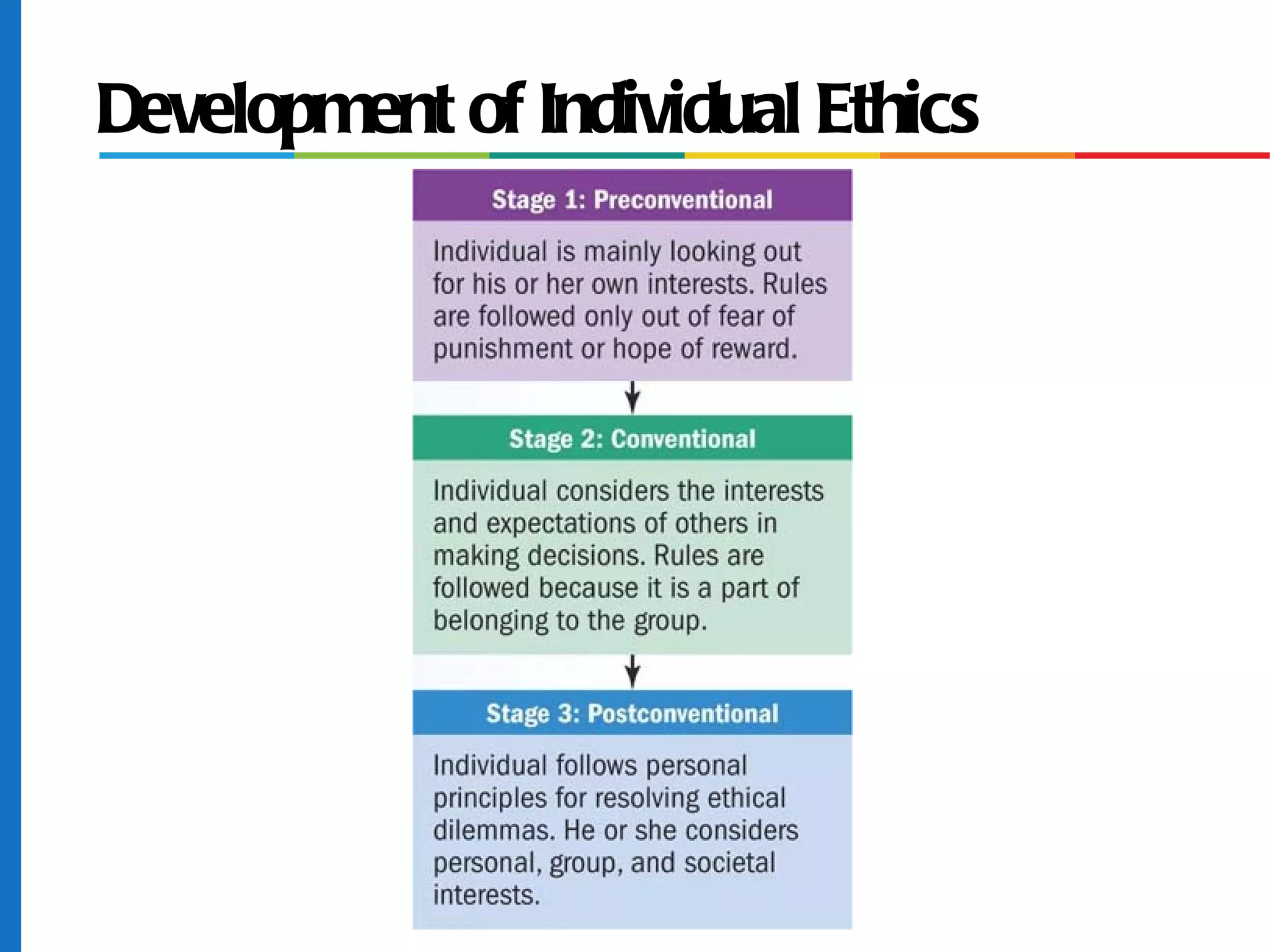
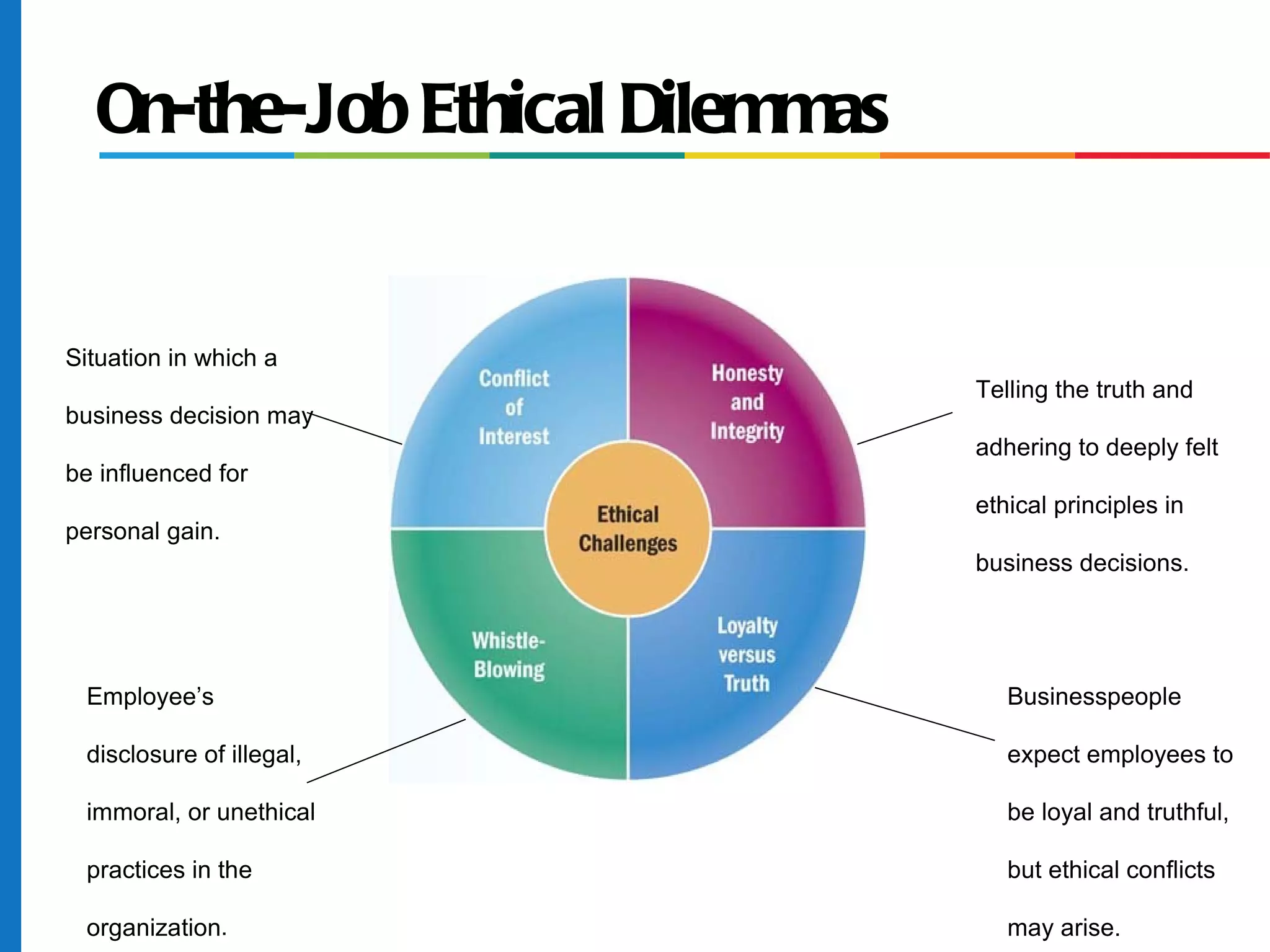
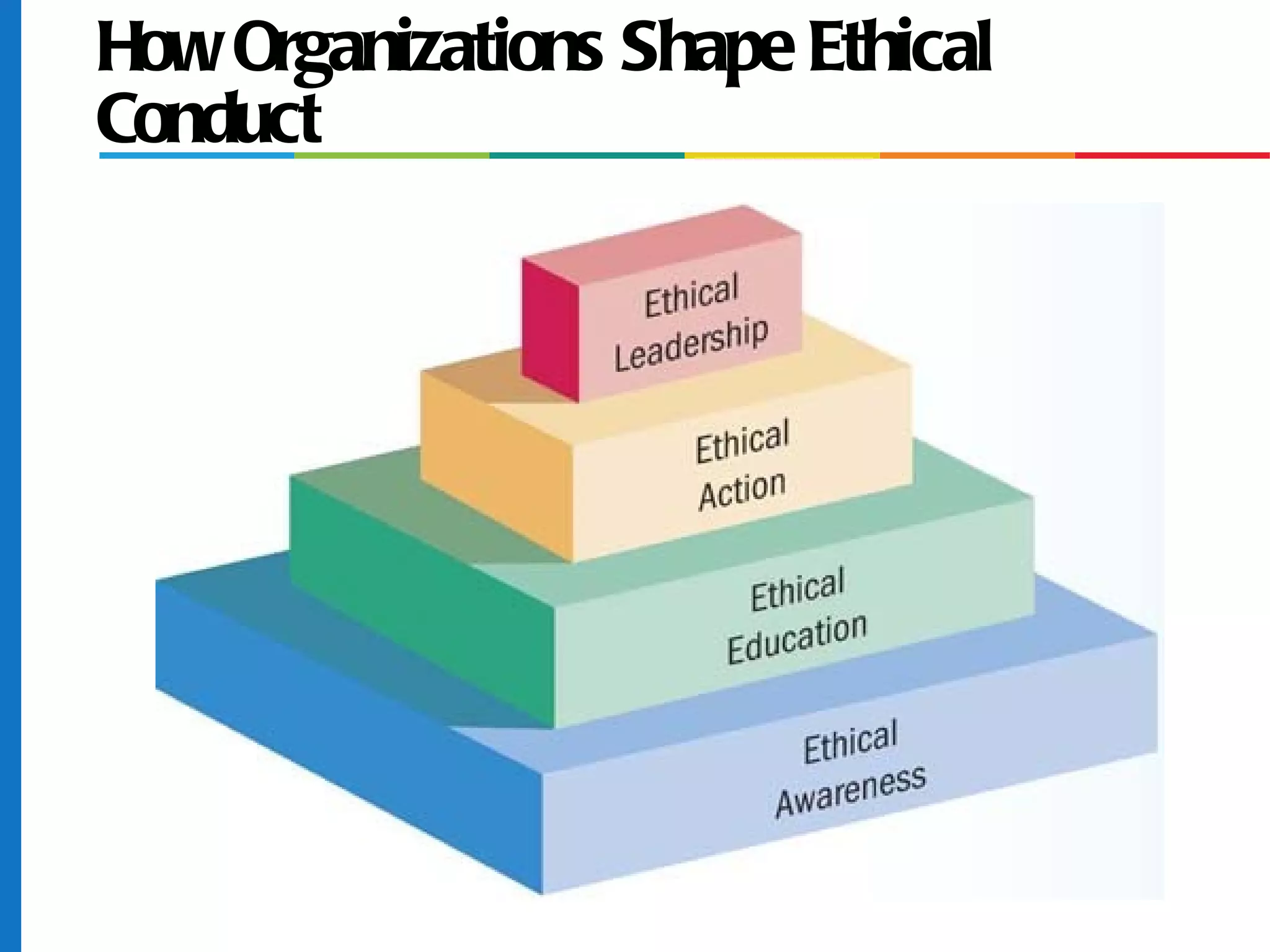
