This document provides an overview of key concepts in business, including:
1) It defines business and identifies the four factors of production.
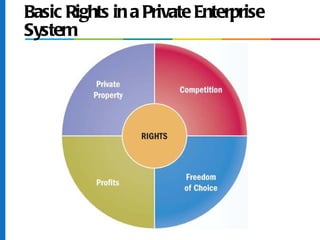
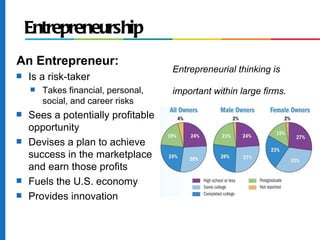
2) It describes the private enterprise system and entrepreneurship.
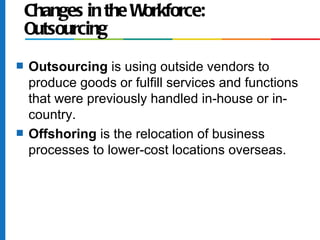
3) It outlines six eras of business history and how relationship management influences contemporary business.