Embed presentation
Downloaded 134 times




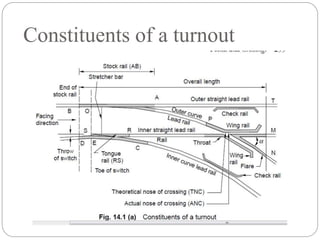
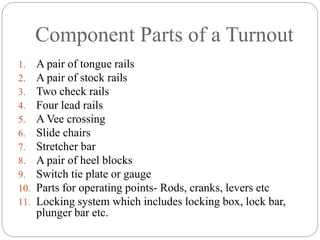




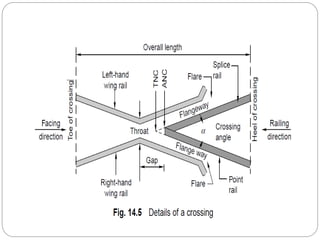


This document discusses railway engineering concepts related to points, crossings, and turnouts. It describes that a crossing allows the flanges of a railway vehicle to pass from one track to another where the gauges cross. A turnout uses lead rails and curved rails to divert rolling stock from one track to another. The key components of a turnout are tongue rails, stock rails, check rails, lead rails, a Vee crossing, and parts for operating the points. The document also describes different types of crossings, including acute angle, obtuse angle, and square crossings, as well as components like wing rails and check rails.












