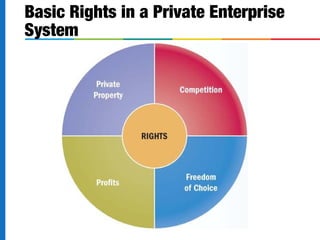
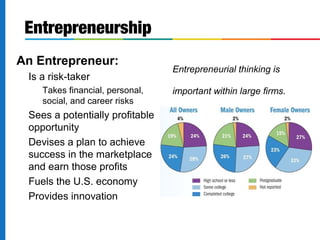
This document discusses the changing face of business. It begins by defining business and describing the key factors of production. It then outlines the private enterprise system and identifies six eras in the history of business. The document notes how today's workforce is changing in terms of skills needed, diversity, and flexibility. It identifies critical thinking, creativity, and ability to lead change as important skills for 21st century managers. Finally, it discusses what makes a company admired based on profits, growth, work environment, ethics and social responsibility.