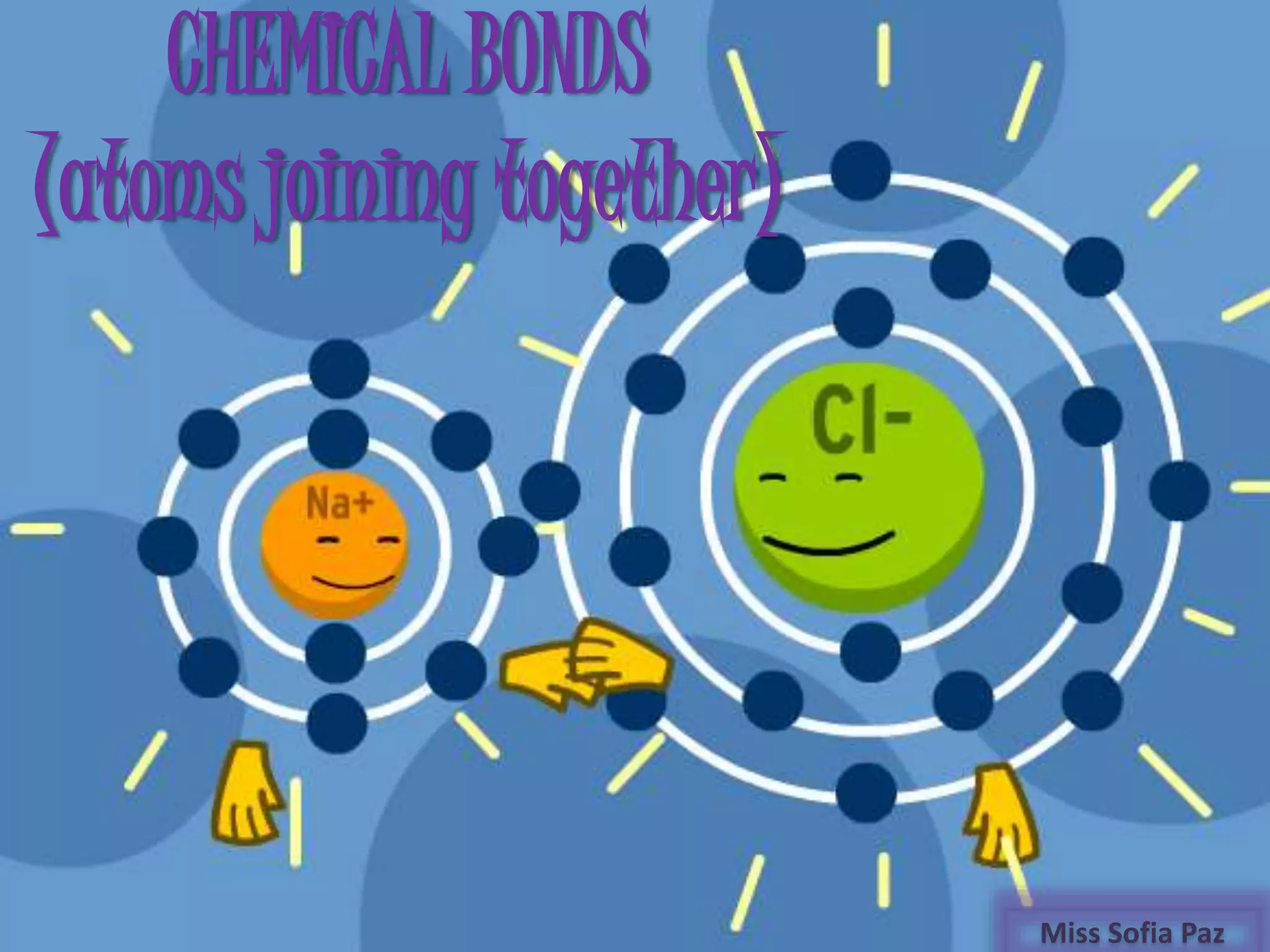
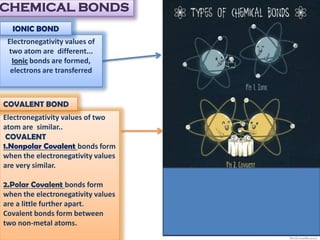
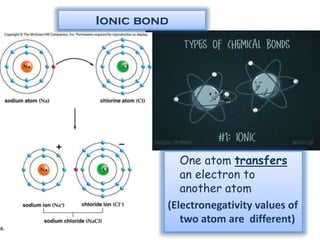
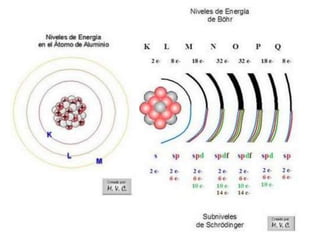
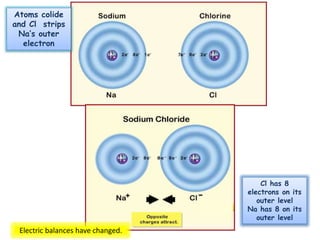
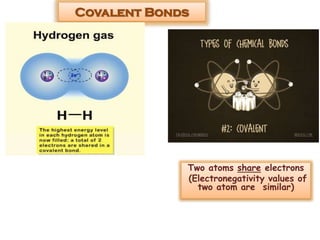
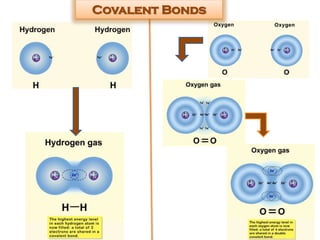
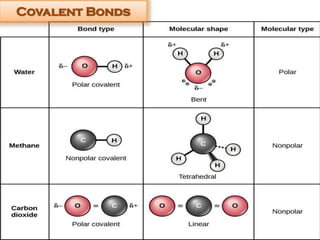
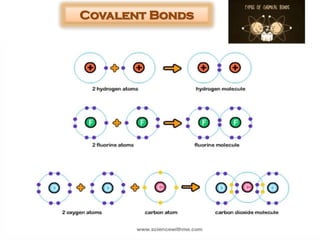
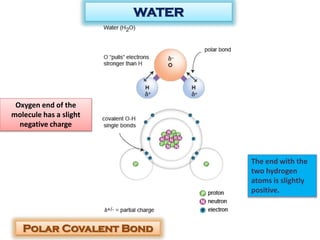
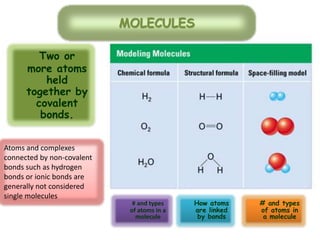
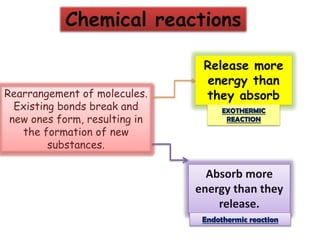
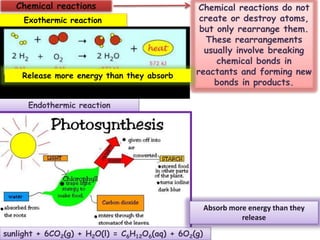
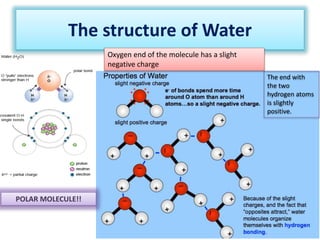
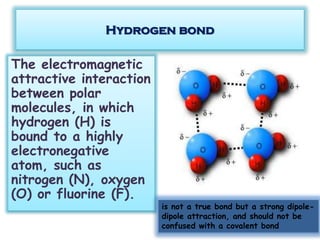
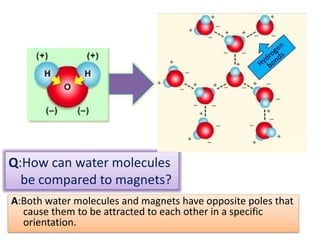
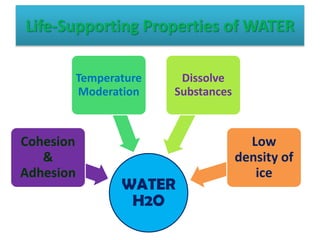
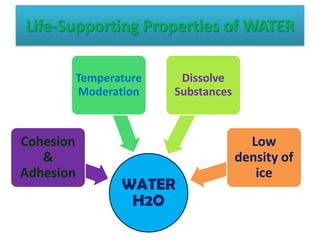
This document discusses different types of chemical bonds: ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom due to differences in electronegativity, while covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons due to similar electronegativity. Ionic bonds result in charged ions, while covalent bonds can be nonpolar or polar depending on electronegativity differences. Water is an example of a polar covalent molecule with partial charges on the oxygen and hydrogen ends. Hydrogen bonds are electrostatic attractions between polar molecules that are stronger than other intermolecular forces.