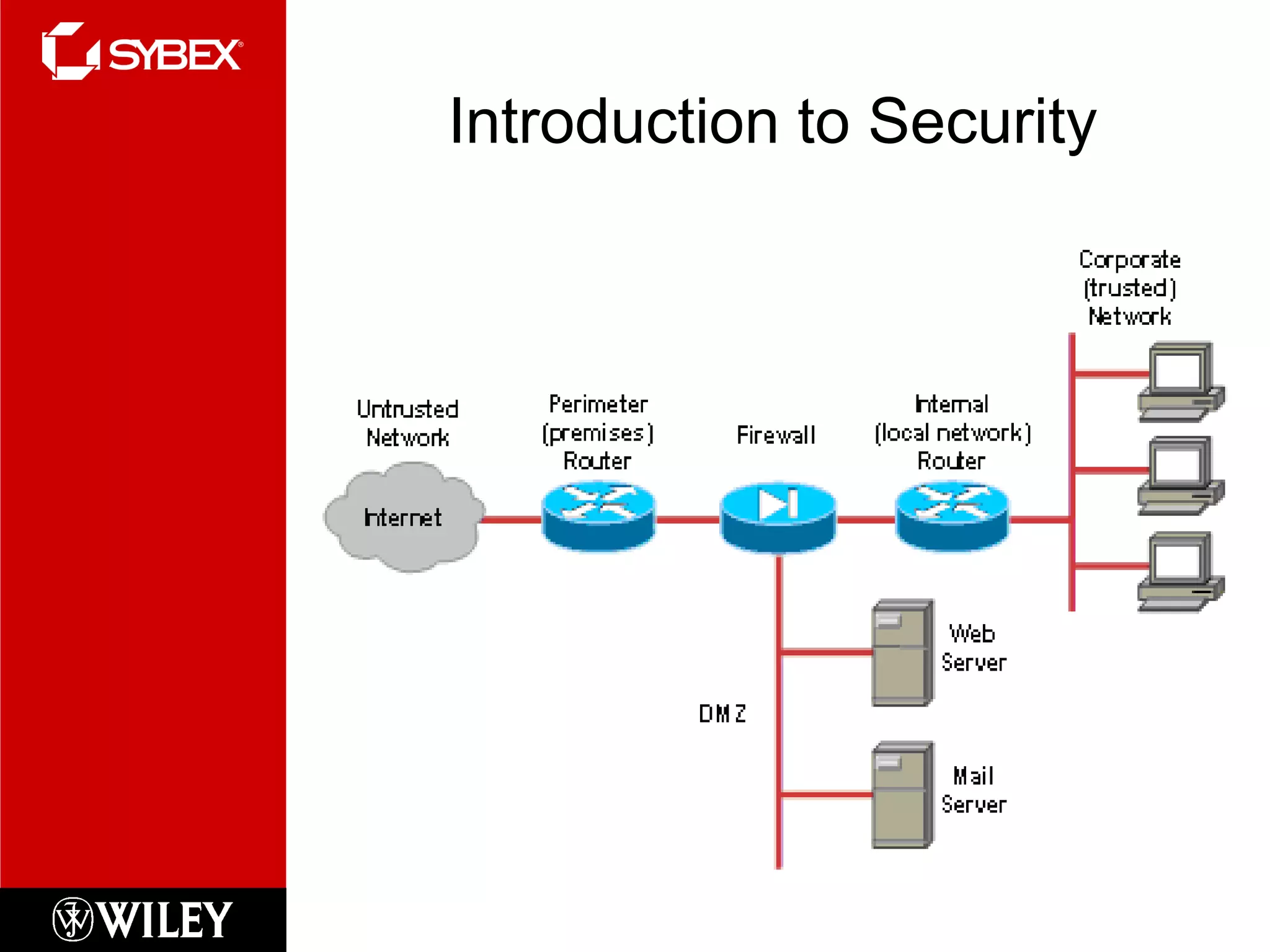
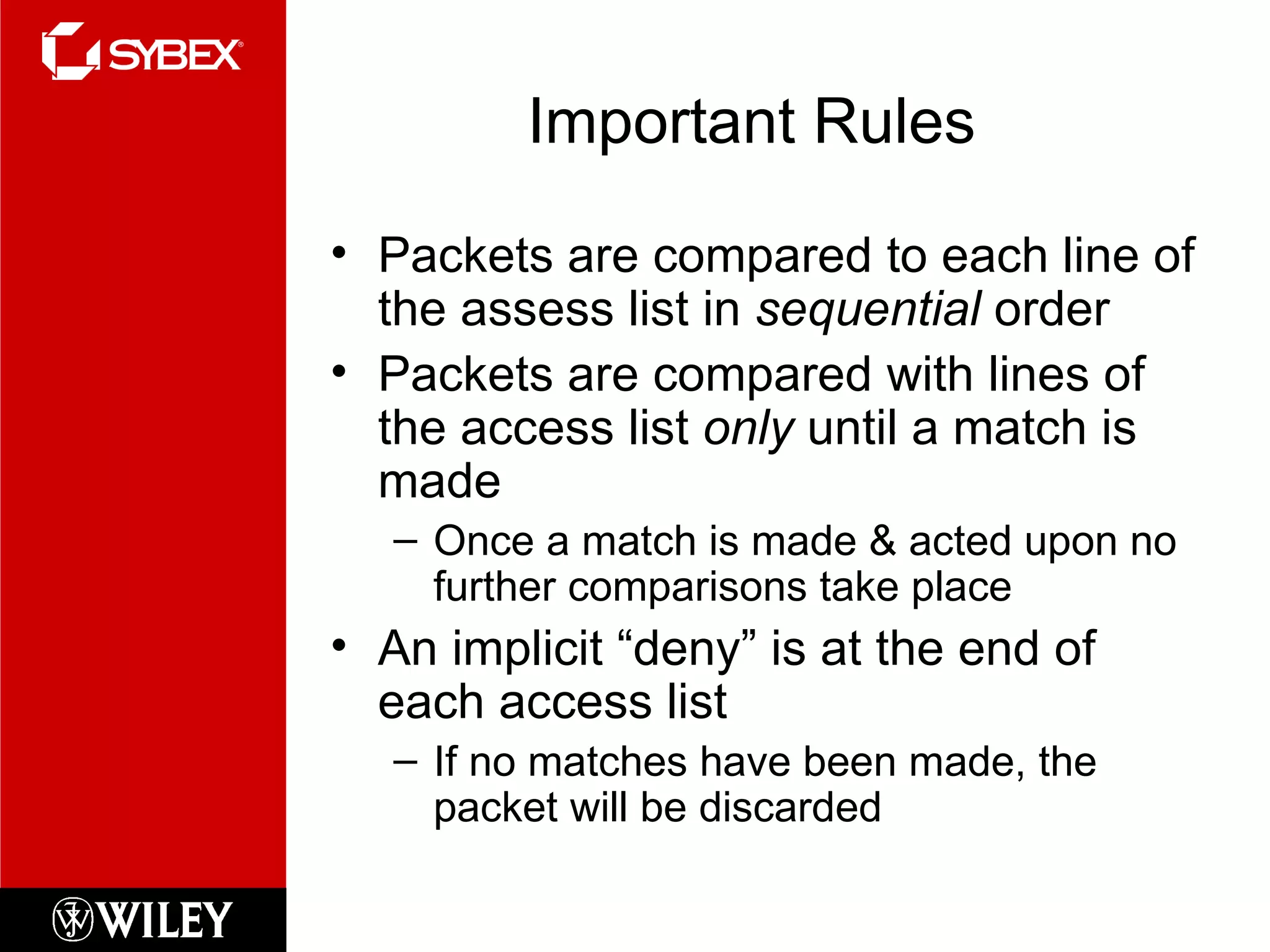
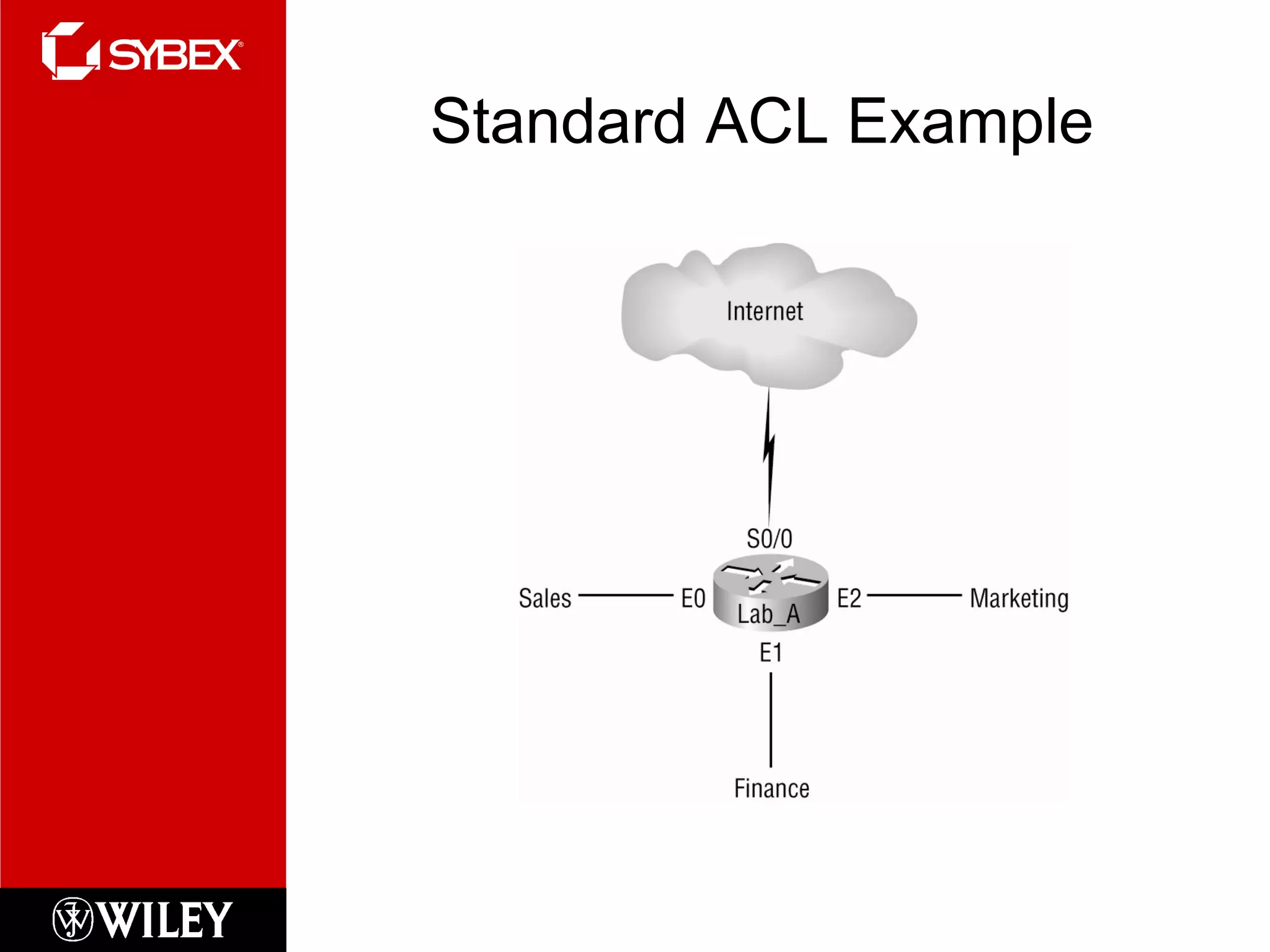
