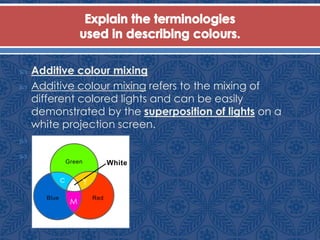
The document defines key color terminology including hue, value, saturation, and luminance. It explains that hue refers to the name of a color, value refers to the lightness or darkness of a hue, and saturation refers to a color's brightness. It also defines additive and subtractive color theories. Additive theory uses projected red, green, and blue lights that combine to create other colors and white light. Subtractive theory uses dyes and pigments that absorb some light wavelengths and reflect others to create colors.