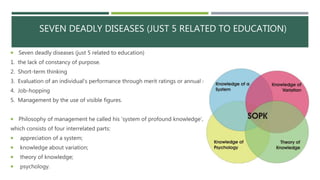
The document summarizes the main contributions of several quality gurus including W. Edwards Deming, Joseph Juran, Philip Crosby, Kaoru Ishikawa, Walter Shewhart, Armand Feigenbaum, and Genichi Taguchi. It discusses how Deming developed the "14 Points" and emphasized management's role in quality. It describes Juran's definition of quality and focus on cost of quality. It notes that Crosby coined the phrase "quality is free" and promoted zero defects. It also outlines Ishikawa's development of cause-and-effect diagrams and concept of the internal customer, as well as Taguchi's emphasis on design quality and development of robust design principles.