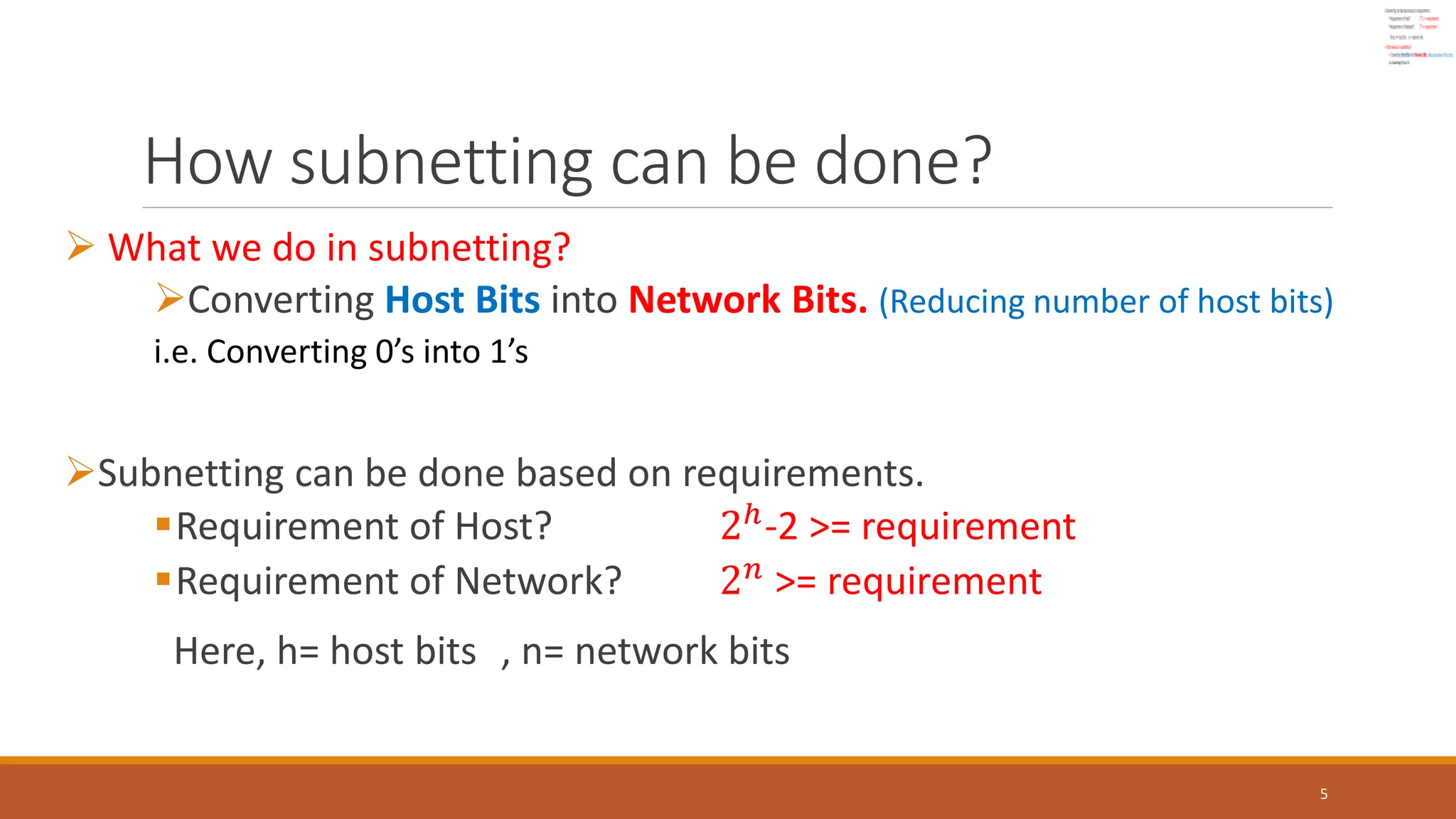
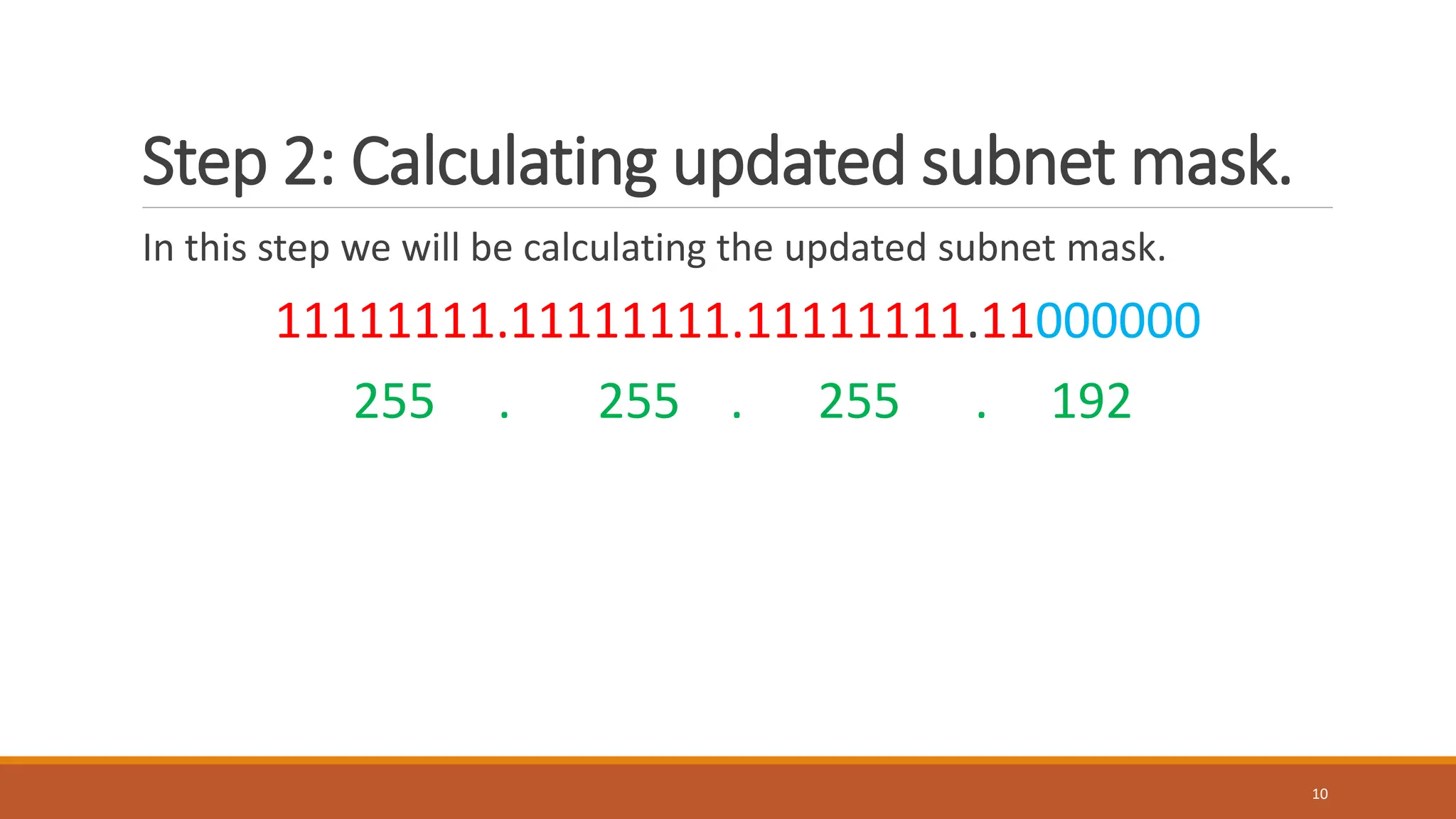
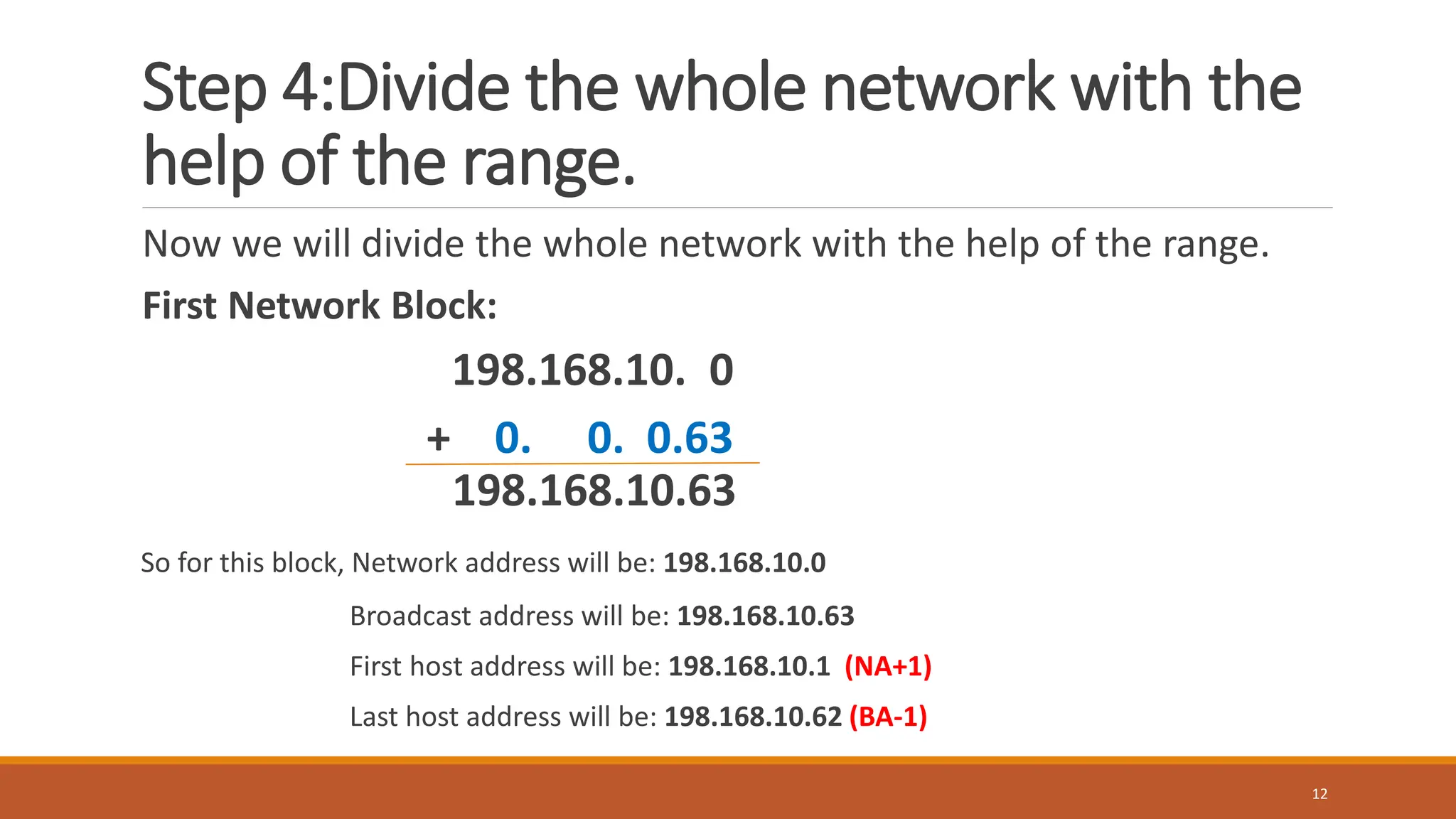
