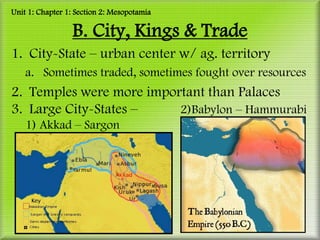
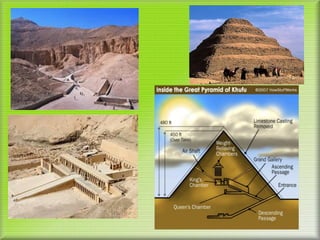
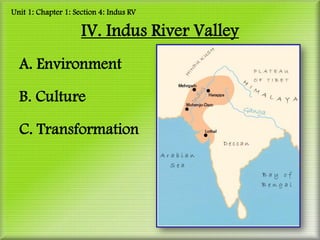
Unit 1 covers the origins of civilization from 8000-1500 BCE. It discusses the Stone Age and Agricultural Revolution that led to more settled communities. Mesopotamia was an early civilization that grew along the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, developing cities, kings, trade networks, and advanced technologies like writing. Egyptian civilization also arose along the Nile River, with powerful pharaohs regarded as divine kings. Egyptians developed monumental architecture like pyramids, a bureaucracy to manage resources and taxes, and advanced knowledge in many fields like mathematics and astronomy.