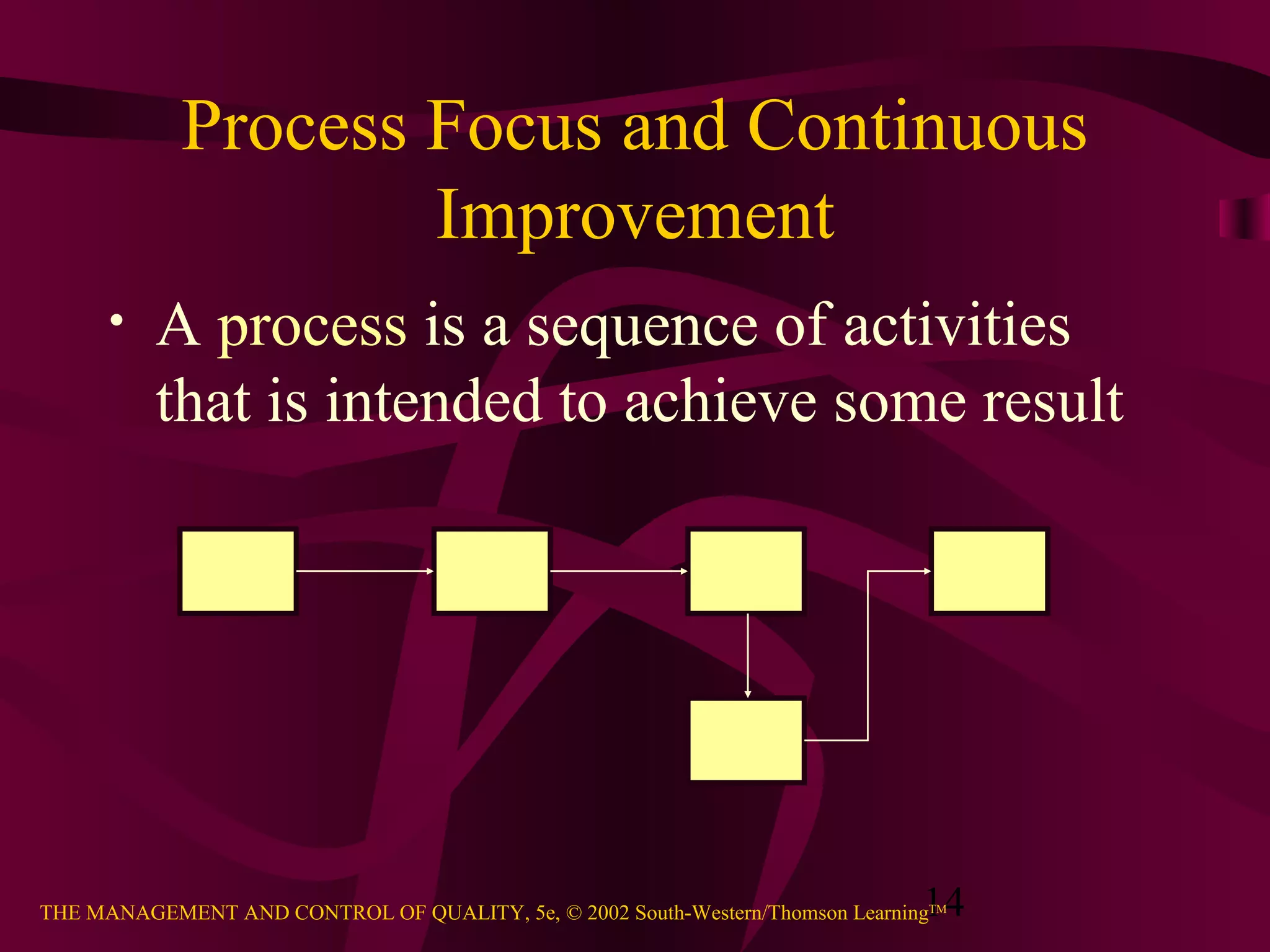
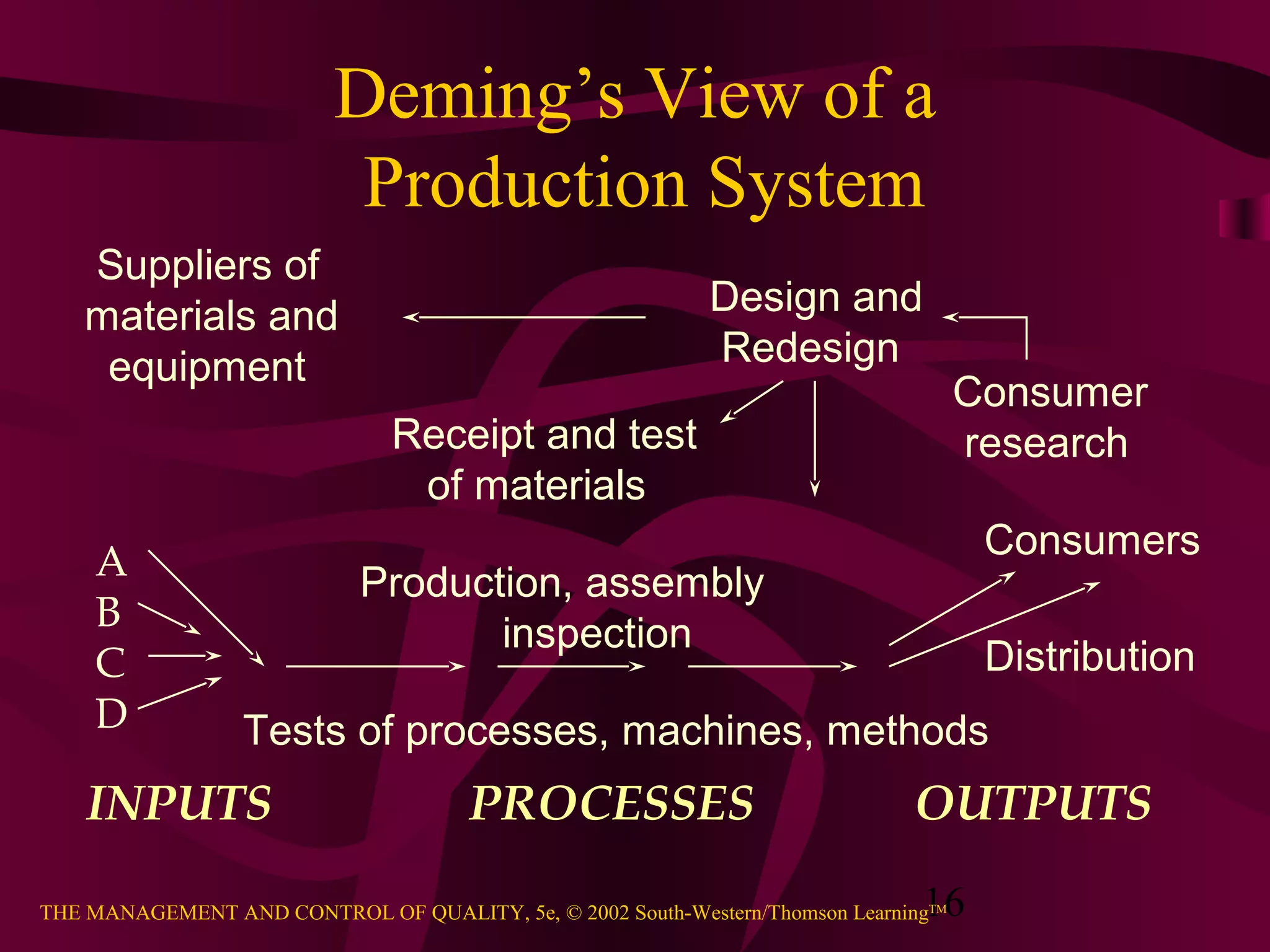
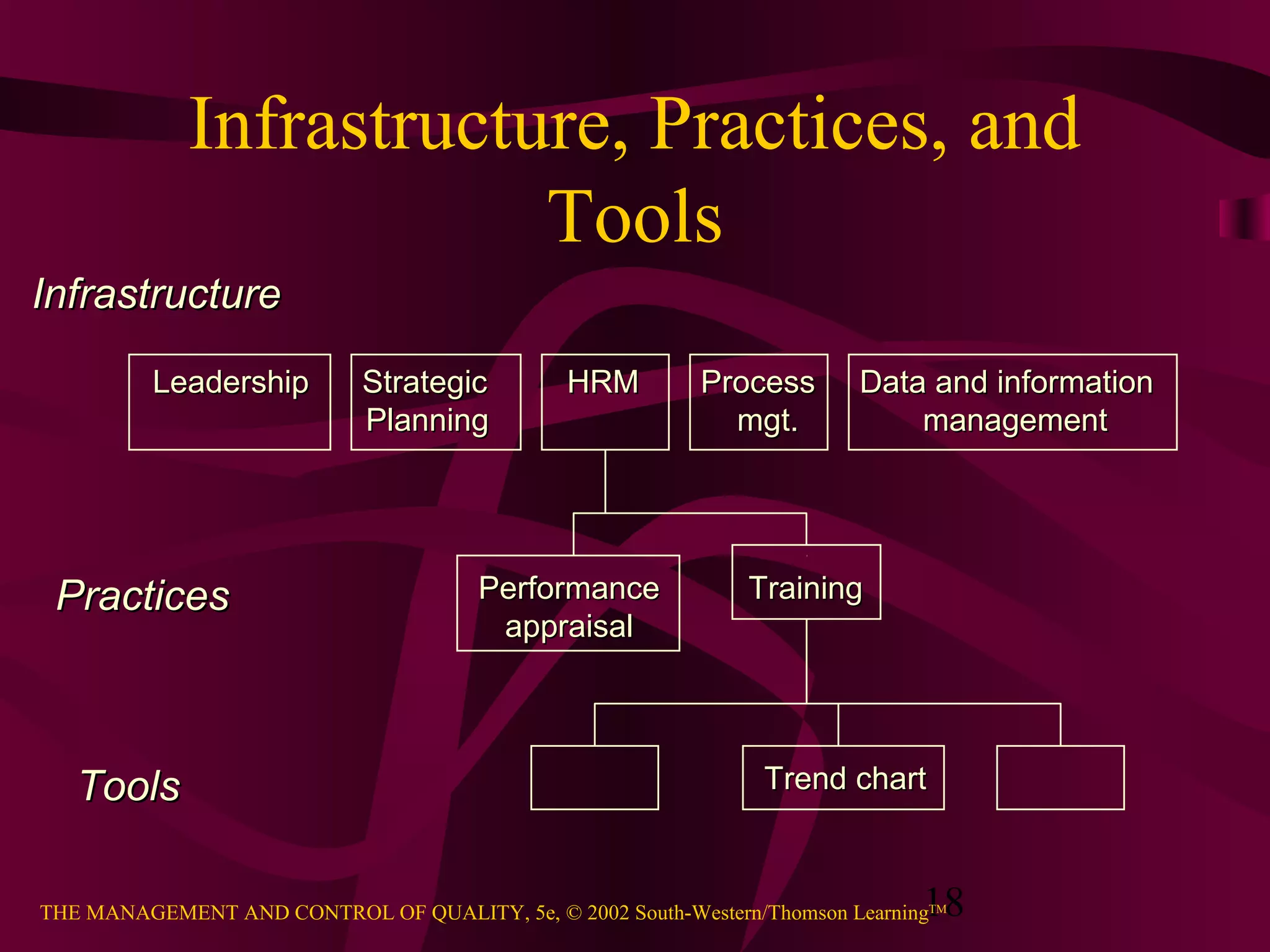
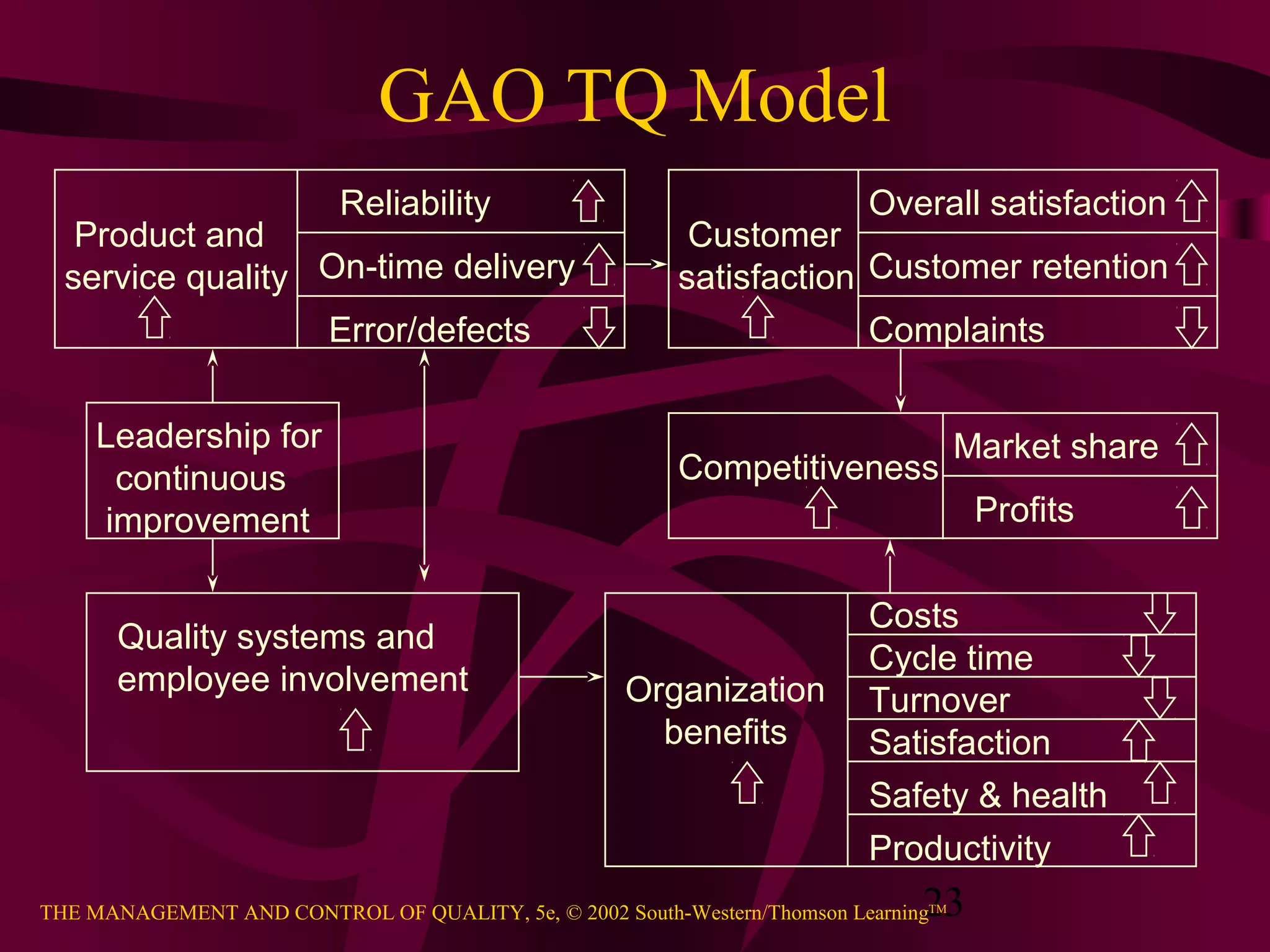
This document provides an overview of quality management. It discusses the history of quality assurance from skilled craftsmanship to modern total quality management practices. Key aspects of quality covered include definitions of quality, perspectives on quality including customer-driven and manufacturing-based views, principles of total quality such as customer focus and continuous improvement, and evidence that quality impacts business results and profitability. The relationship between quality and competitive advantage is also examined.