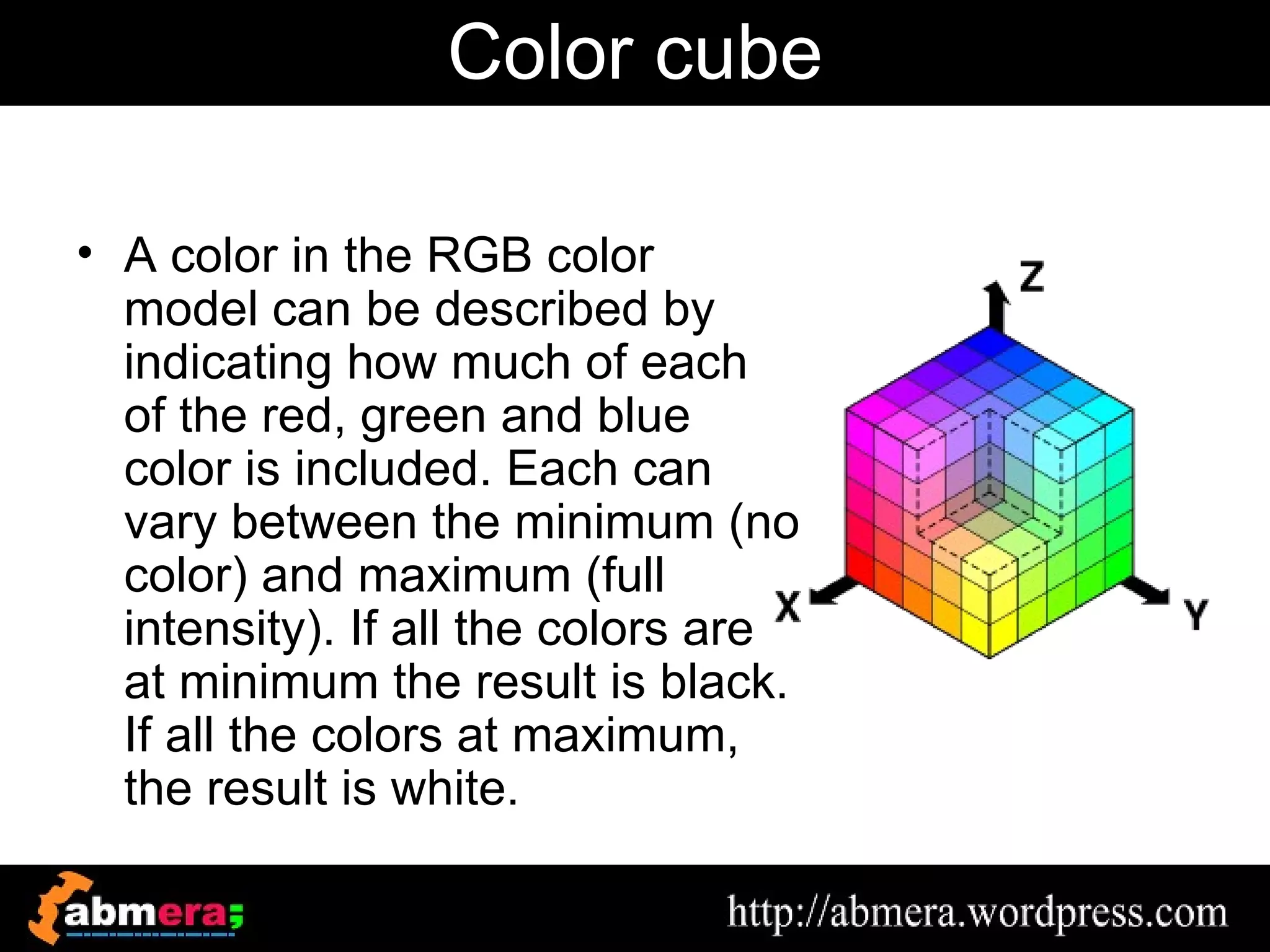
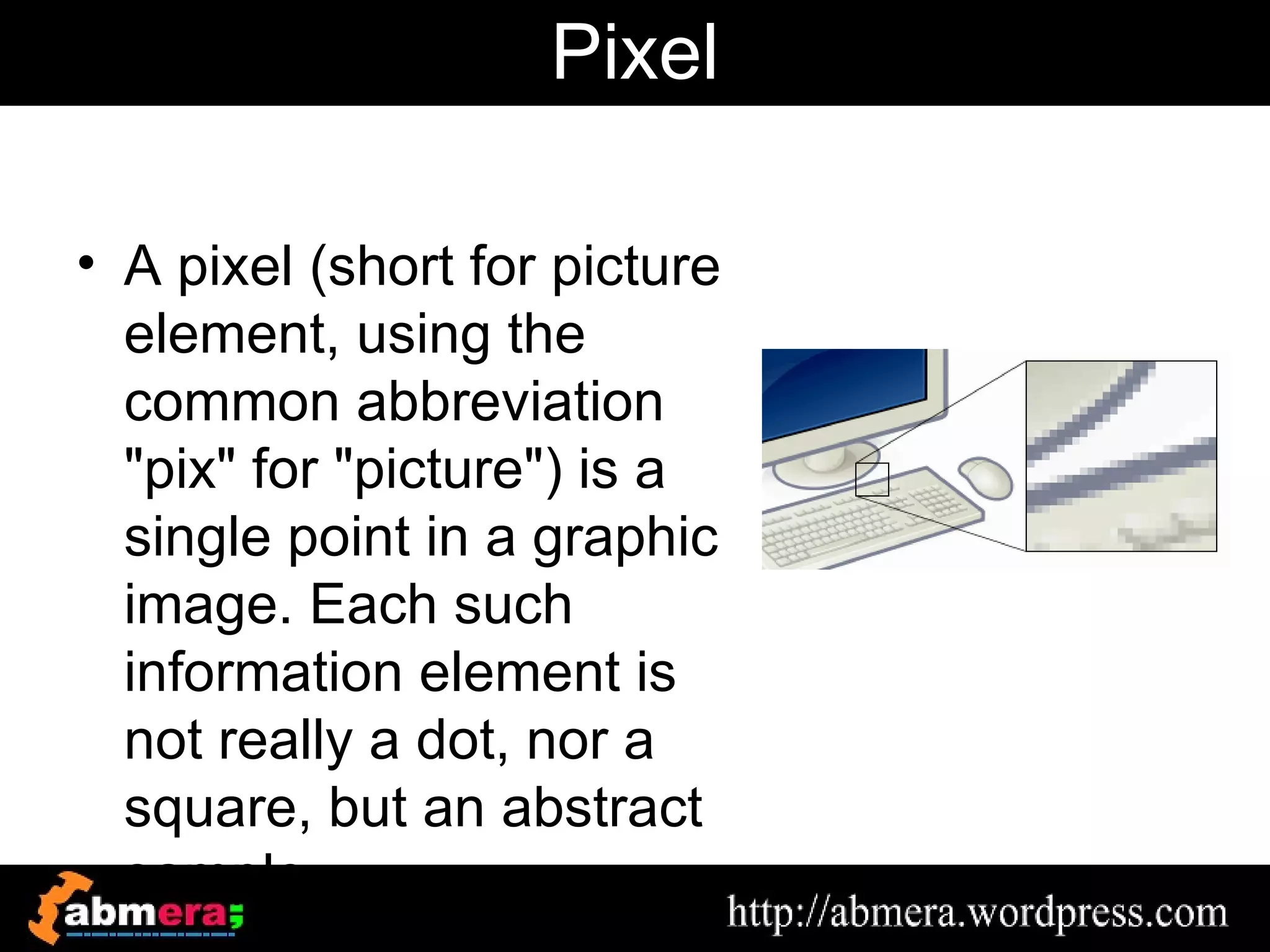
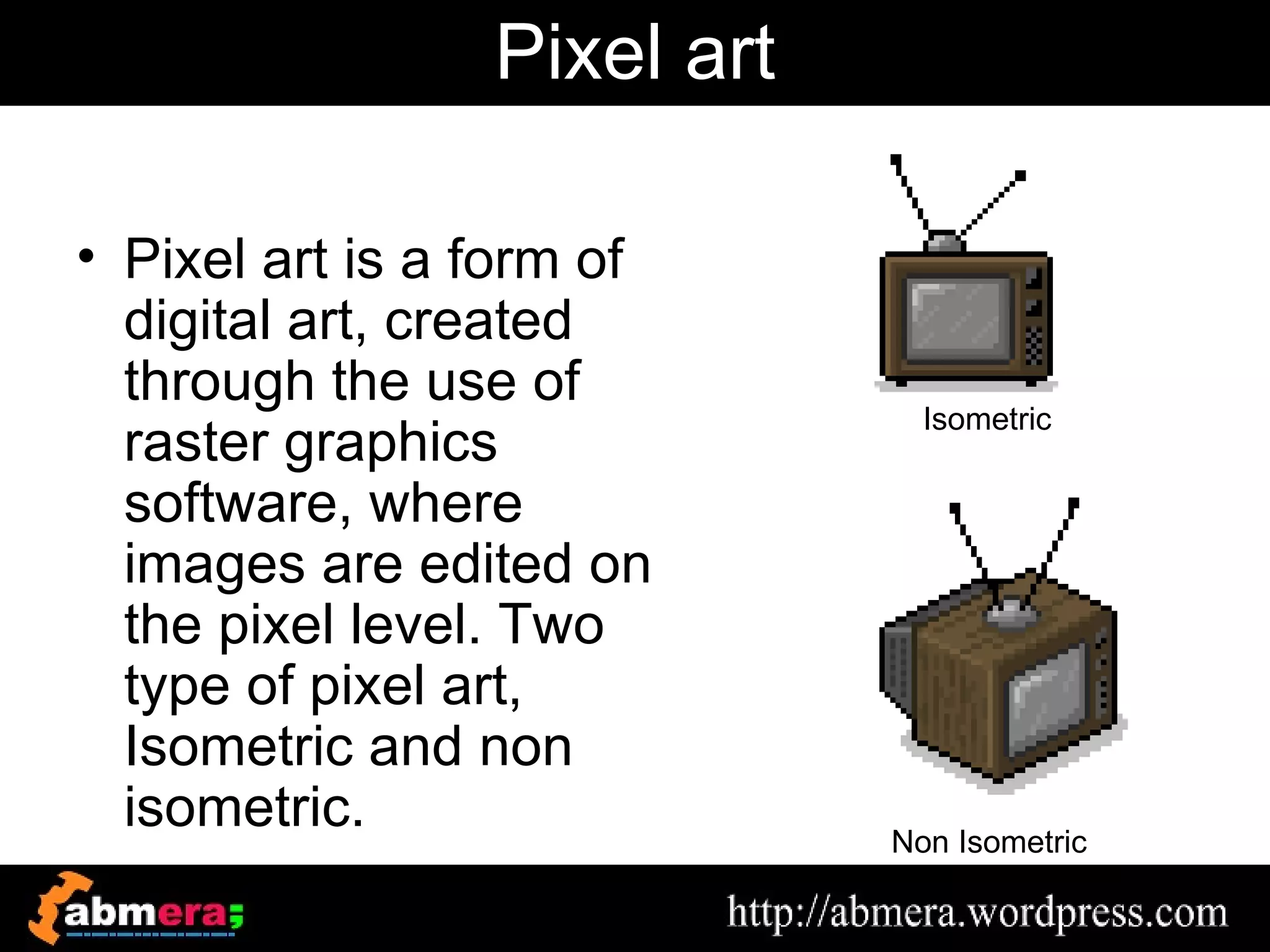
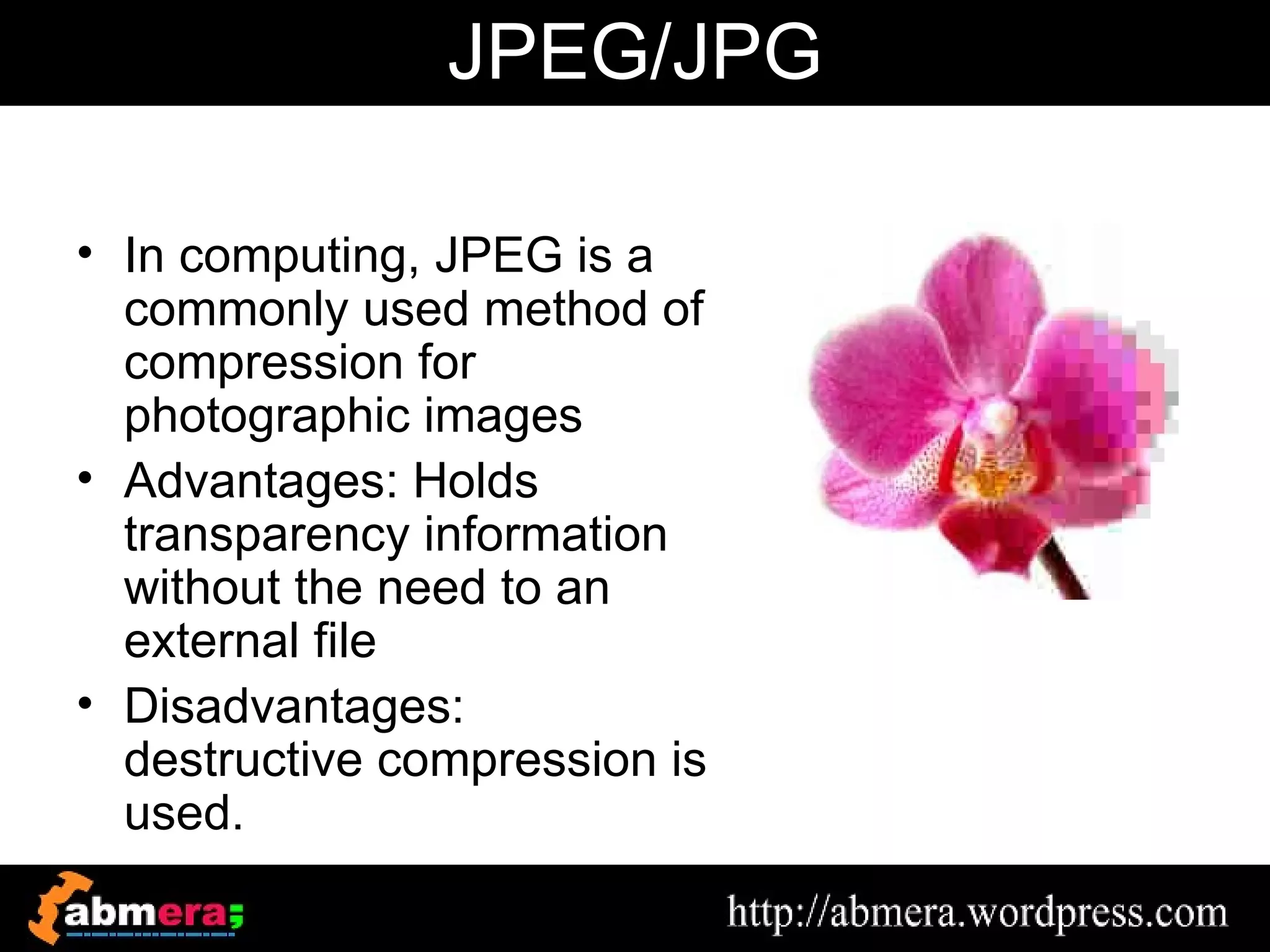
