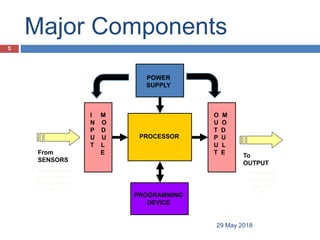
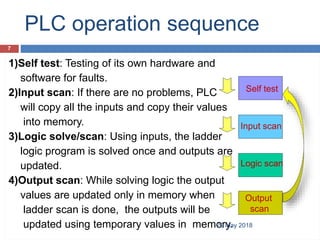
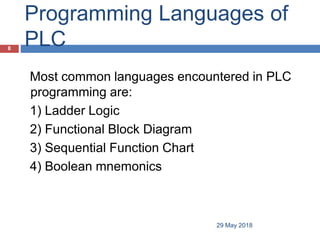
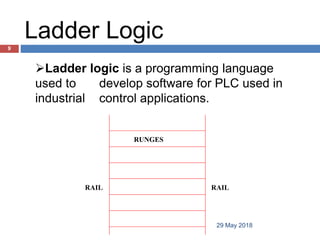
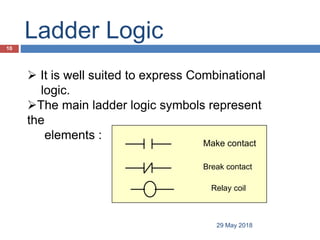
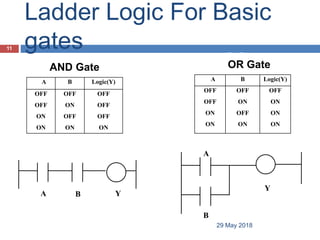
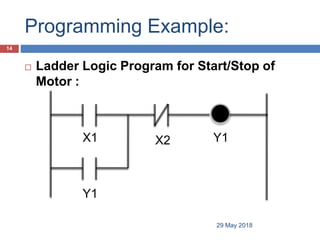
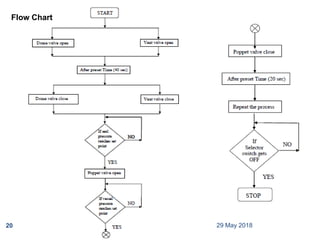
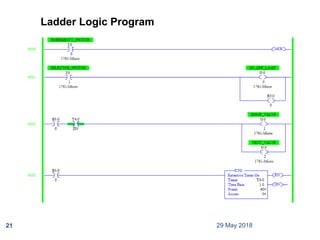
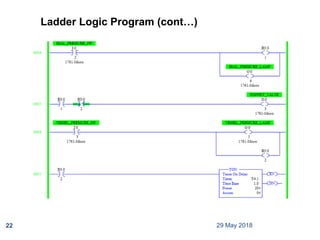
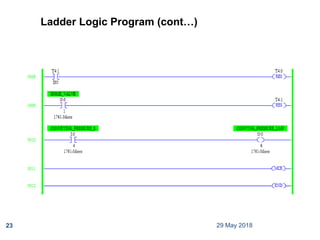
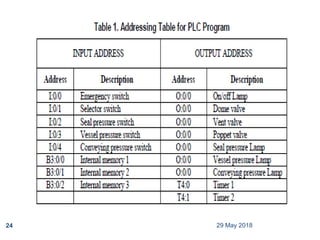
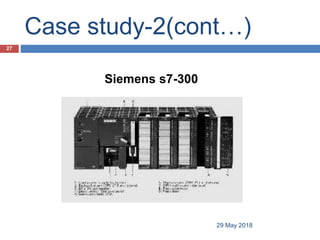
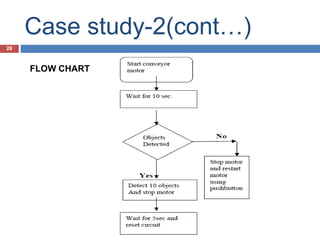
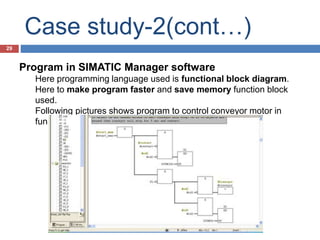
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), including their definition, history, major components, operational sequences, programming languages, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. It discusses the evolution of PLCs from simple relay replacements to advanced industrial computers and provides case studies demonstrating their use in automation systems. The document highlights how PLCs enhance reliability, flexibility, and efficiency in various industrial applications.