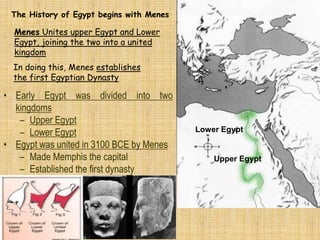
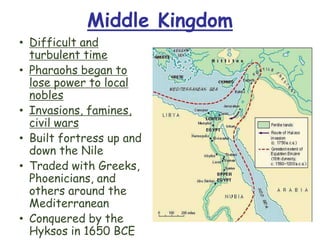
The document provides an overview of ancient Egyptian civilization, highlighting the significance of the Nile River and the rich alluvial soil it brought, as well as the role of religion in daily life. It details key historical periods, including the Old Kingdom known for pyramid construction, the Middle Kingdom marked by invasions, and the New Kingdom with powerful pharaohs like Ramses II. Additionally, it addresses societal aspects such as social classes, women's rights, writing systems, and advancements in math and medicine.