This chapter discusses subnetting, VLSM, and troubleshooting IP addressing. It covers subnetting basics like reducing network traffic and optimizing performance. The key points are:
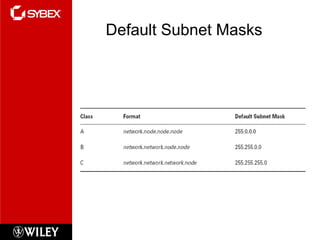
1) Subnetting involves using some bits from the host portion of an IP address to create subnets. Subnet masks define which bits are used.
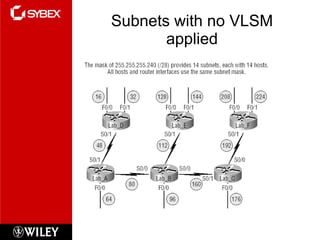
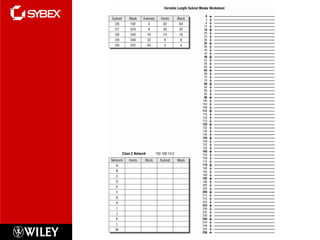
2) Class C subnetting allows for up to 4 subnets with a maximum of 62 hosts per subnet using a 255.255.255.192 subnet mask.
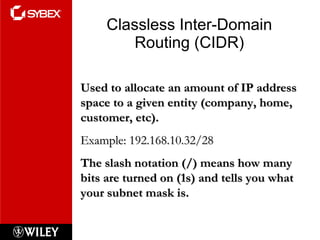
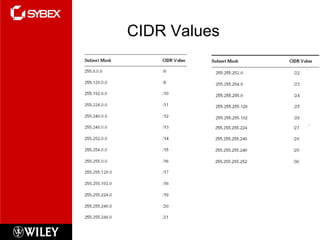
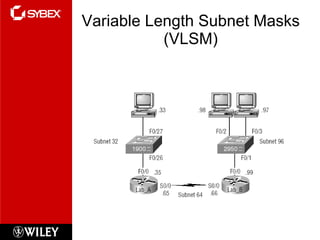
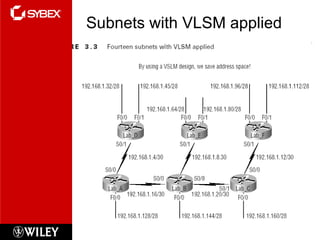
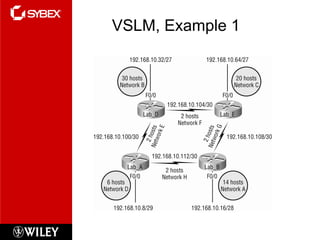
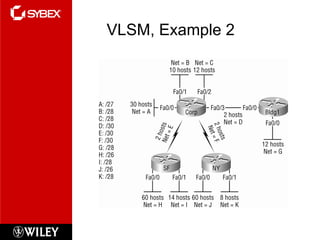
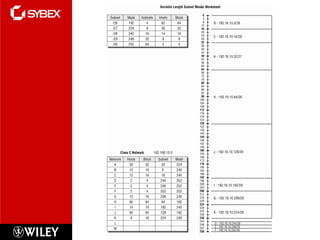
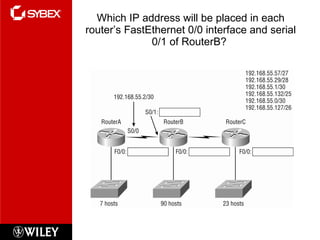
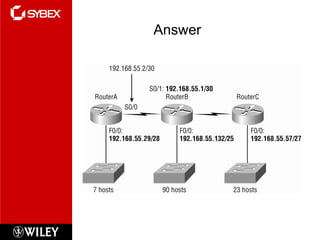
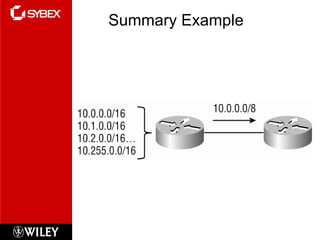
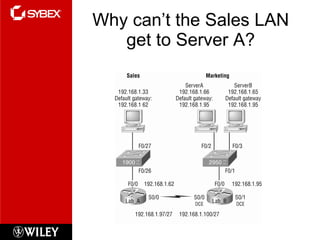
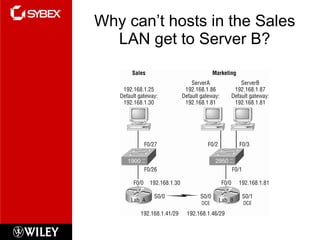
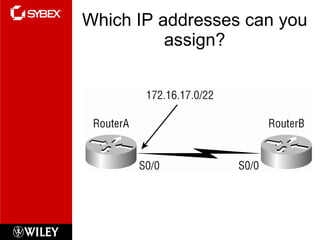
3) VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Masking) allows for subnets of different sizes, improving address utilization. Troubleshooting examines why hosts can't communicate and valid IP addresses.