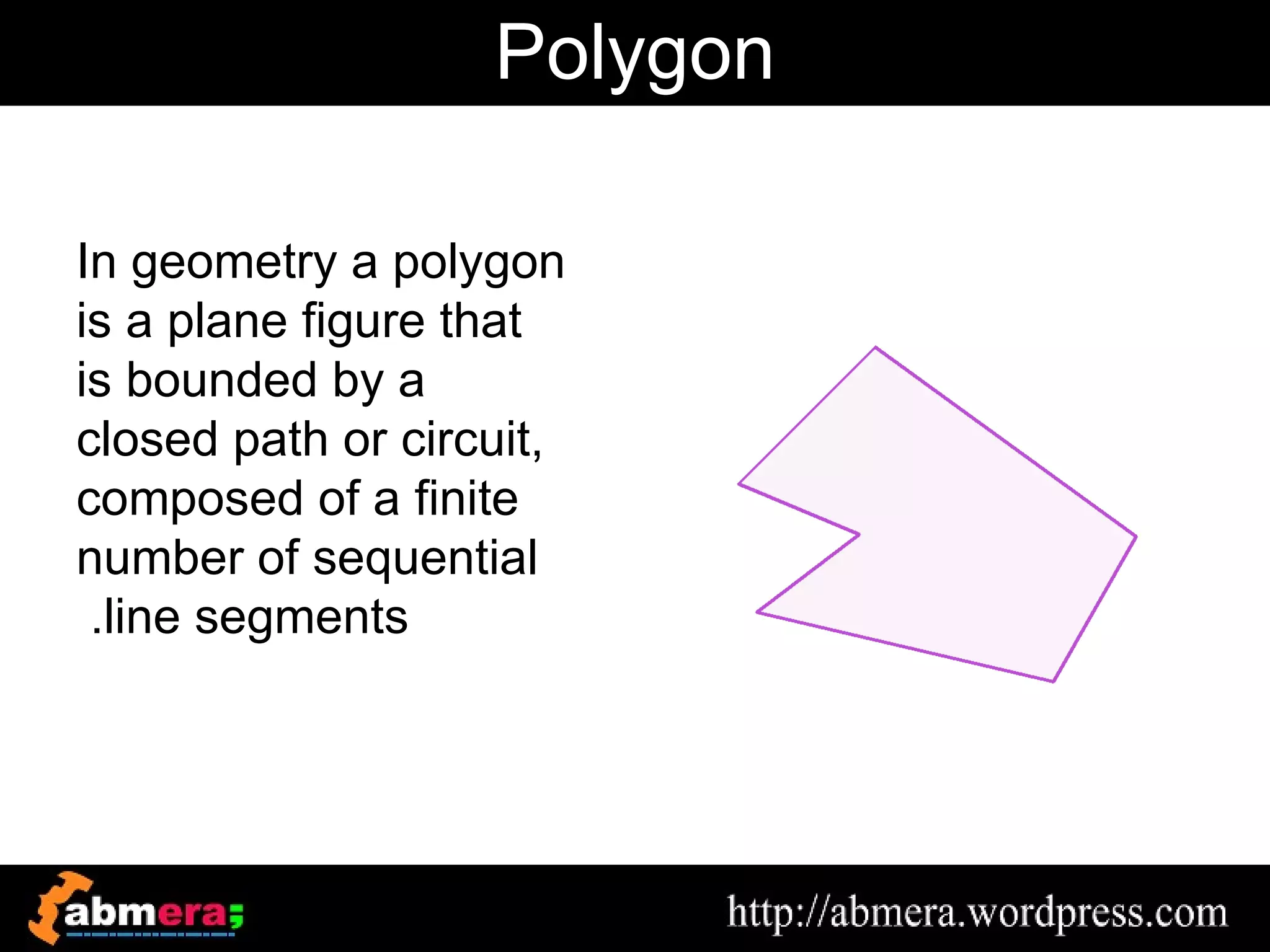
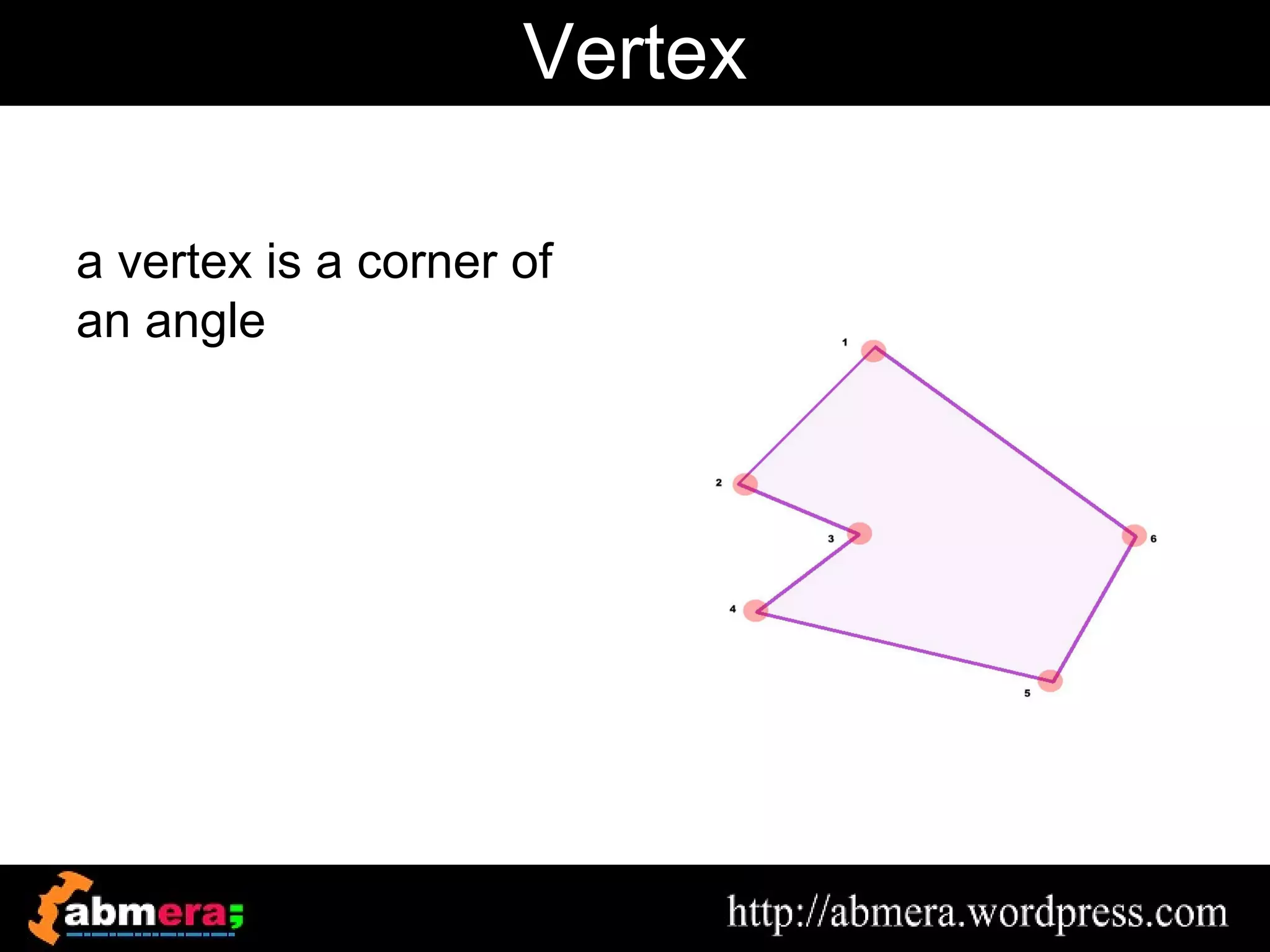
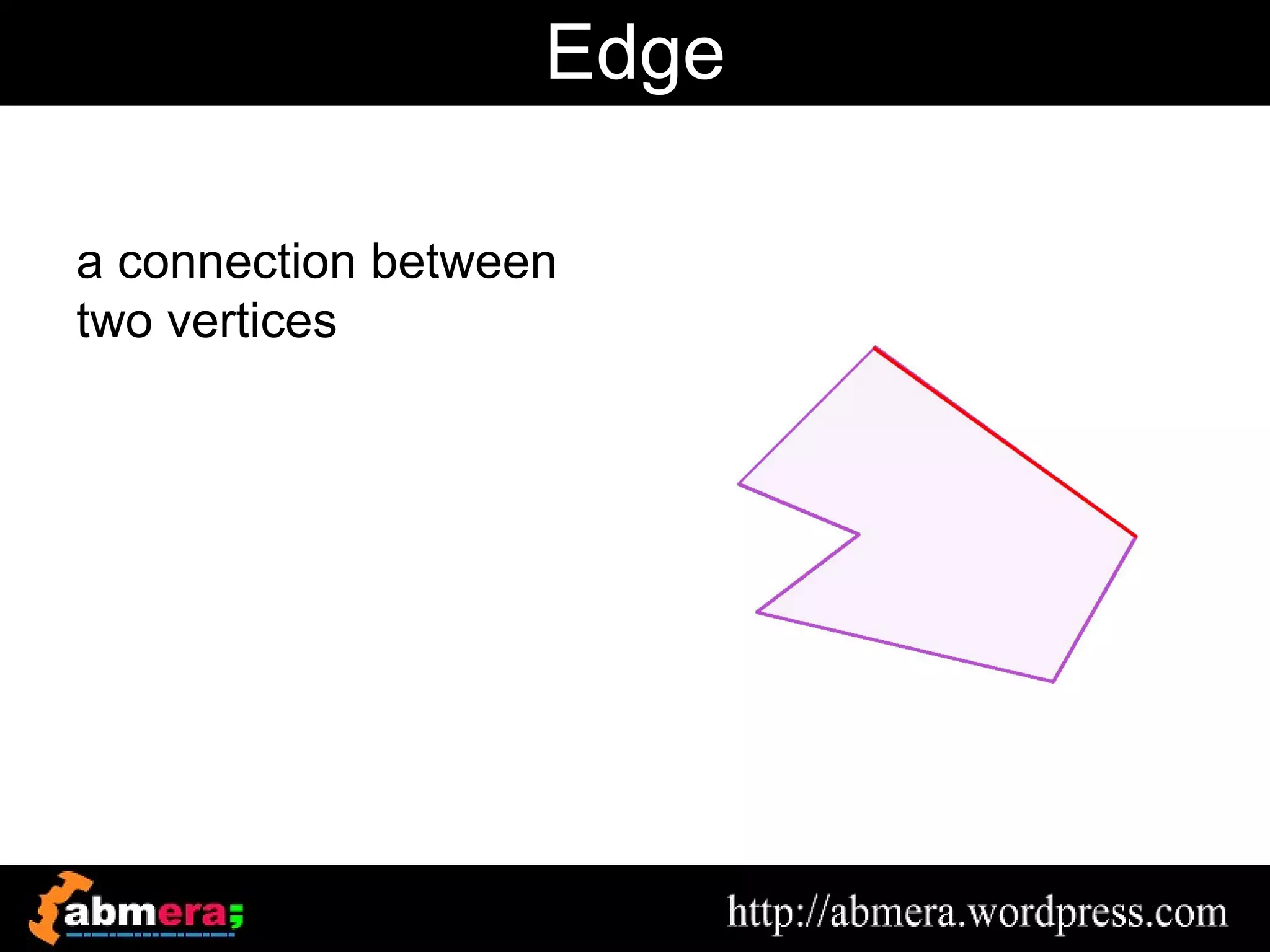
