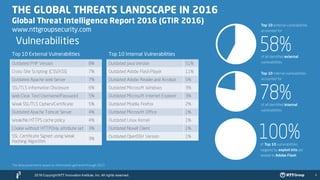
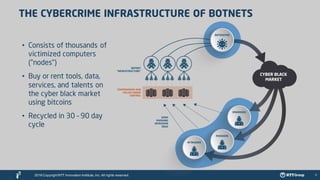
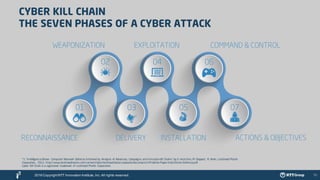
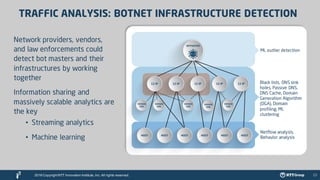
The document outlines the global cyber threat landscape in 2016, highlighting the sophisticated nature of cybercriminals and the vulnerabilities faced by enterprise security teams. It discusses key vulnerabilities, notable cyber attacks, and the importance of threat intelligence in predicting and preventing cyber incidents. Additionally, it emphasizes advancements in security technologies, including machine learning and threat intelligence platforms, to enhance predictive capabilities and response measures.