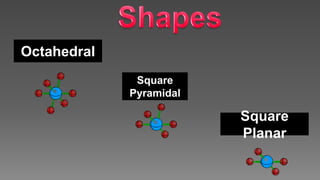
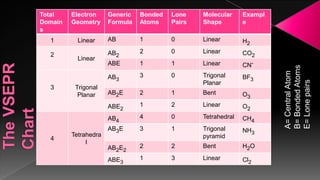
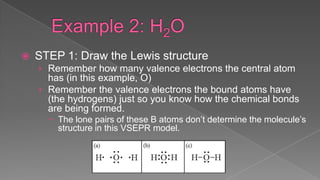
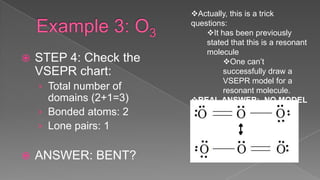
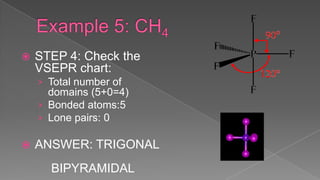
The document discusses the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model, which uses the number of electron pairs around an atom to predict the geometry of molecules. It can be used to predict structure by considering the number of bonded atoms and lone pairs on the central atom. The model works well but is an oversimplification in some cases, failing to accurately describe resonant or planar structures.