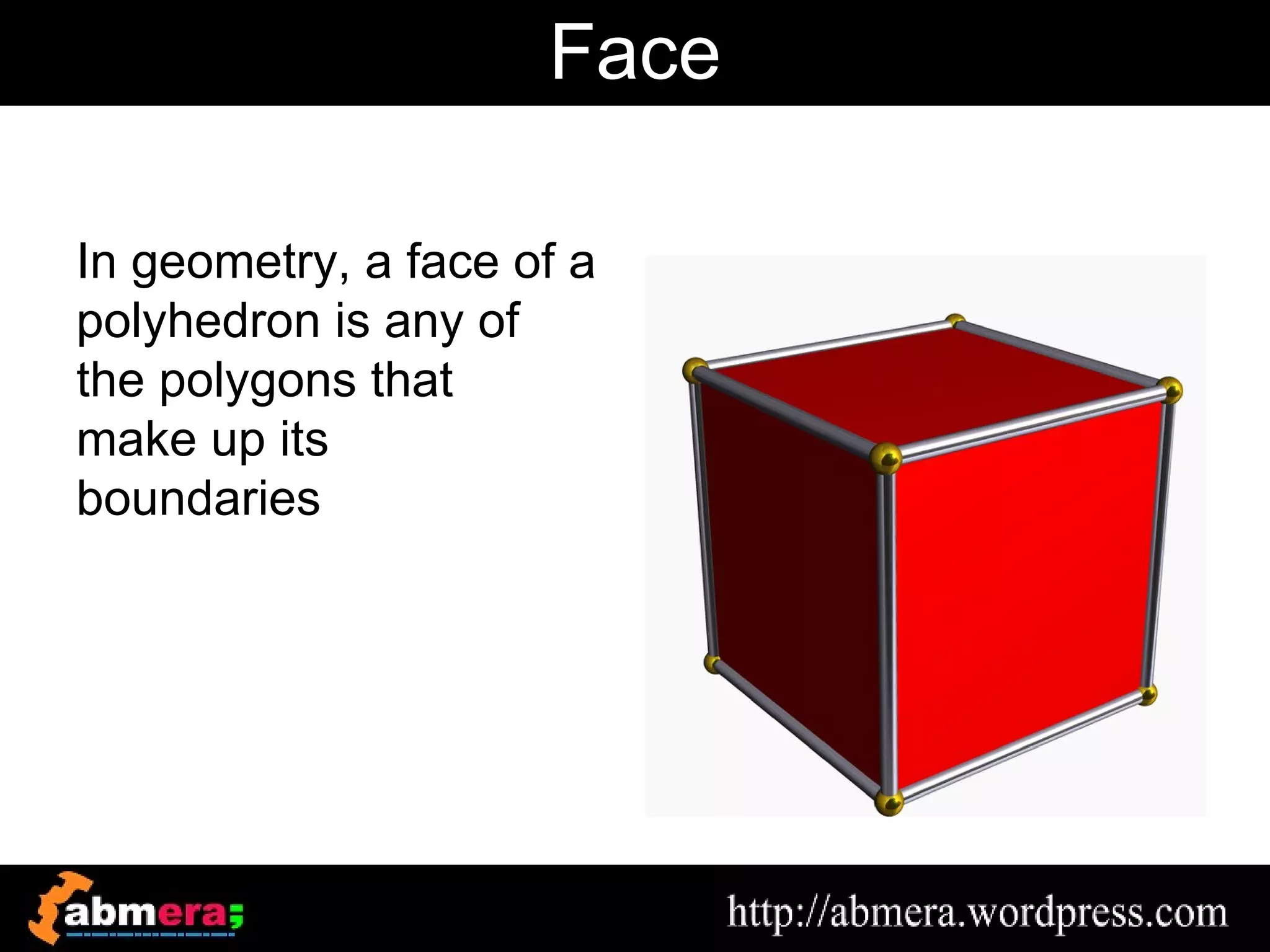
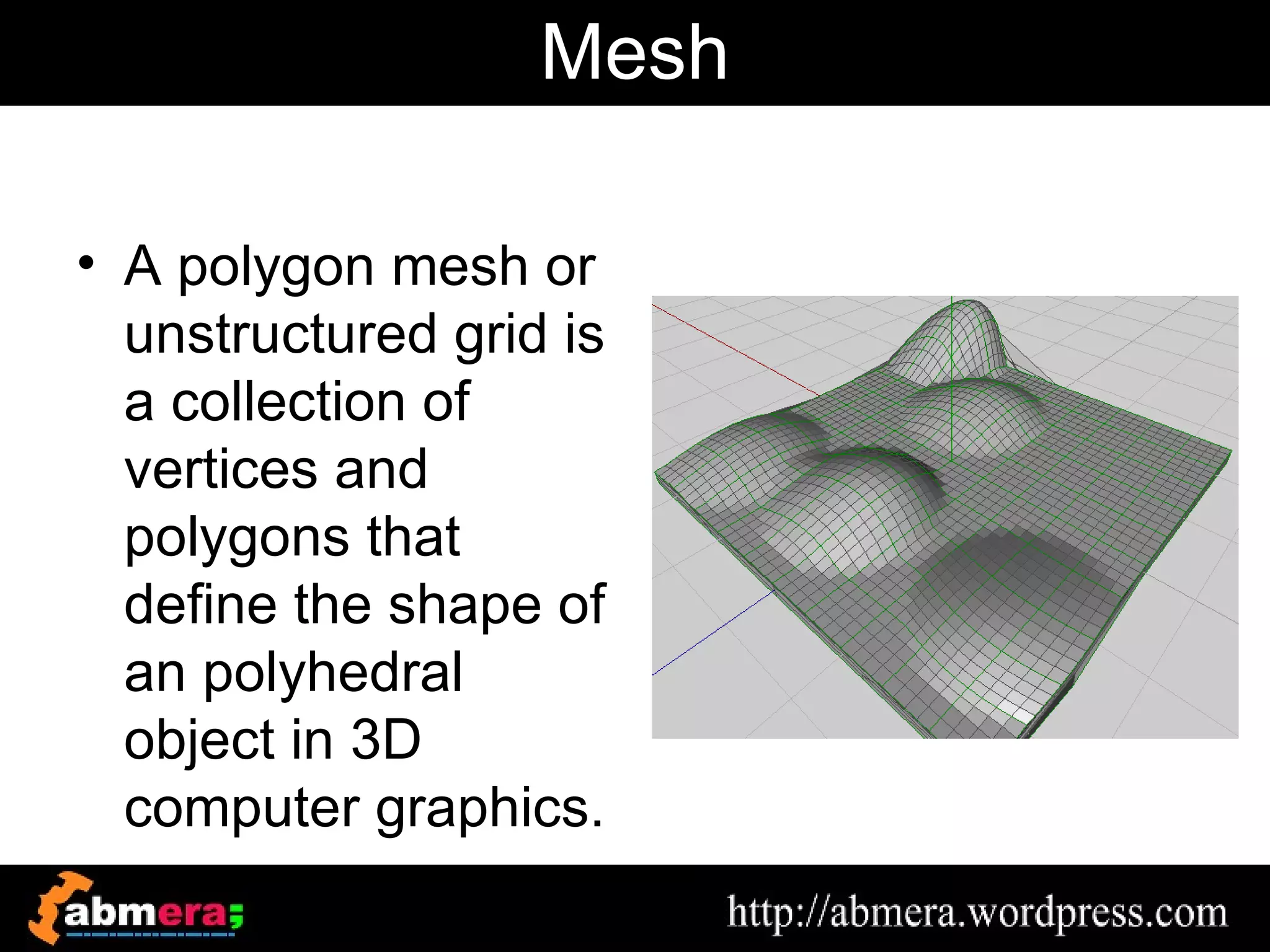
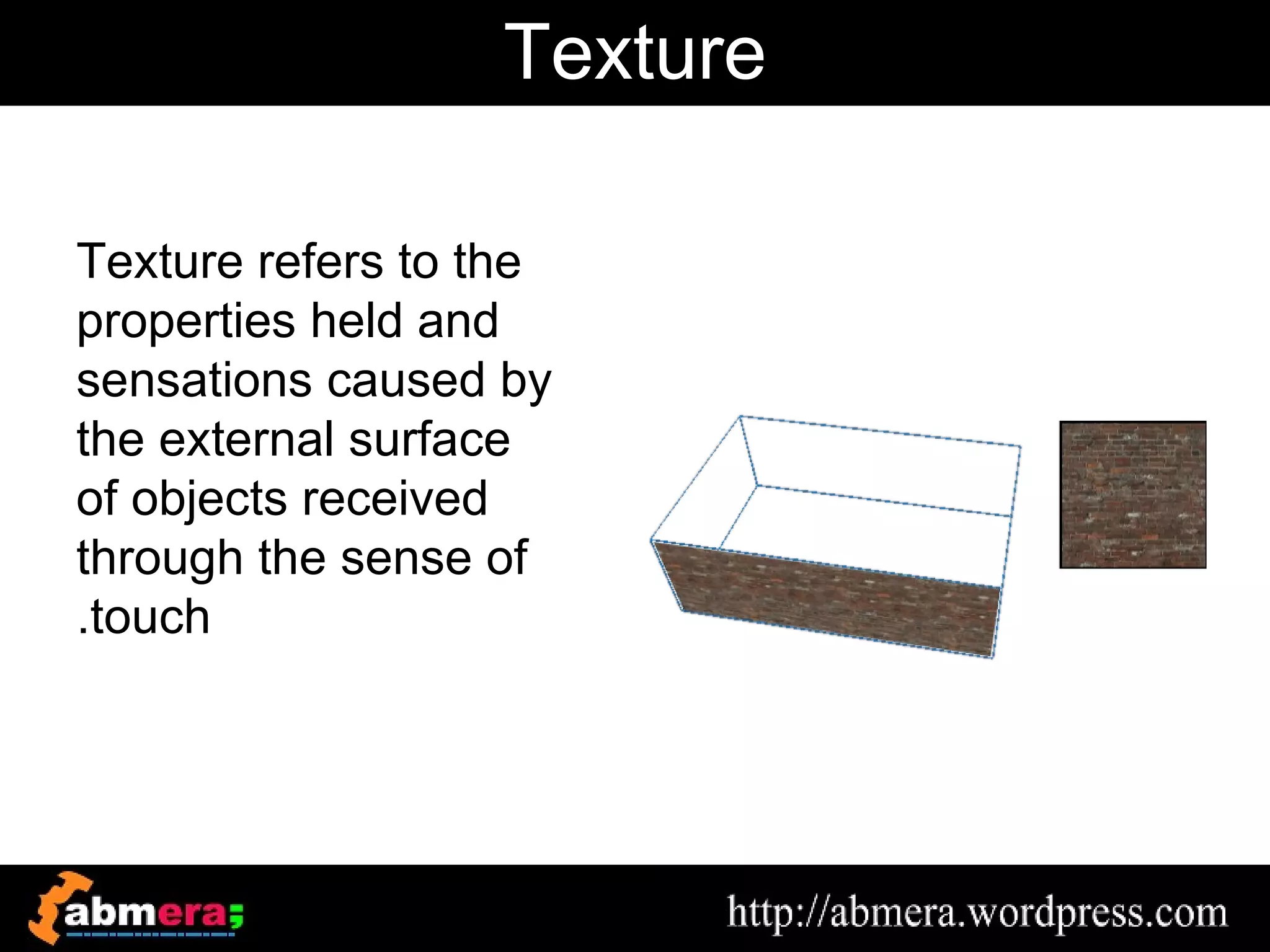
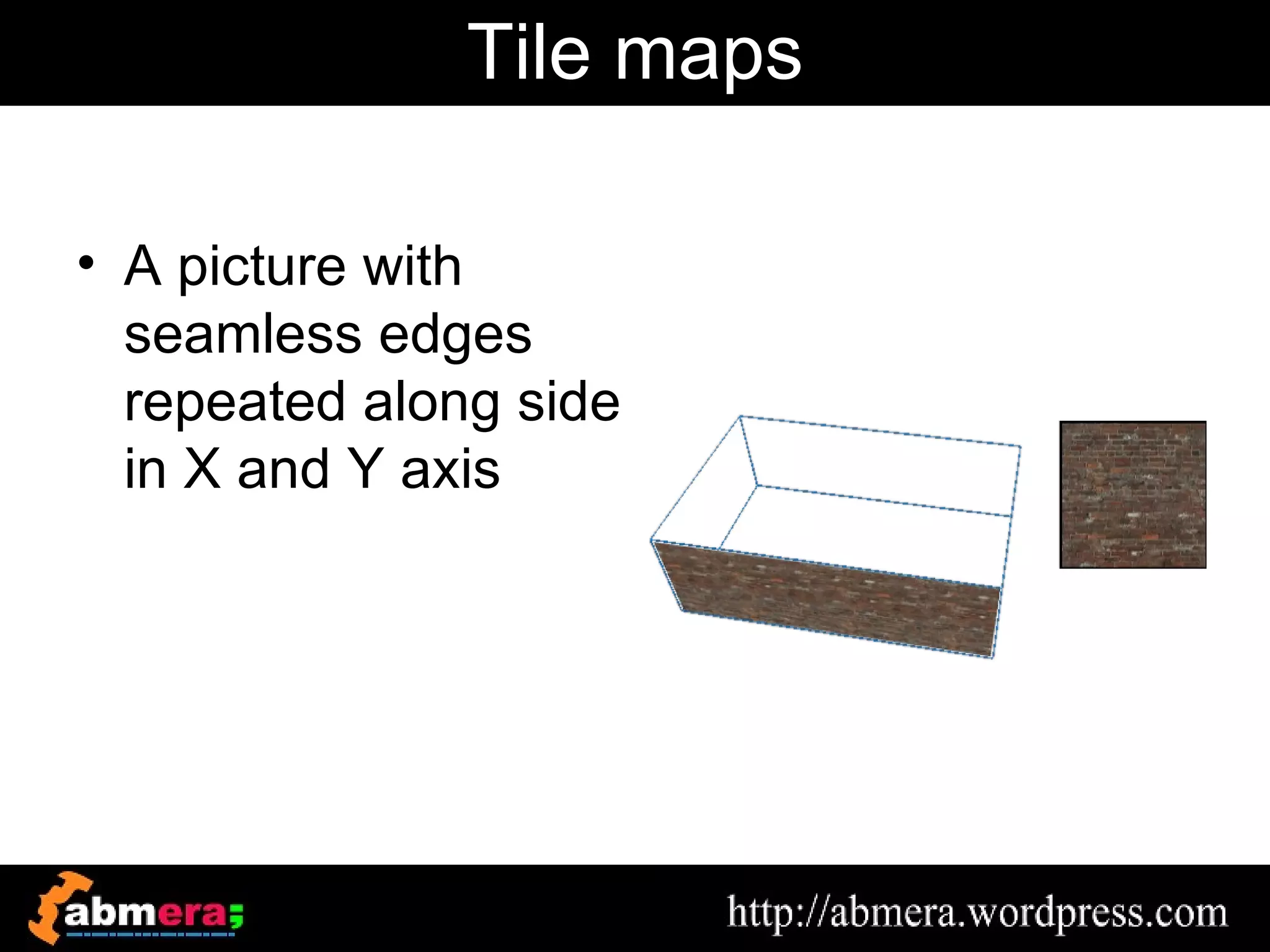