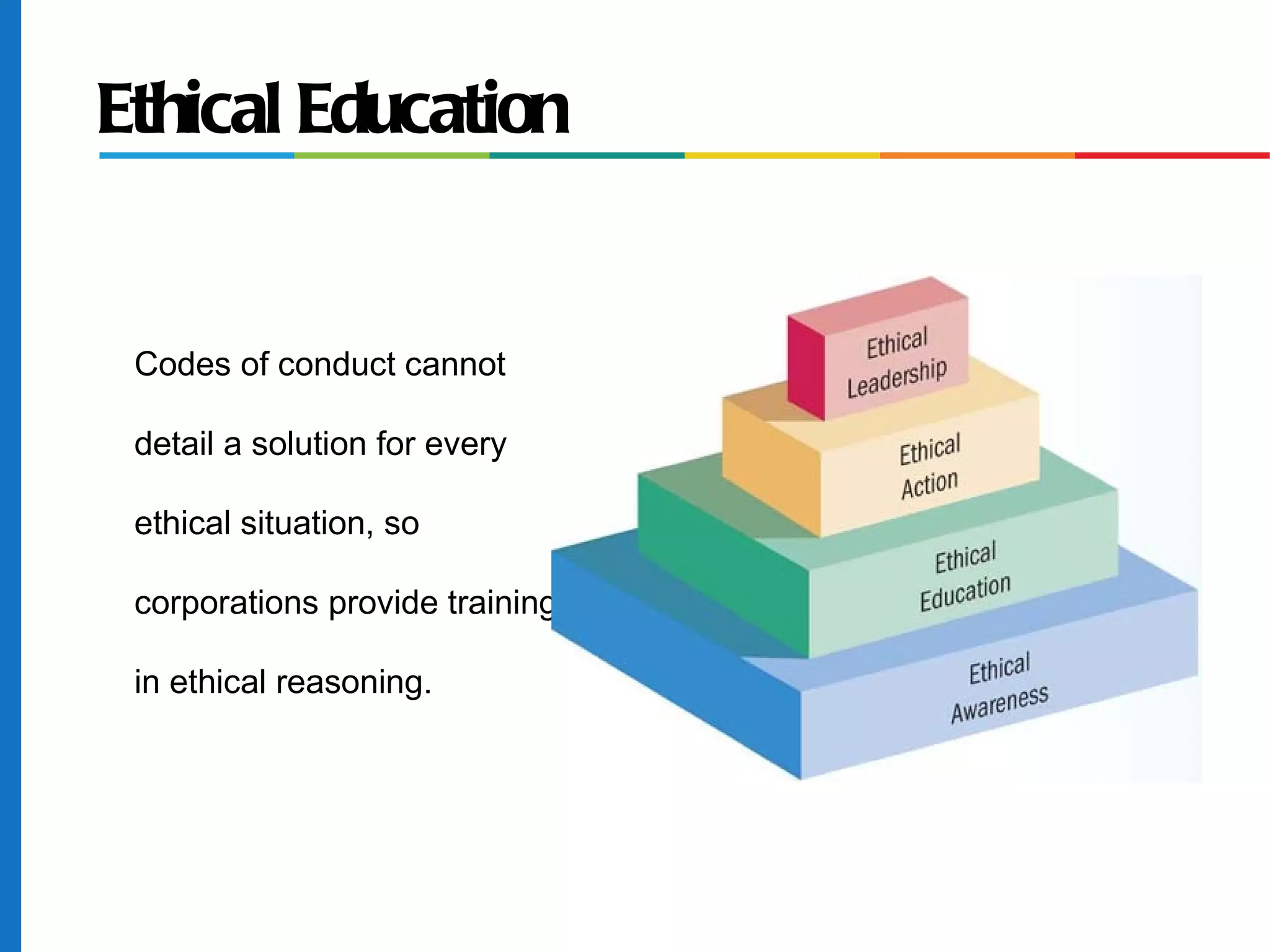
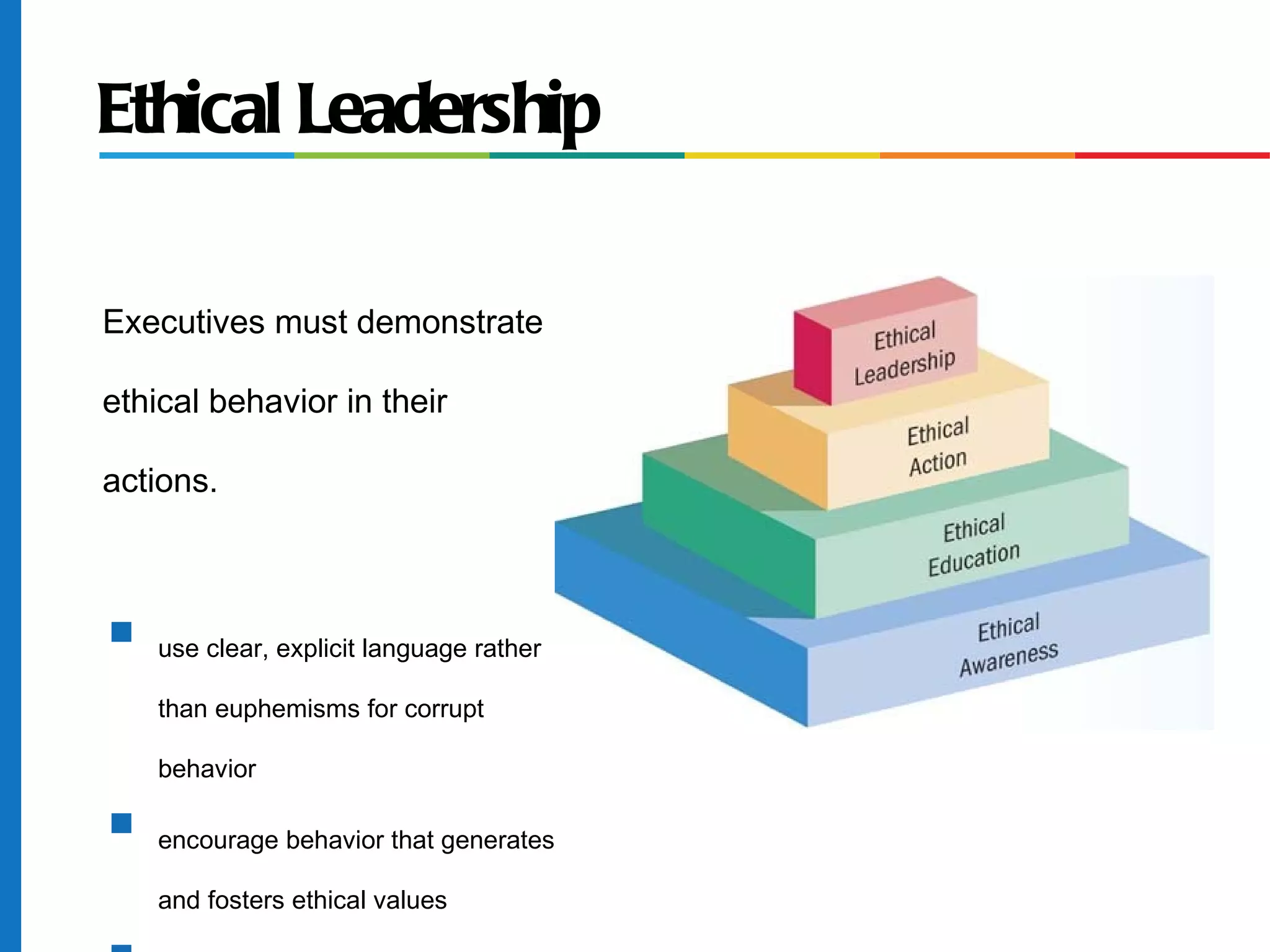
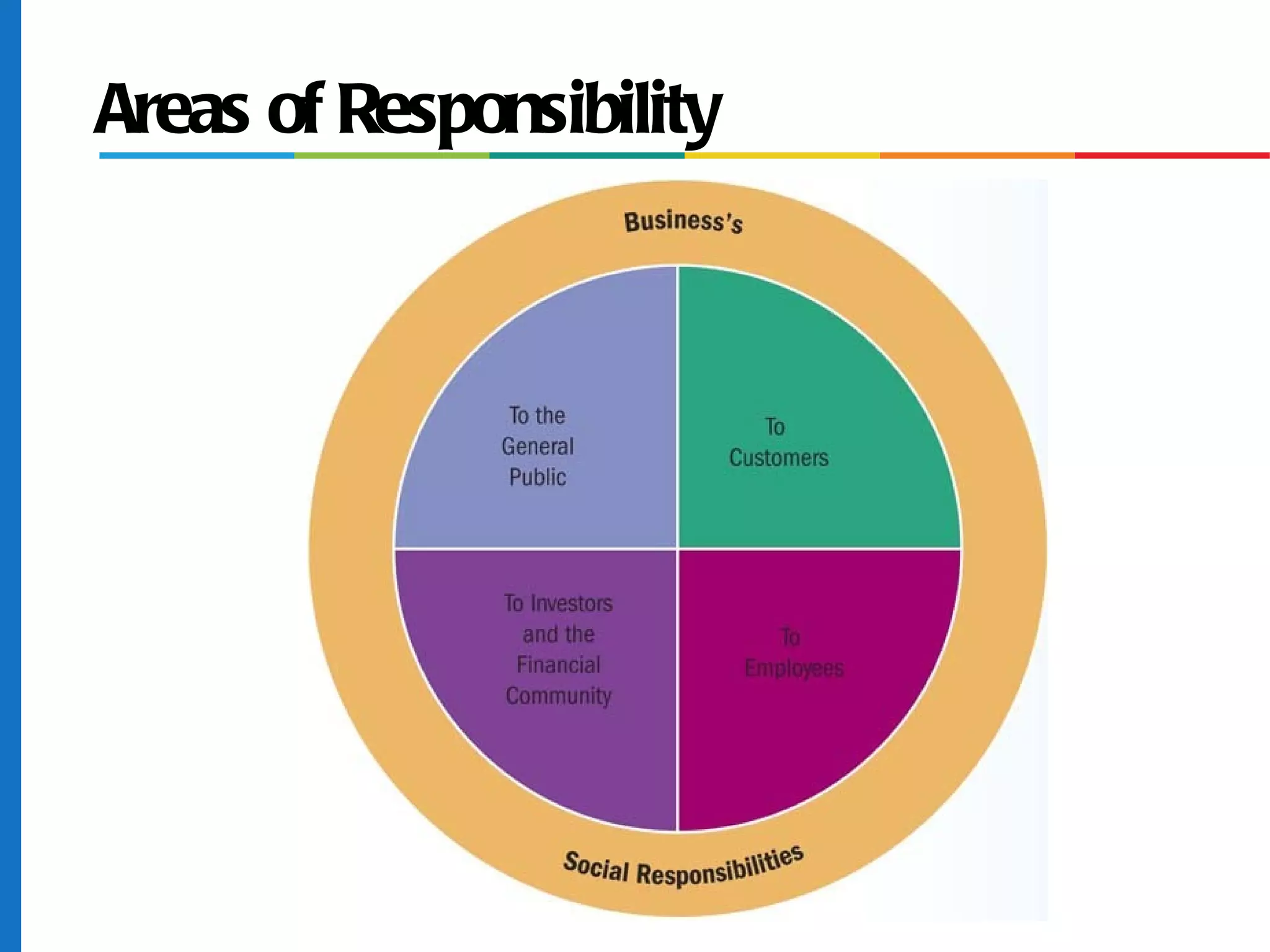
The document discusses business ethics and social responsibility, outlining how organizations can shape ethical behavior through codes of conduct, training, and leadership. It also describes the responsibilities of businesses to various stakeholders like customers, employees, investors, and the general public in areas like product safety, the environment, and equal opportunity. Managing ethics and social responsibility appropriately helps businesses balance profits with societal well-being.