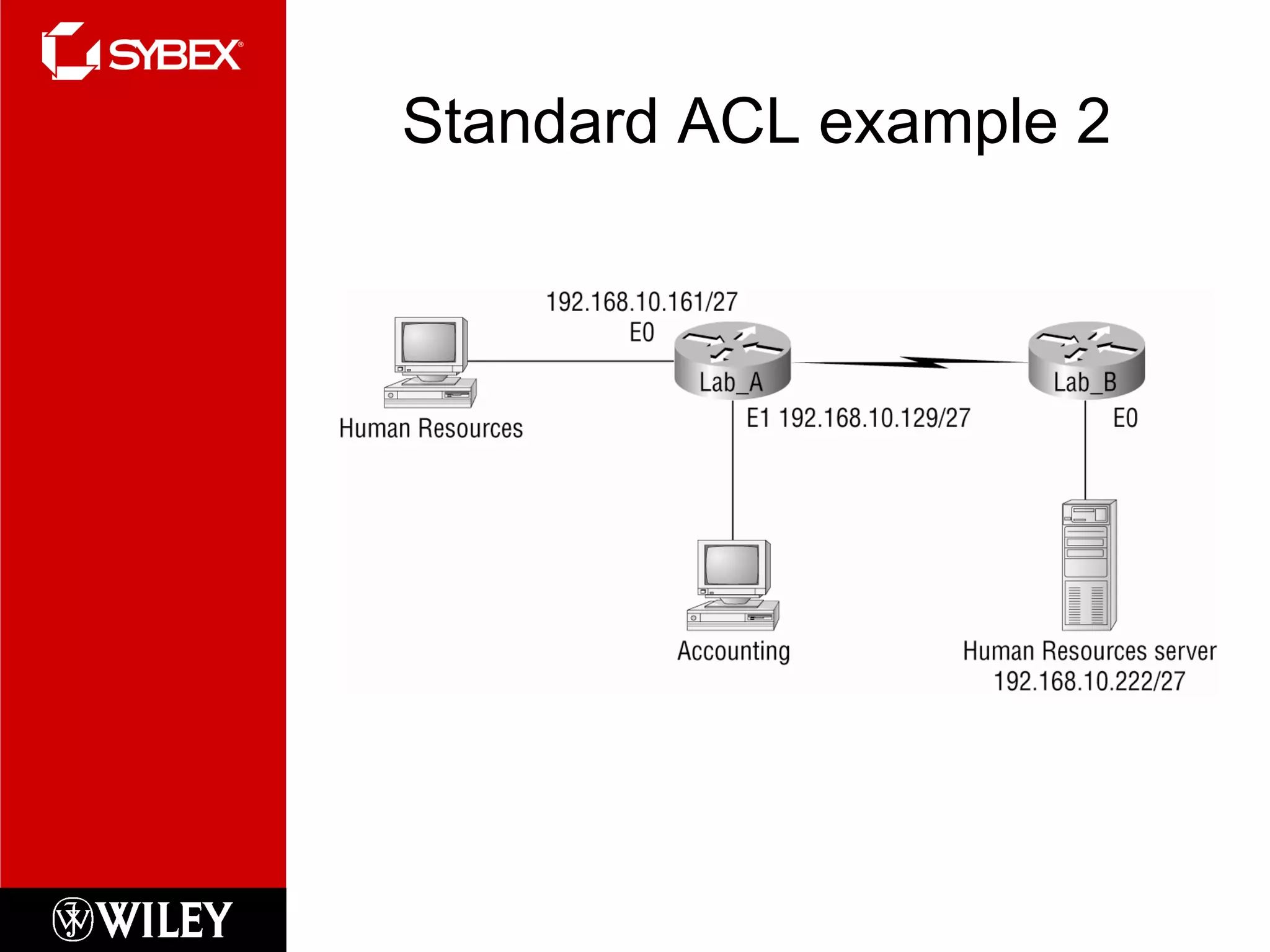
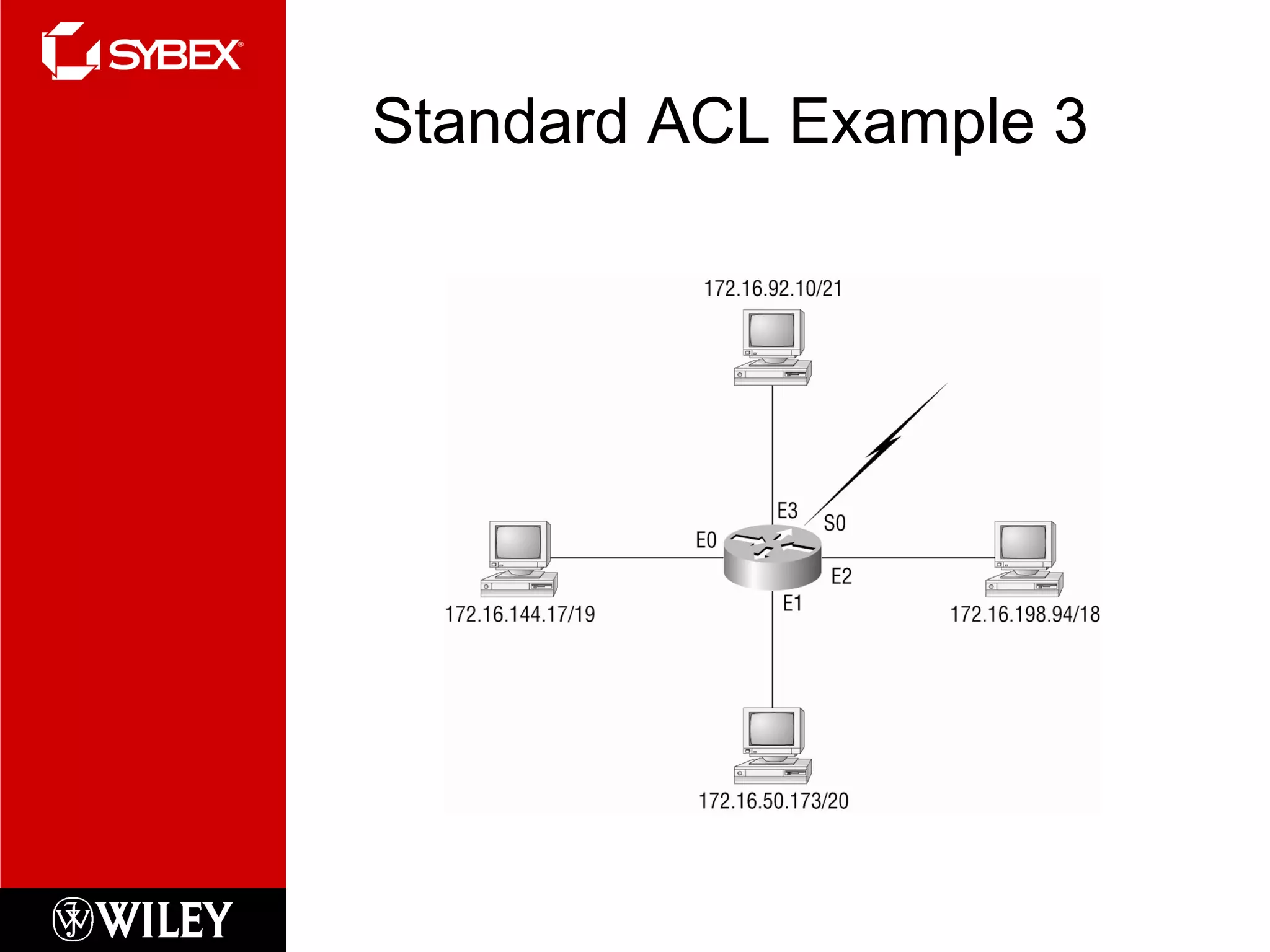
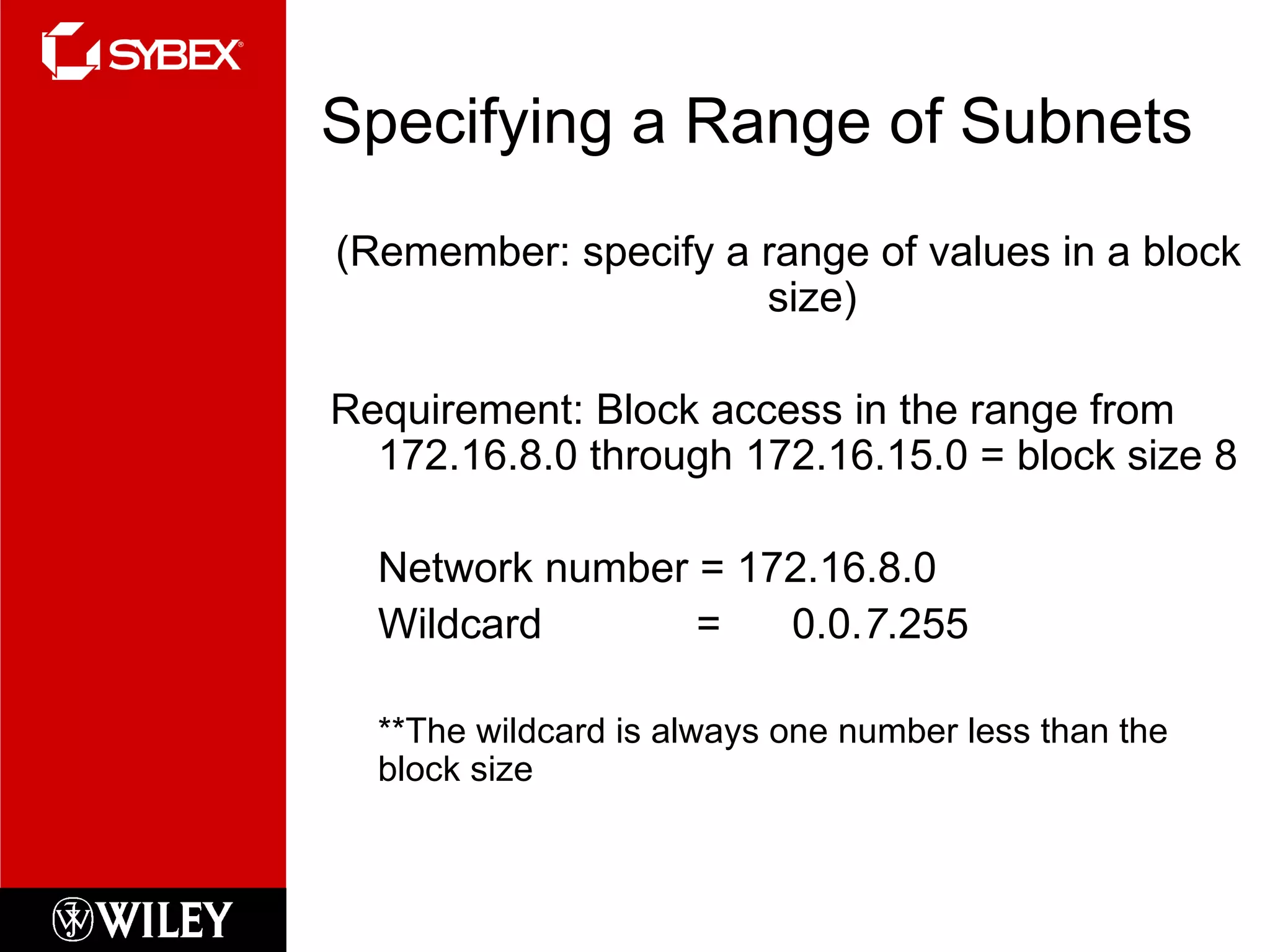
