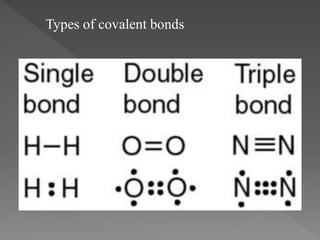
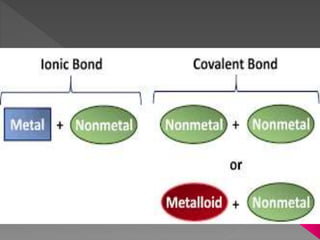
Chemical bonding can occur through either ionic bonds or covalent bonds. Ionic bonds result from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, while covalent bonds form through the sharing of electrons between atoms. The strength of these bonds can vary considerably, from strong primary bonds to weaker secondary bonds.



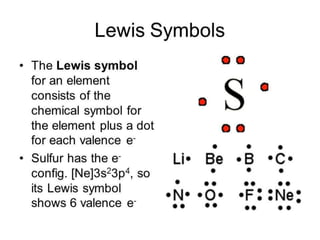
![LEWIS STRUCTURE
Lewis structures, also known as Lewis dot
diagrams, Lewis dot formulas, Lewis dot
structures, electron dot structures, or Lewis
electron dot structures (LEDS), are diagrams that
show the bonding between atoms of a molecule and
the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the
molecule.[1][2][3] A Lewis structure can be drawn for
any covalentlybonded molecule, as well as coordination
compounds. The Lewis structure was named
after Gilbert N. Lewis, who introduced it in his 1916
article The Atom and the Molecule.[4]Lewis structures
extend the concept of the electron dot diagram by
adding lines between atoms to represent shared
pairs in a chemical bond.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalbonding-200316092844/85/Chemical-bonding-6-320.jpg)





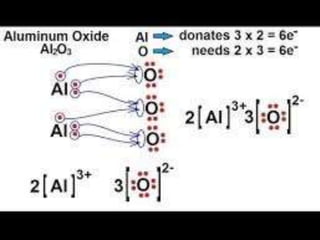
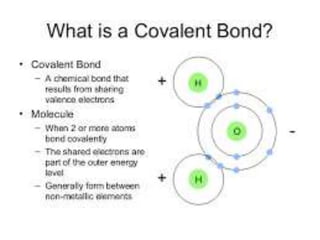
![A covalent bond, also called a molecular
bond, is a chemical bond that involves the
sharing of electron pairsbetween atoms.
These electron pairs are known as shared
pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable
balance of attractive and repulsive forces
between atoms, when they share electrons,
is known as covalent
bonding.[1][better source needed] For
many molecules, the sharing of electrons
allows each atom to attain the equivalent of
a full outer shell, corresponding to a stable
electronic configuration.
Covalent bond](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalbonding-200316092844/85/Chemical-bonding-14-320.jpg)