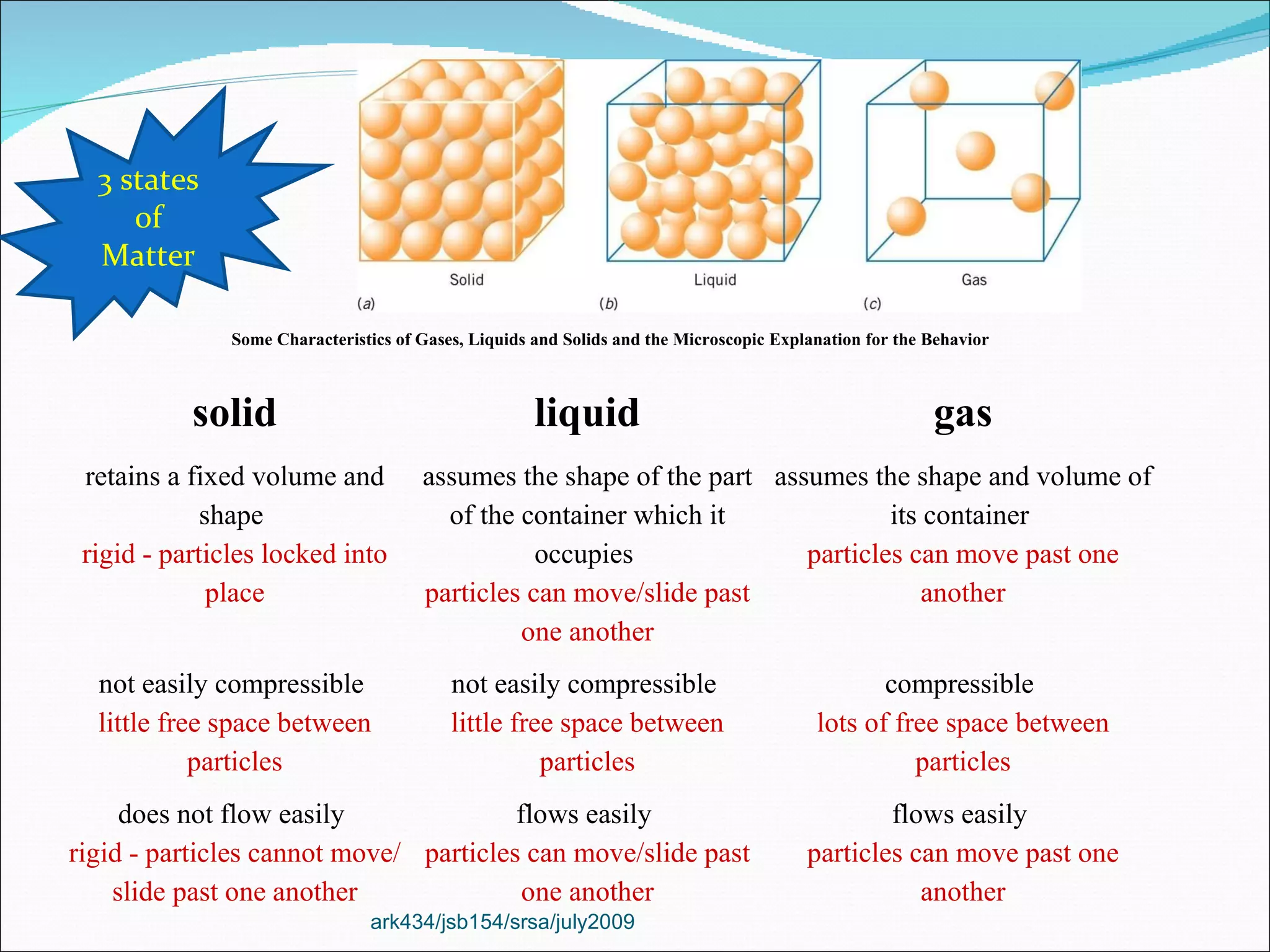
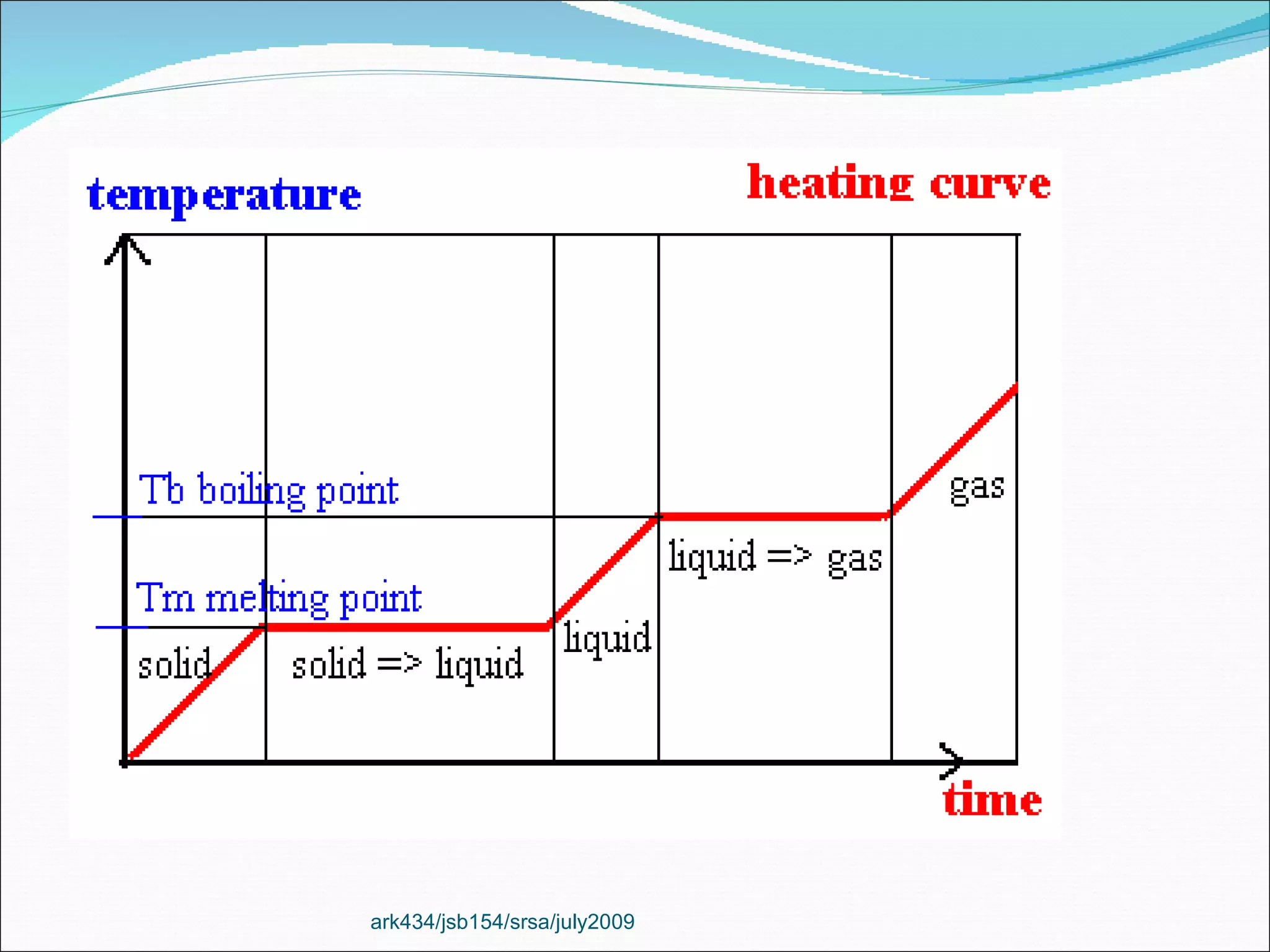
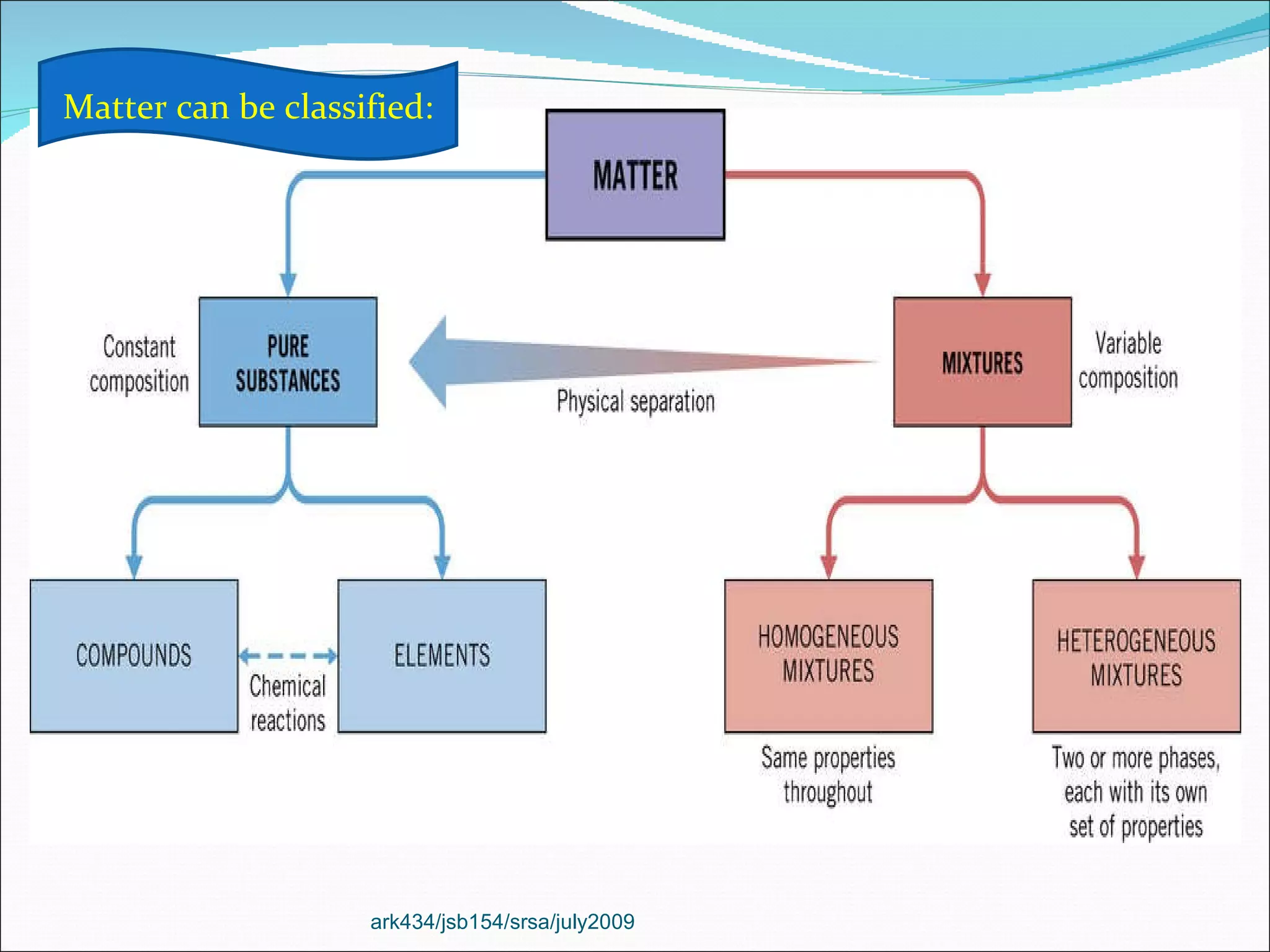
The document discusses the key differences between the three states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. It explains that solids retain a fixed shape and volume, liquids take the shape of their container, and gases fill their entire container and are easily compressed. On a microscopic level, solids have particles that are locked in place, liquids have particles that can move past one another, and gases have many empty spaces between particles allowing them to move freely. The document also defines physical and chemical properties of matter and physical and chemical changes.