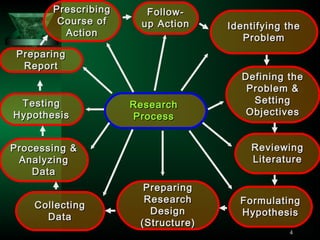
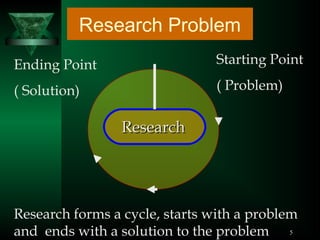
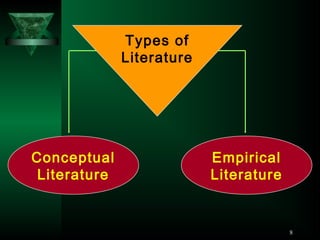
This document outlines the key steps in the research process, including:
1) Identifying a research problem and reviewing relevant literature and concepts.
2) Formulating testable hypotheses to focus the research.
3) Designing the research through determining sample size and data collection methods.
4) Collecting and analyzing data, which may involve statistical tests and examining relationships between variables.