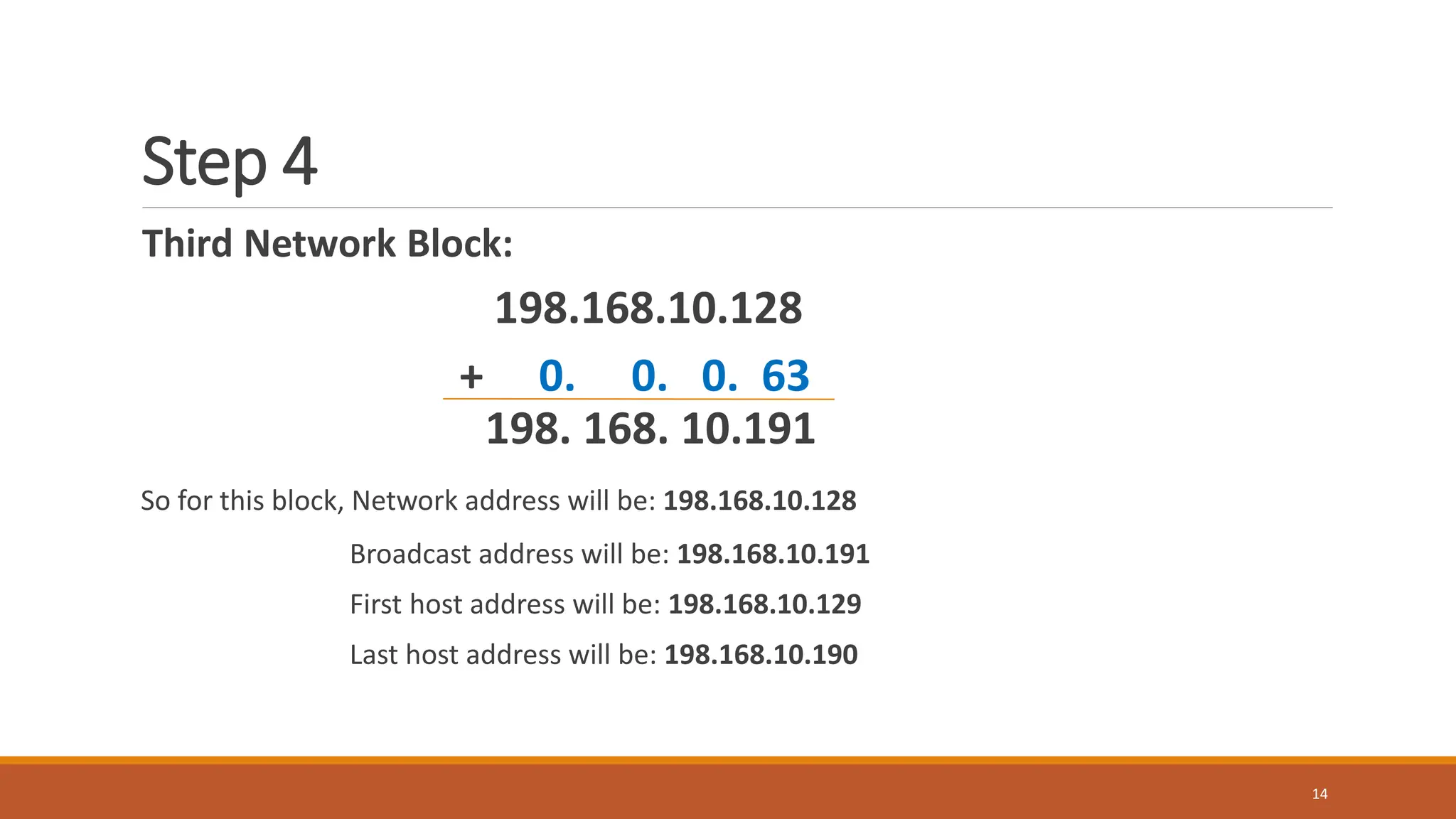
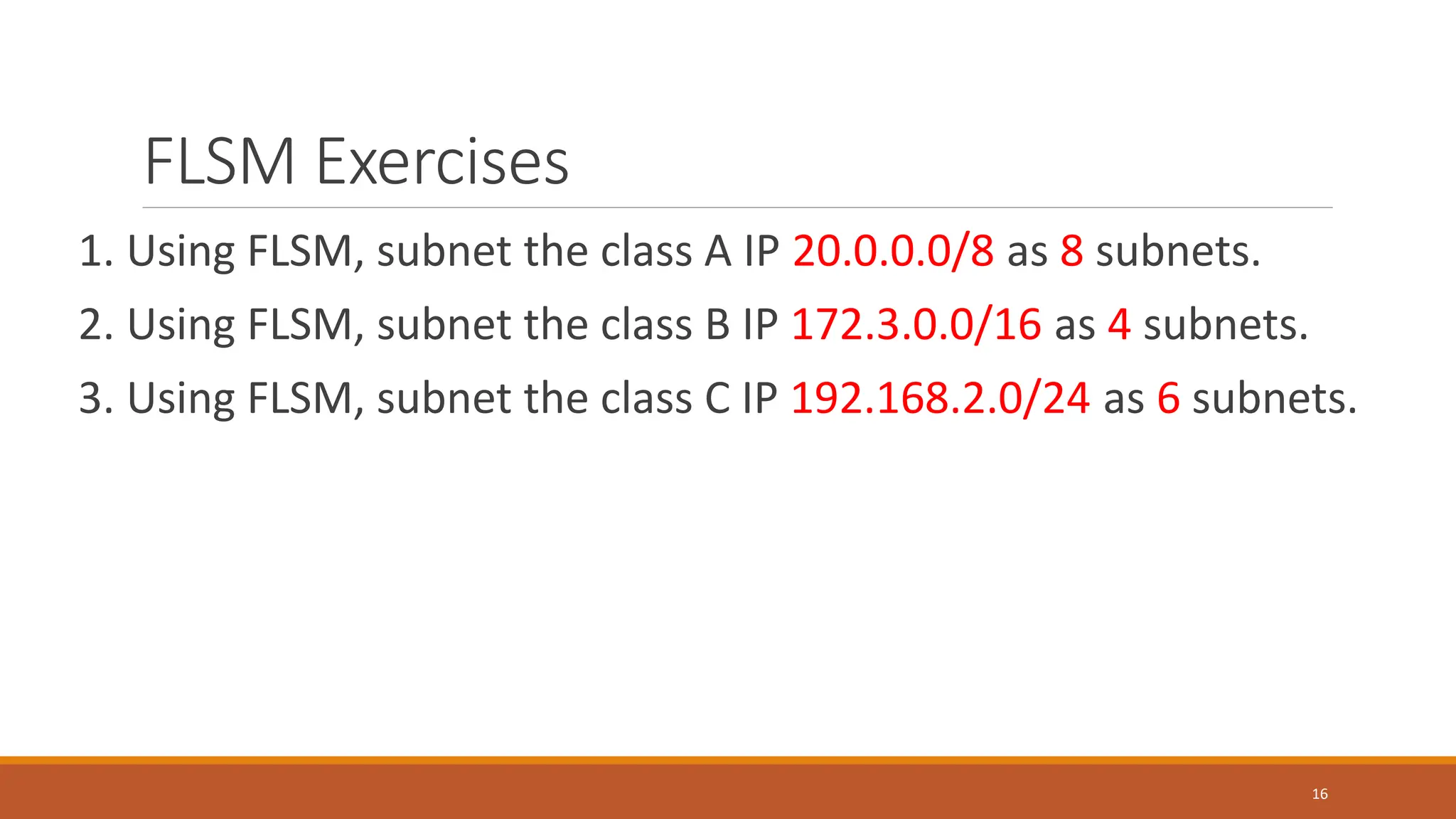
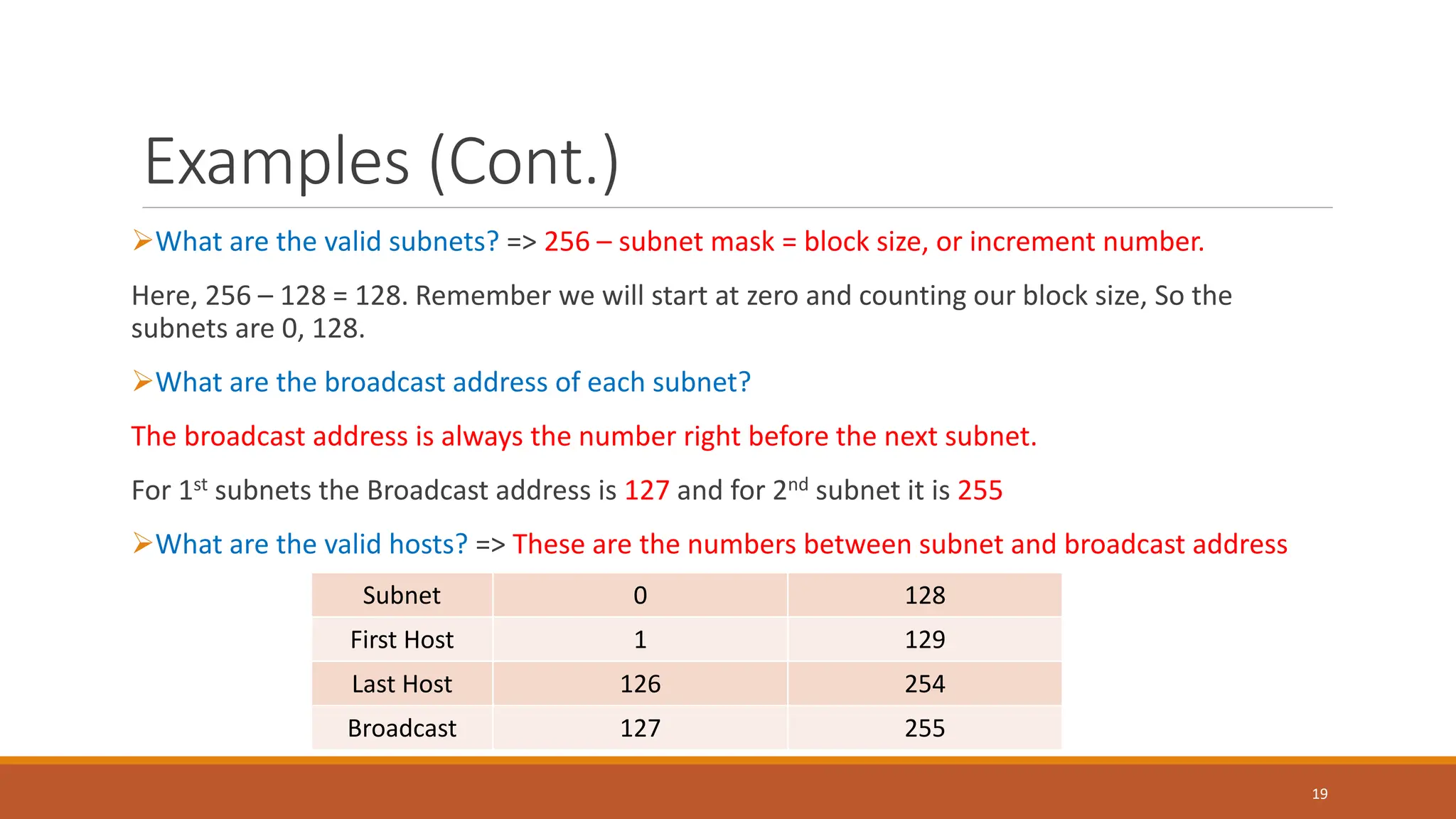