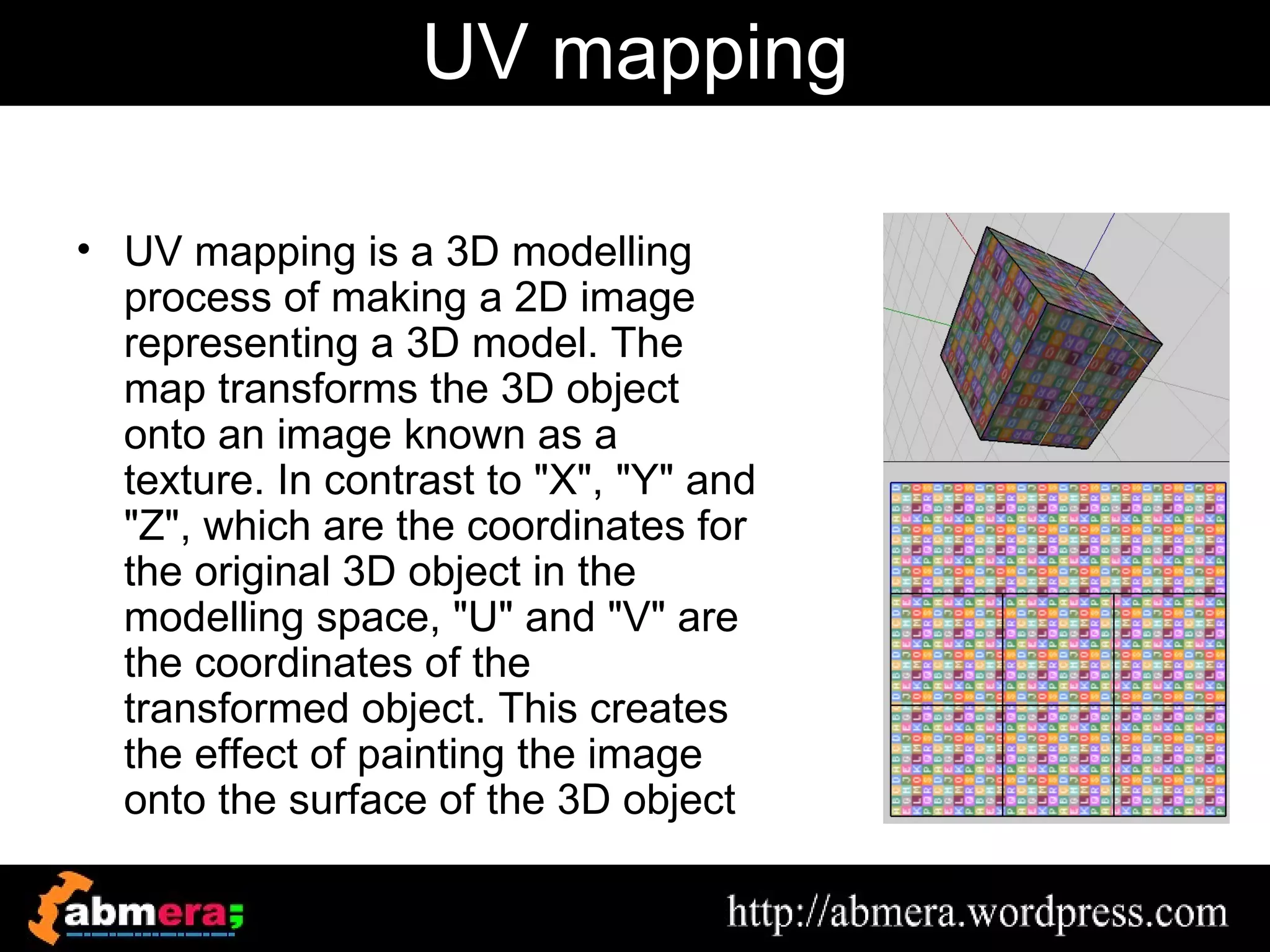
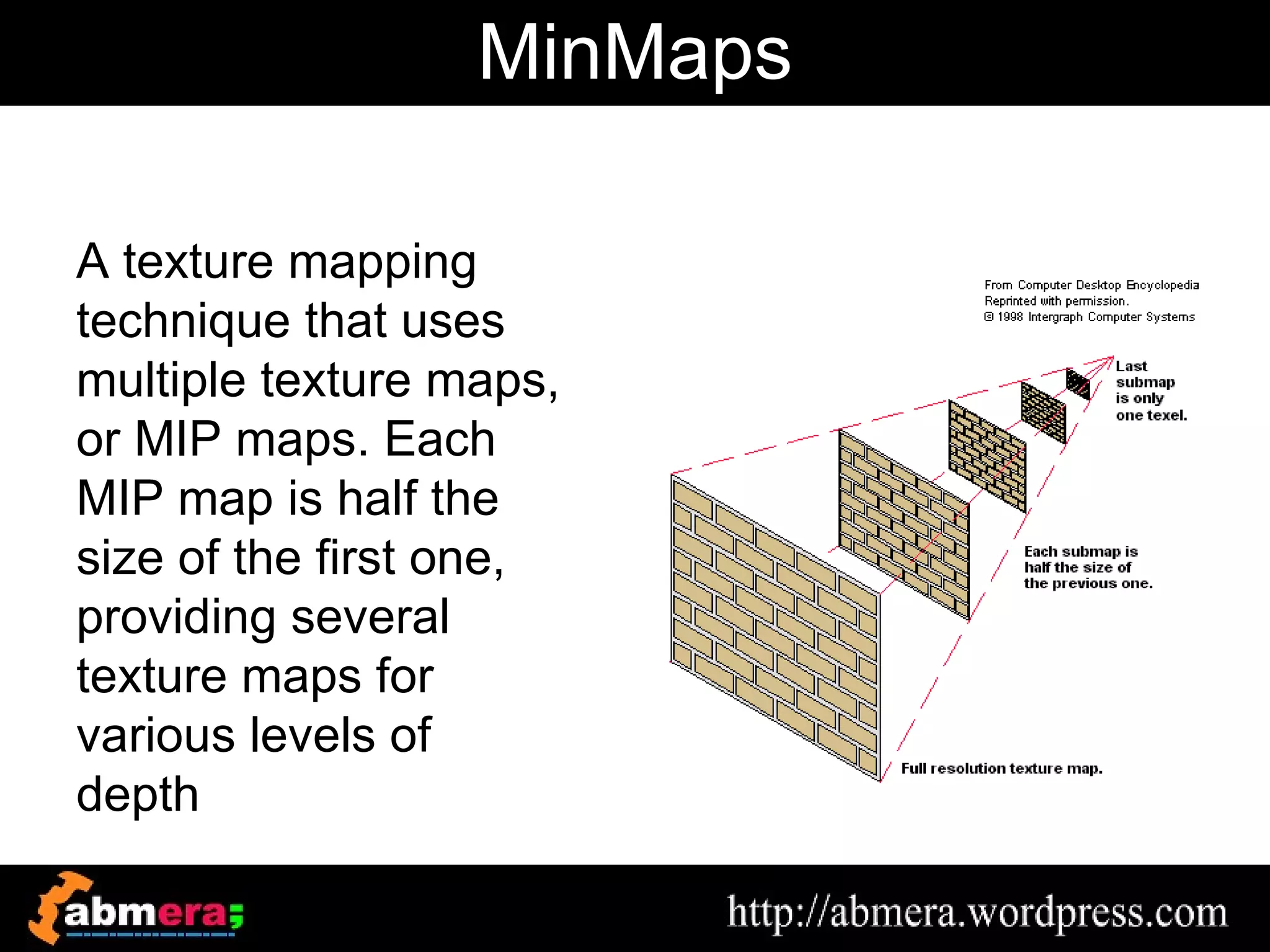
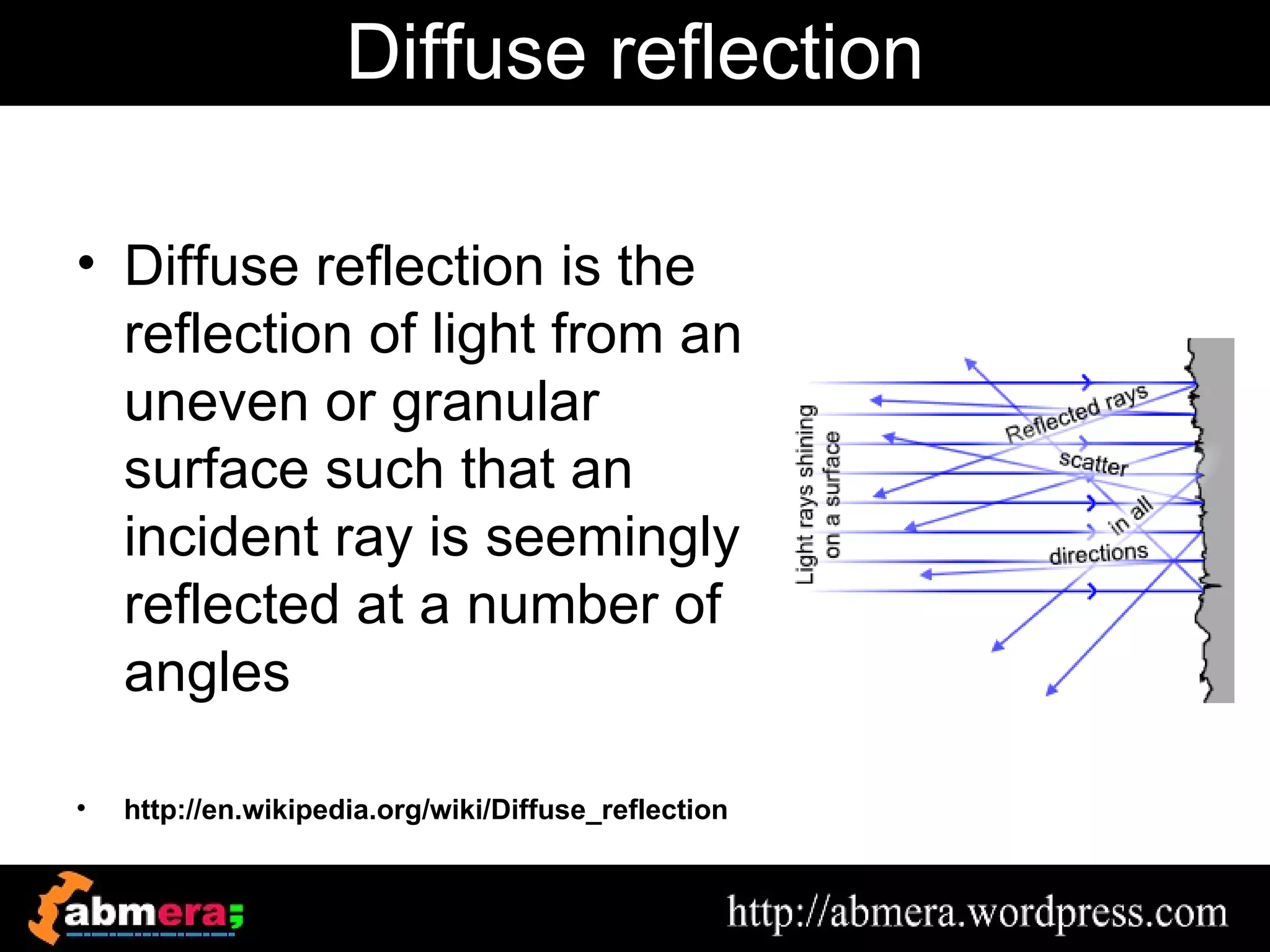
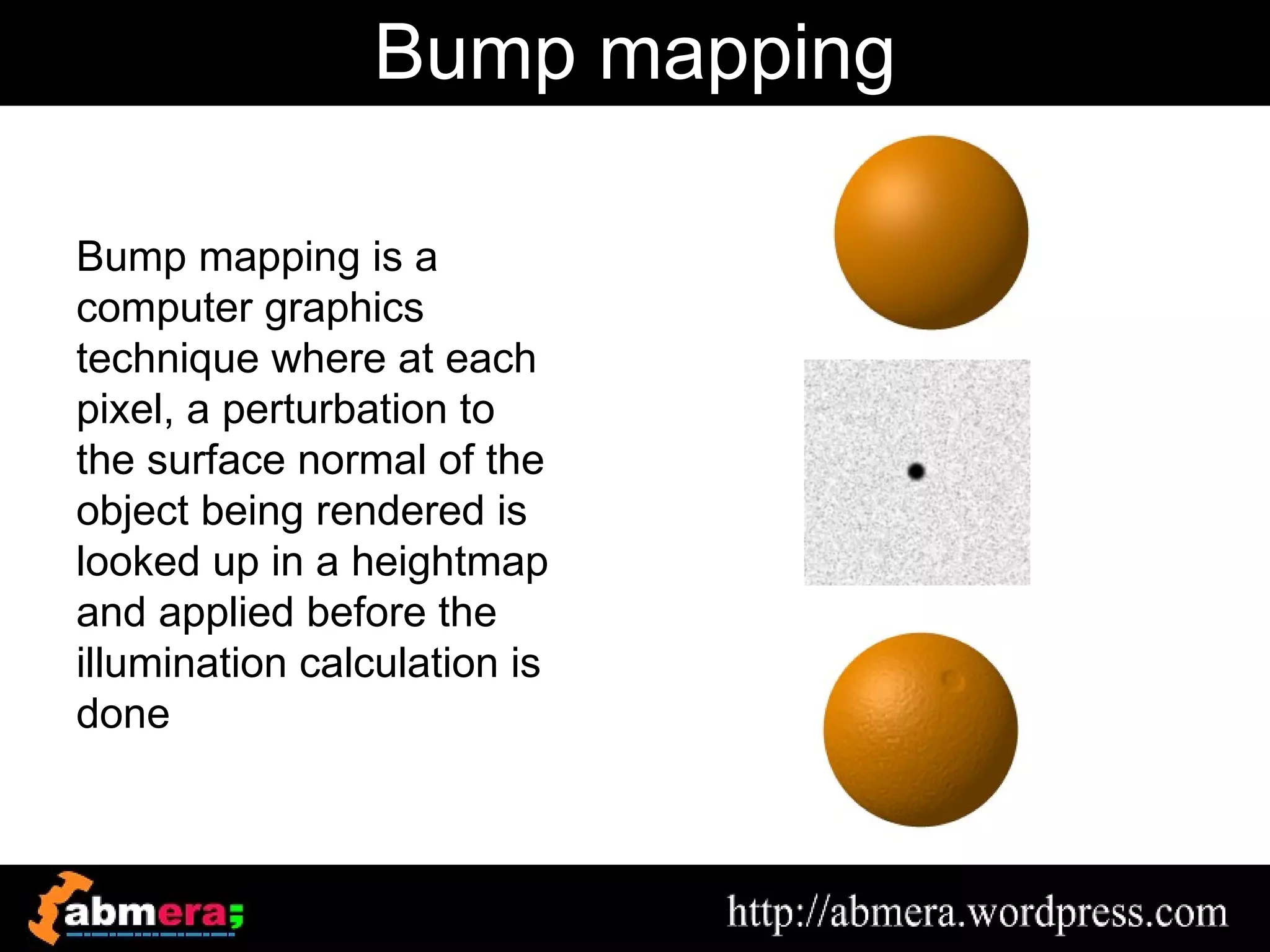
