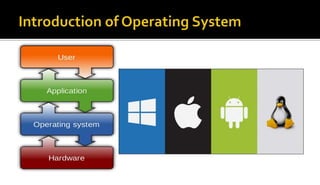
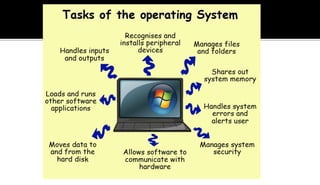
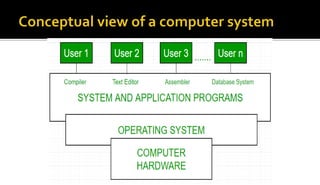
The document covers an overview of key computer science topics, including security, privacy, operating systems, and artificial intelligence. It details concepts such as cryptography, the functionalities of operating systems, and the essence of artificial intelligence in modern technology. Additionally, it outlines the significance of AI in various applications and the interdisciplinary factors that contribute to its development.