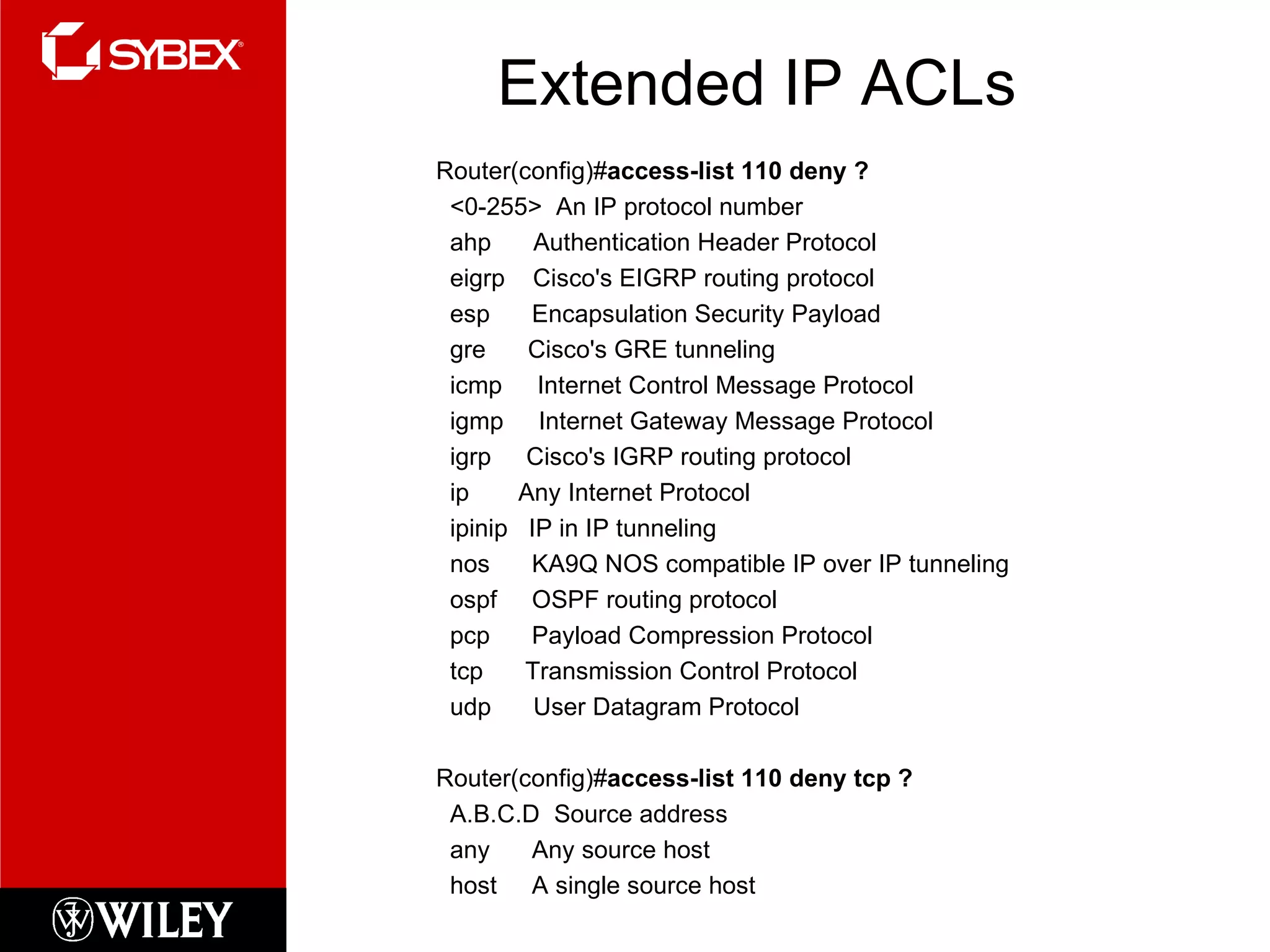
This chapter discusses network security concepts like types of attacks, mitigation techniques, and access control lists. Standard access lists filter based on source IP addresses while extended lists can filter on additional attributes like destination address, protocol, and port numbers. Access lists are applied to router interfaces to permit or deny traffic and help implement security policies. The document provides examples of how to configure standard and extended access lists on Cisco routers to control network access.