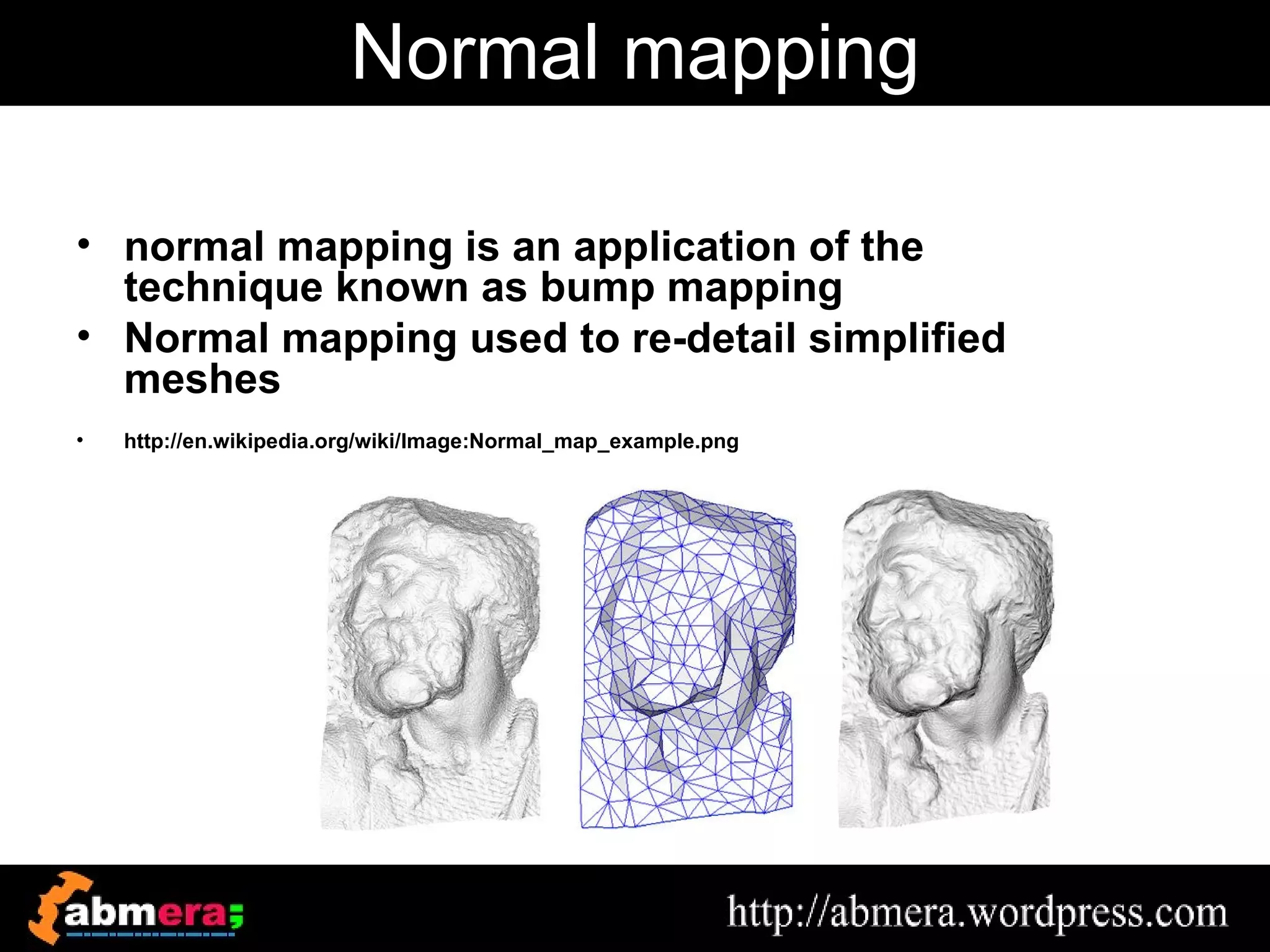
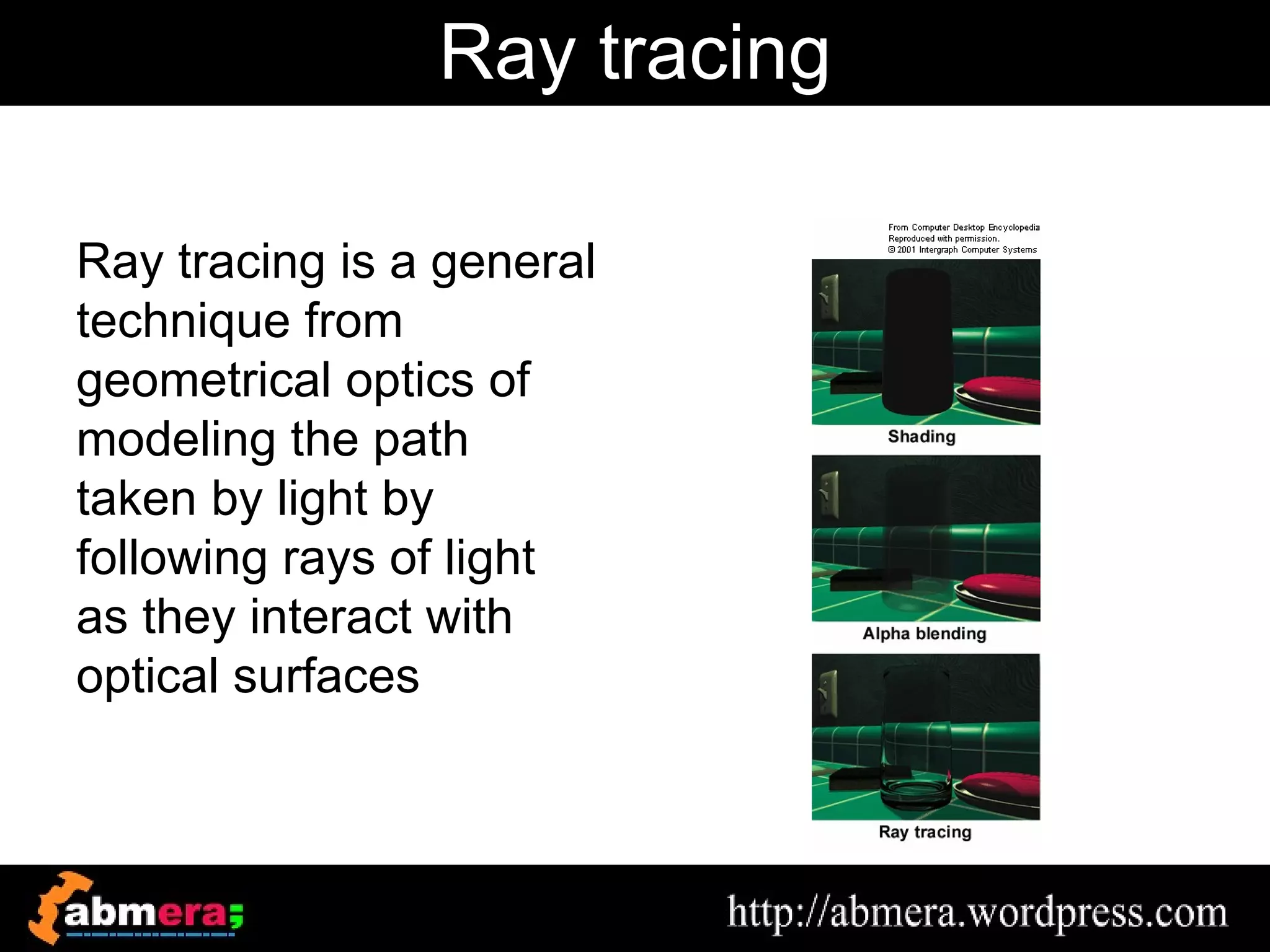
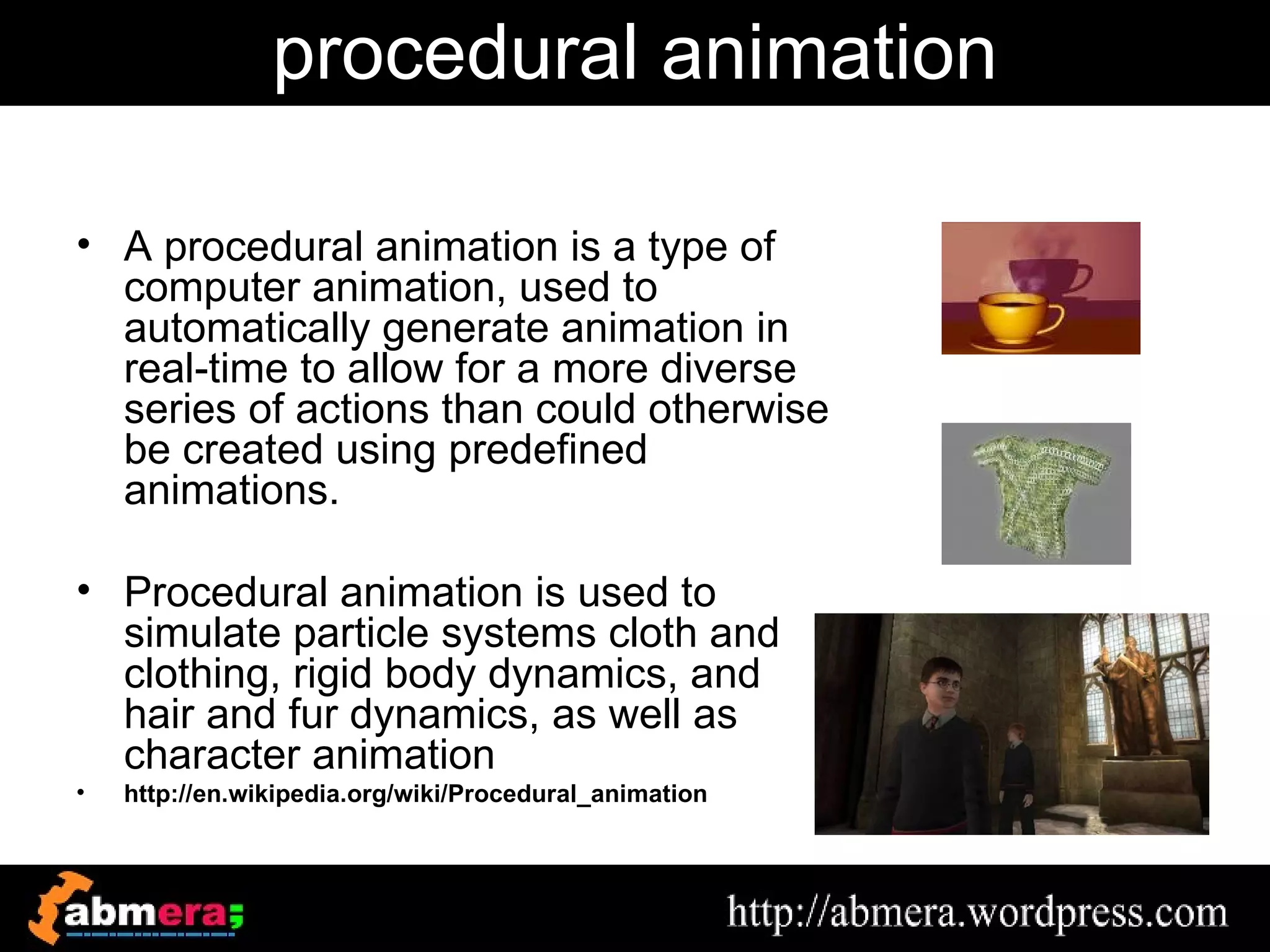