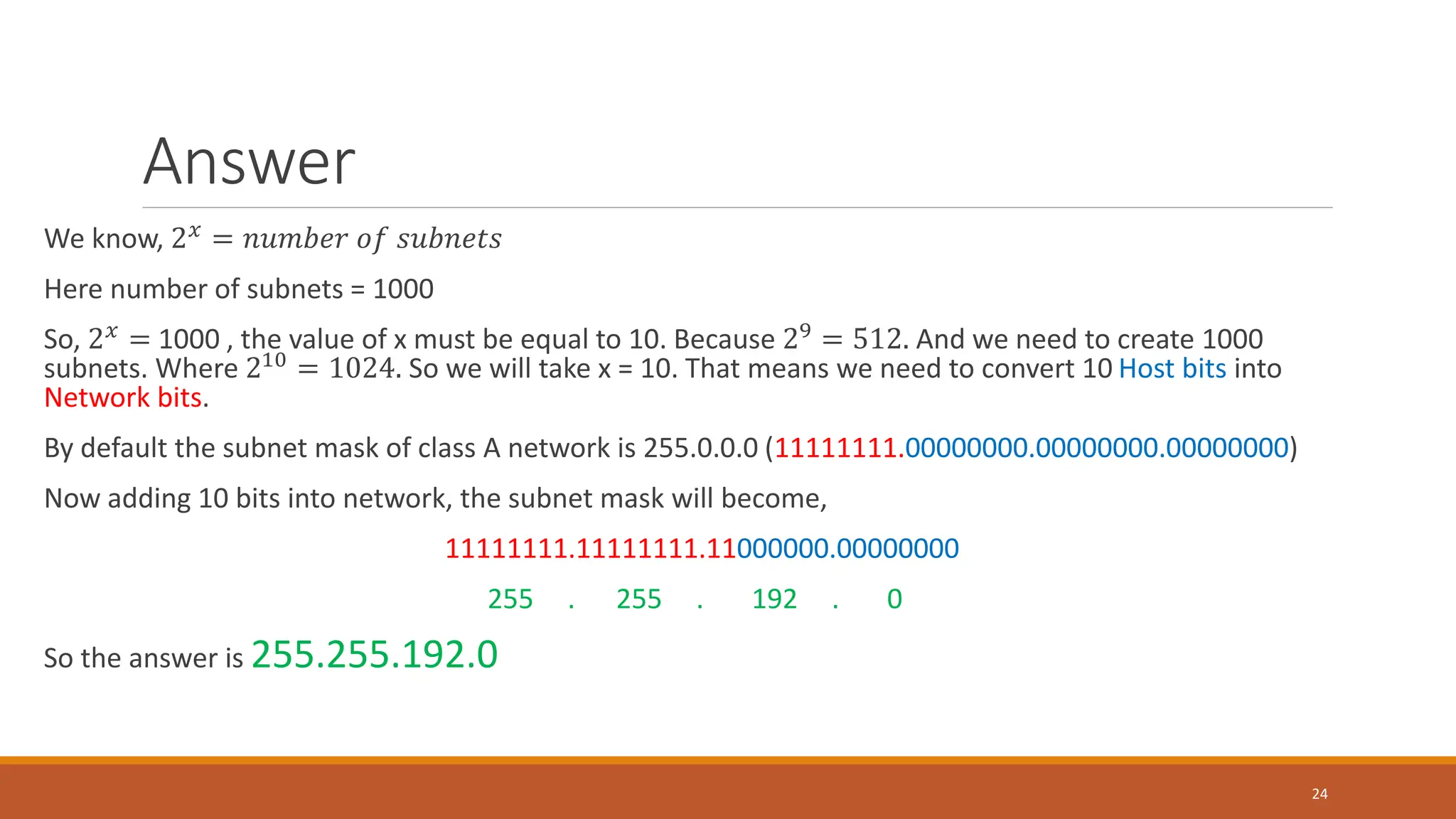
The document explains subnetting, which is the process of dividing a network into smaller sub-networks to optimize IP address usage, replacing classful addressing. It details types of subnetting, specifically Fixed Length Subnetting (FLSM) and Variable Length Subnetting (VLSM), and outlines steps for performing subnetting, including determining subnet and broadcast addresses. Practical examples and exercises reinforce concepts such as calculating subnet masks and analyzing network requirements for hosts.