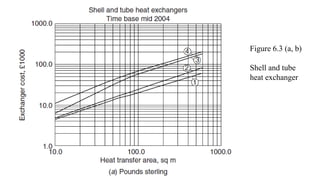
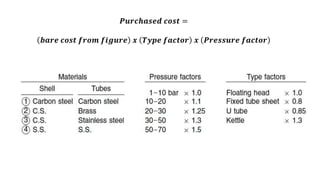
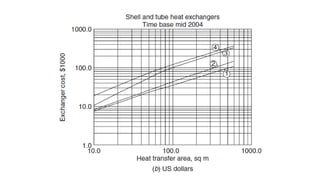
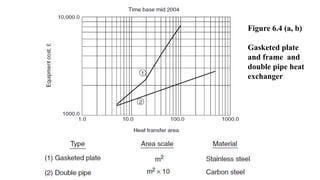
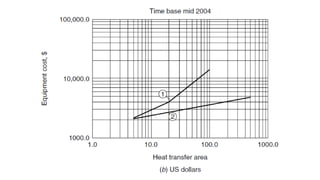
The document outlines essential information required for obtaining cost estimates for heat transfer equipment, focusing on both process and mechanical details. Key process parameters include fluid properties, flow rates, temperatures, and operating conditions, while mechanical details cover dimensions, materials, and design specifications. The document also references various engineering economy textbooks used to prepare the notes.