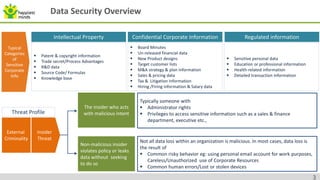
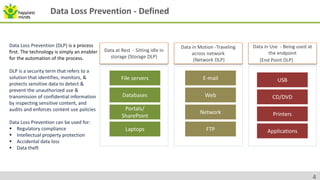
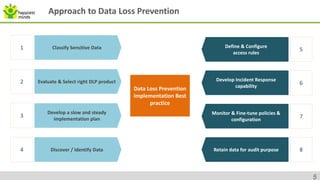
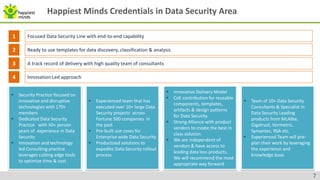
The document provides an overview of data security, highlighting threats from malicious and non-malicious insiders and the various types of sensitive corporate information at risk. It discusses Data Loss Prevention (DLP) as a critical process and technology to protect sensitive data across different states - at rest, in motion, and in use. Best practices and common mistakes in implementing DLP frameworks are detailed, along with capabilities and credentials of Happiest Minds in the data security sector.