1. Information systems involve collecting, storing, and communicating data through organized methods to gain knowledge and support business operations and management.
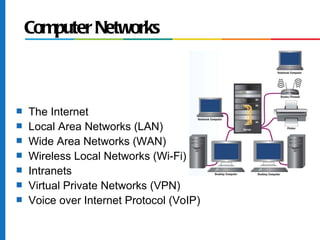
2. Key components of information systems include computer hardware, software, telecommunications networks, and data resource management.
3. Common types of information systems provide operational support like transaction processing or management support through systems like management information systems.