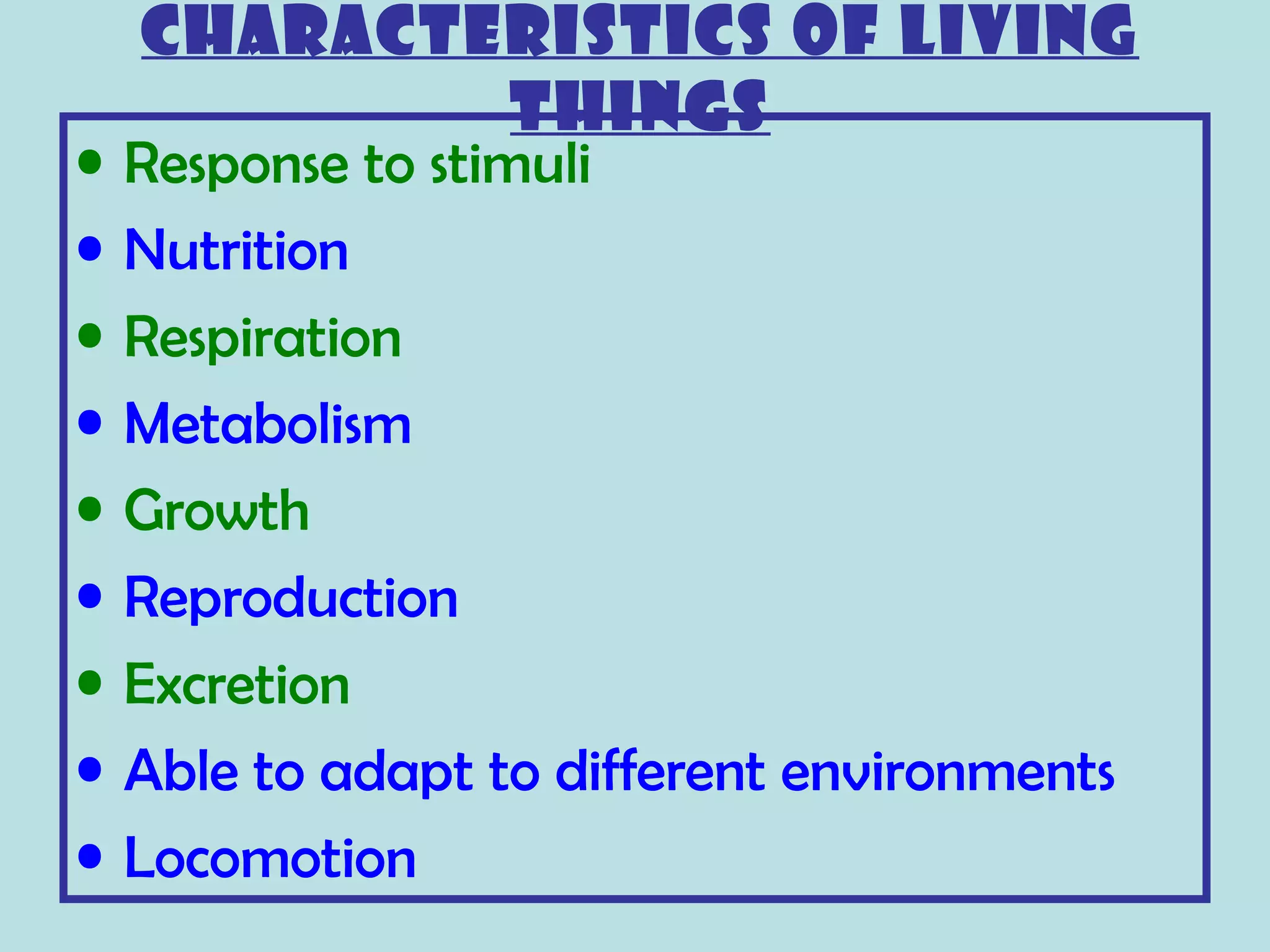
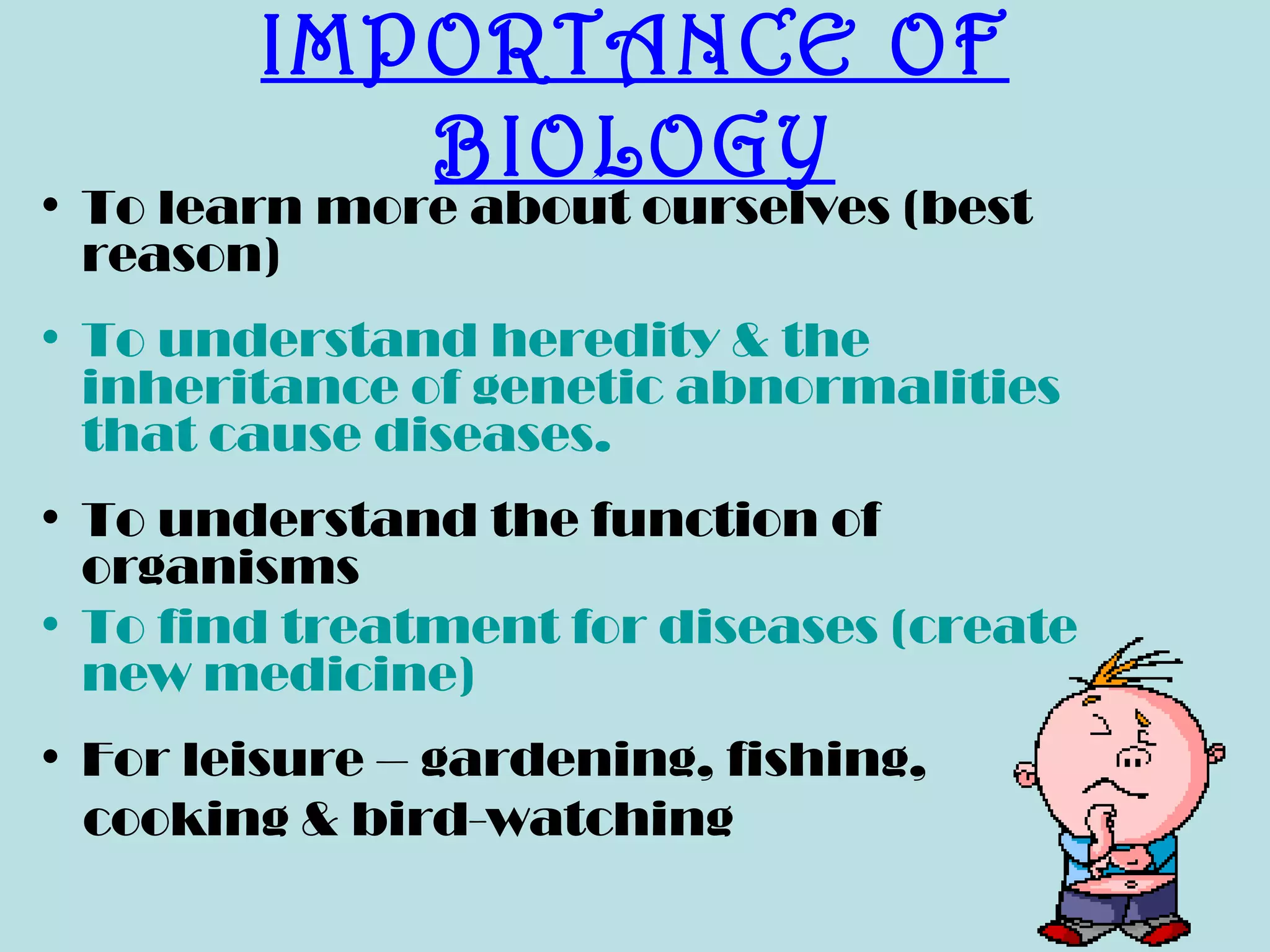
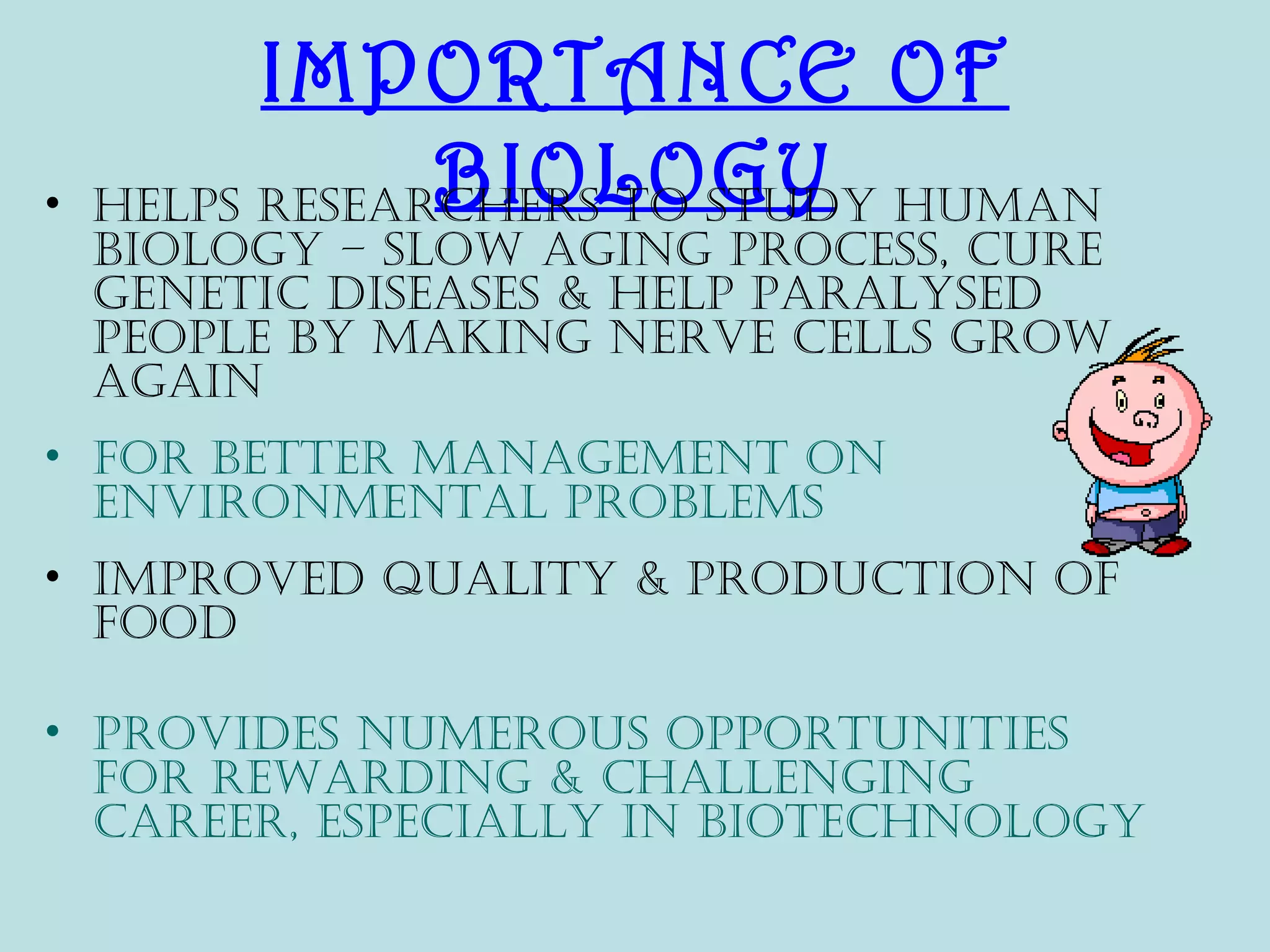
This document provides an overview of biology as an academic subject. It begins by defining biology as the study of living things, including their structure, life processes, characteristics, and interactions with the environment. It outlines several key characteristics of living things and discusses the importance of studying biology to understand ourselves, diseases, and find new treatments. The document also describes several major fields of study within biology, including areas focused on structure and function, grouping of organisms, development, environments, and applied fields. It concludes by listing various careers that are related to the study of biology.