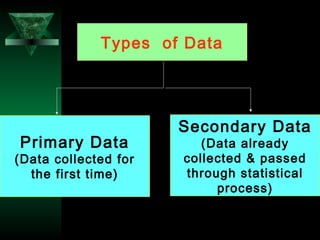
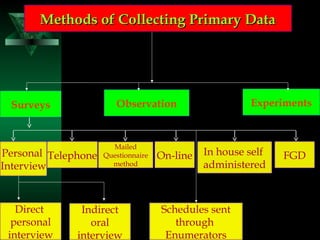
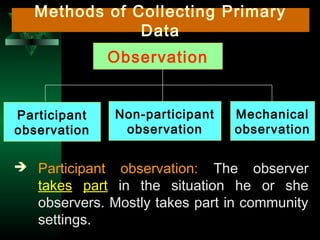
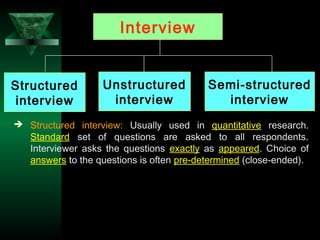
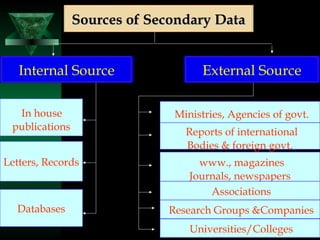
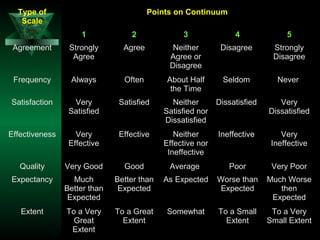
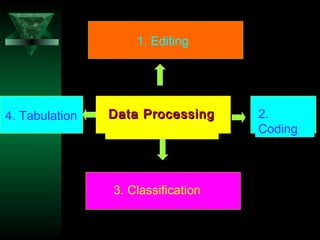
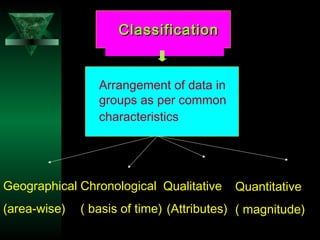
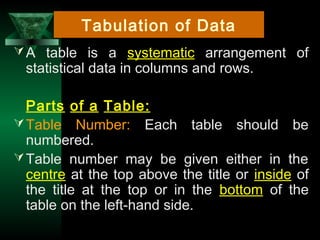
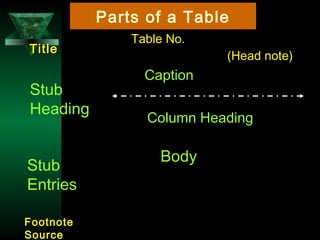
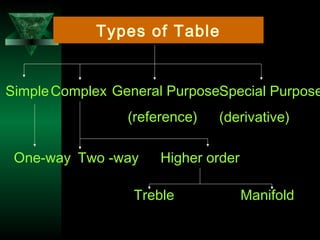
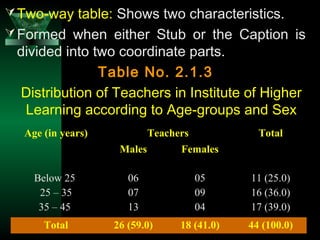
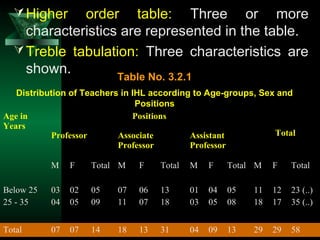
This chapter discusses procedures for data collection, processing, and analysis including primary and secondary data collection methods, guidelines for questionnaires, data editing, coding, classification, tabulation, and presenting data through diagrams and graphs for analysis and answering research questions.