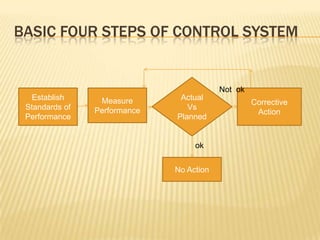
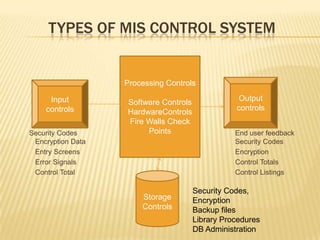
Controls are used to secure systems and reduce risks. They ensure policies are implemented and nonsensical data is not entered. A control system has objectives, performance standards, feedback, and a control center. It establishes standards, measures performance, compares actual to planned results, and takes corrective action. Features include early warnings, strategic focus, accurate and timely feedback, and information flow. Types of MIS controls are administrative, information system, procedural, physical facility, input, processing, output, storage, and software/hardware controls. MIS helps strategy with reports and data processing to save time.