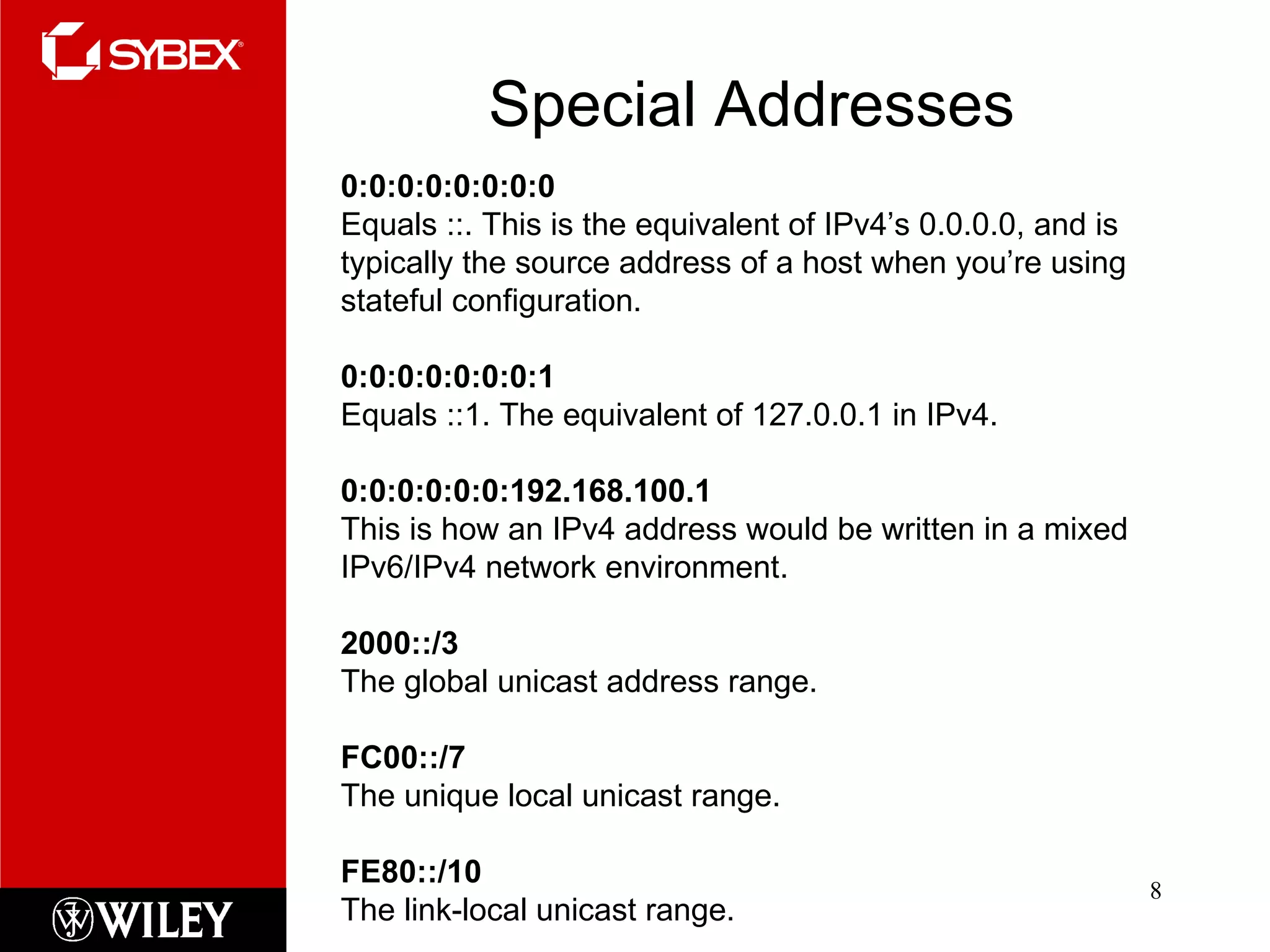
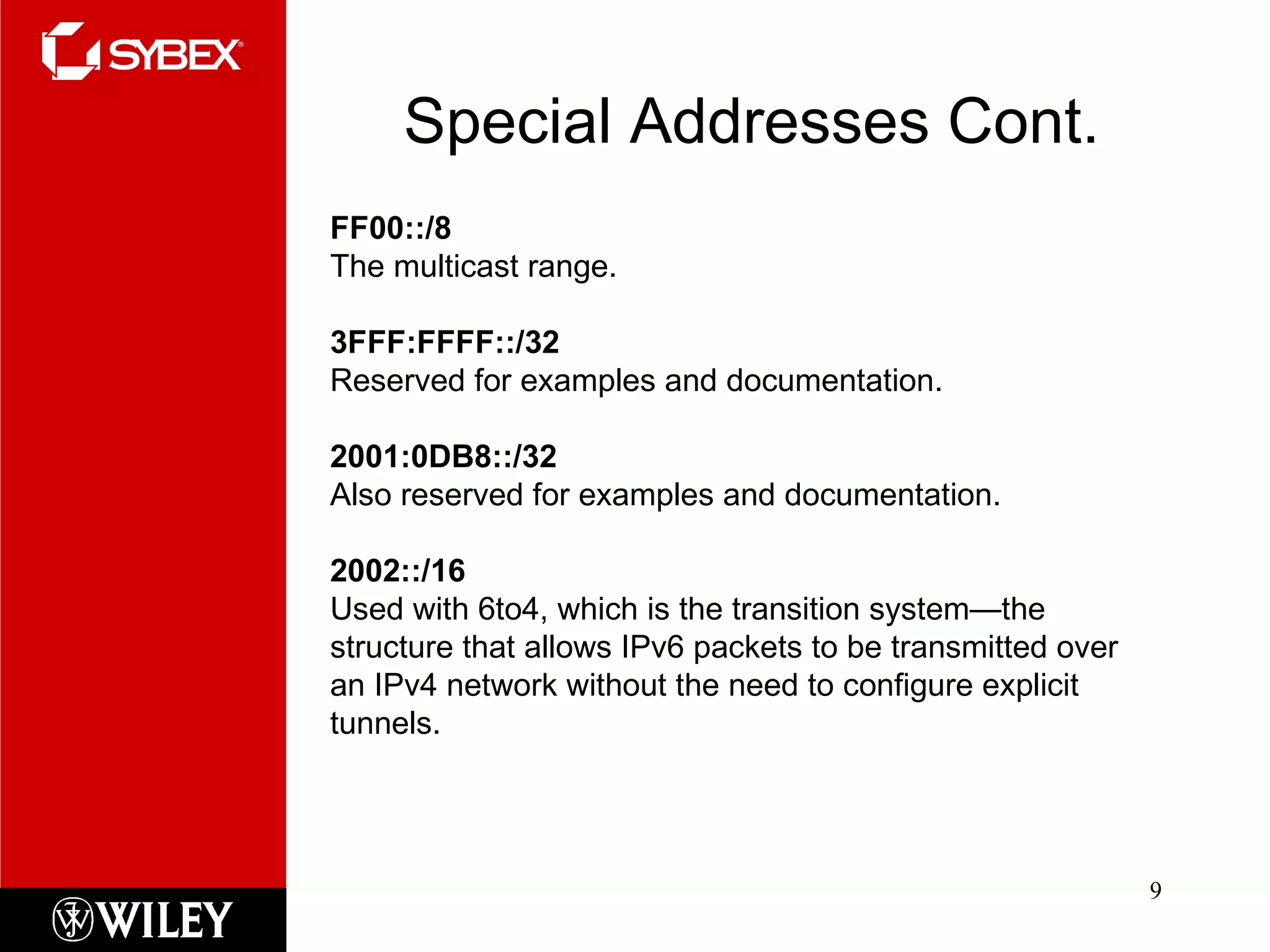
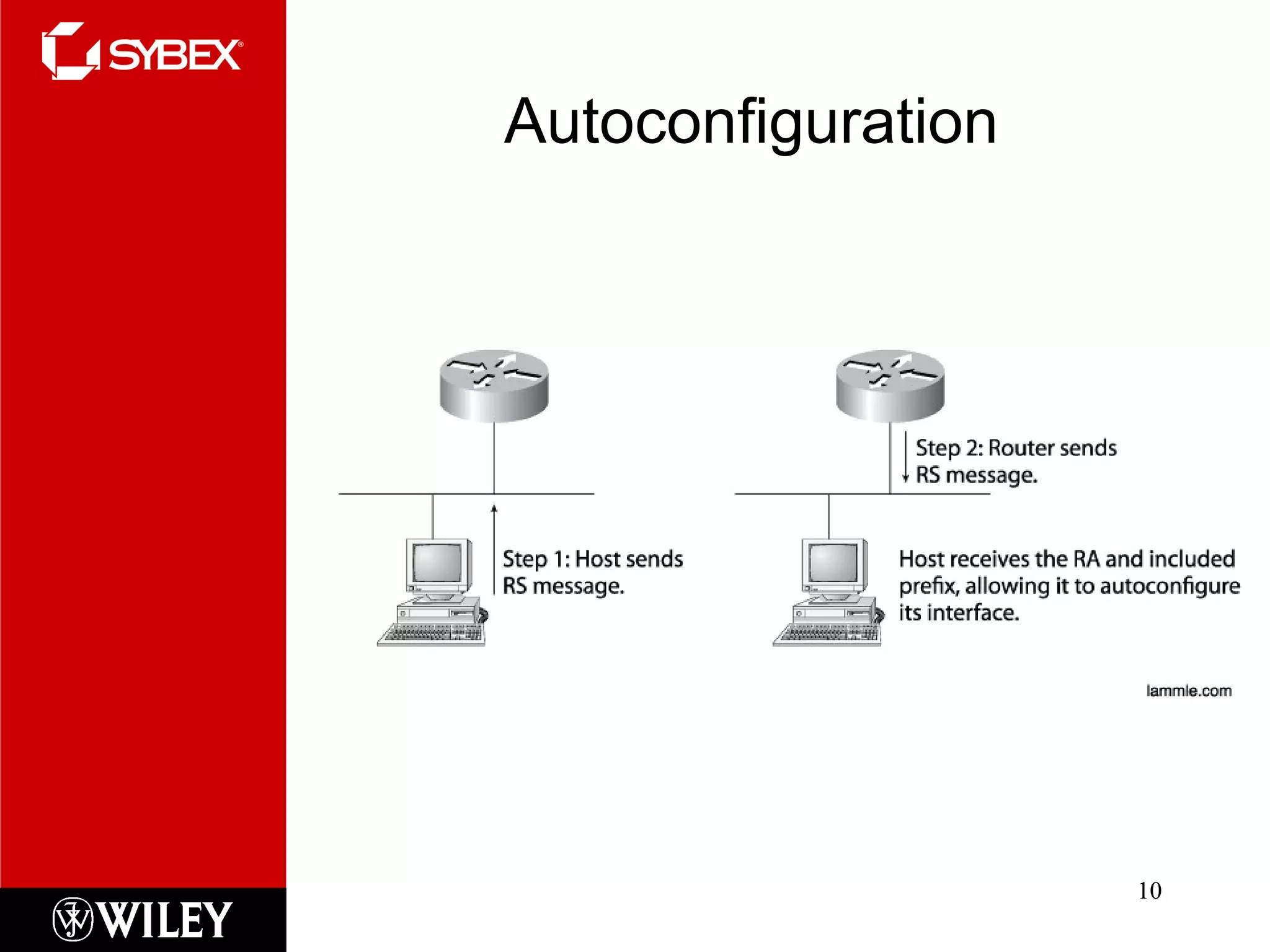
This chapter discusses IPv6, the next-generation Internet protocol. IPv6 was created to address the impending exhaustion of IPv4 addresses as the number of internet-connected devices grows rapidly. IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses compared to 32-bit addresses in IPv4. It supports various address types including unicast, multicast, and anycast. IPv6 also introduces mechanisms for address autoconfiguration and tunneling to support transition from IPv4 to IPv6.







![Configuring IPv6 In order to enable IPv6 on a router, you have to use the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command: Corp(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing IPv6 isn’t enabled by default on any interfaces either, so we have to go to each interface individually and enable it. You use the interface configuration command ipv6 address <ipv6prefix>/<prefix-length> [eui-64] to get this done. Here’s an example: Corp(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:3c4d:1:0260.d6FF.FE73.1987/64 You can specify the entire 128-bit global IPv6 address or you can use the eui-64 option. Remember, the eui-64 format allows the device to use its MAC address and pad it to make the interface ID. Corp(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:3c4d:1::/64 eui-64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter13ccna-120118120155-phpapp01/75/Chapter13ccna-11-2048.jpg)