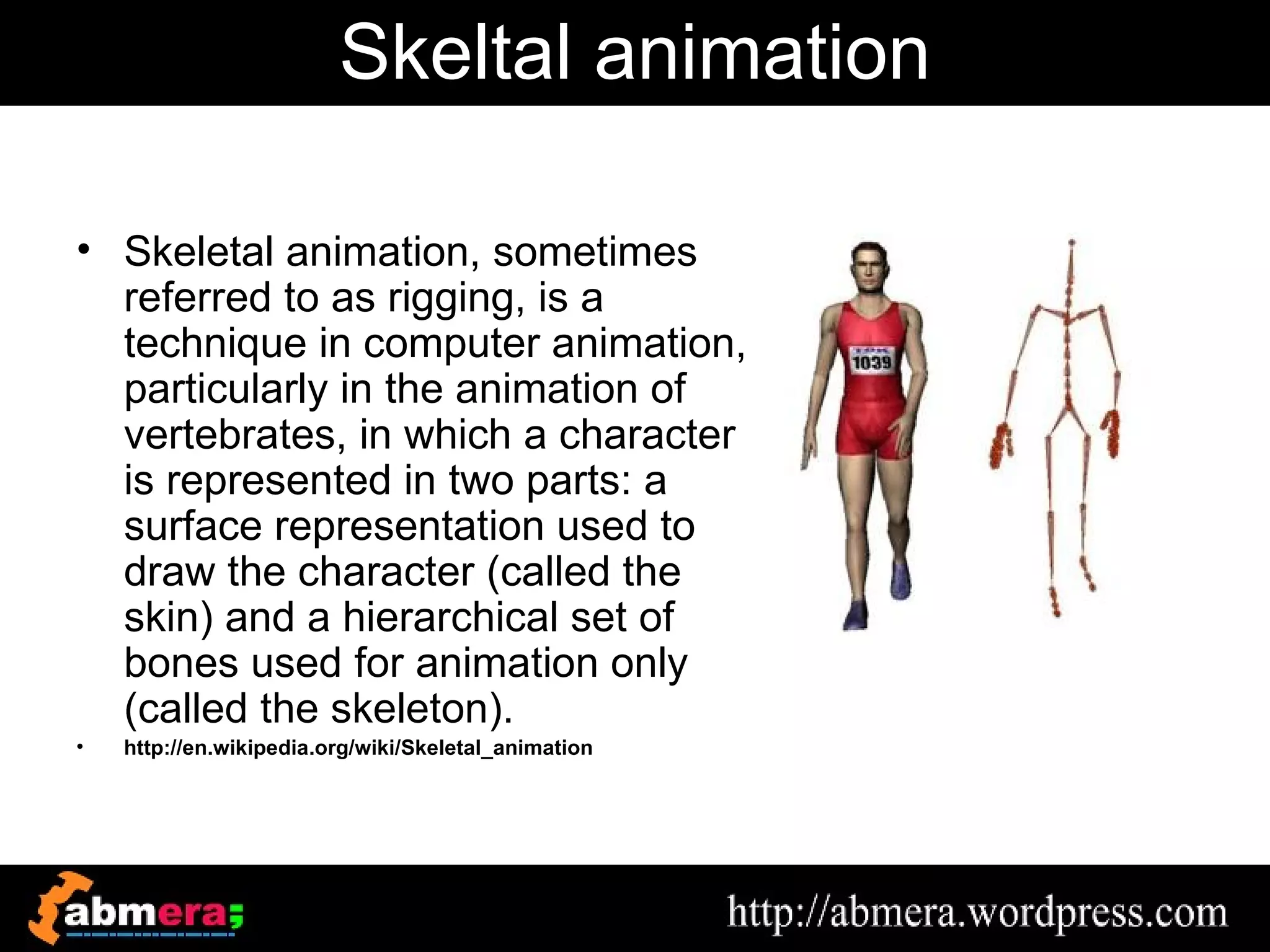
The document outlines various game terminologies and concepts related to computer graphics, including the RGB color model, pixel art, texture mapping, and rendering techniques. It covers essential terminology such as sprites, polygons, models, and animation methods like skeletal and procedural animation. Additionally, it discusses advanced topics like lightmaps, ray tracing, and the role of game engines in video game development.