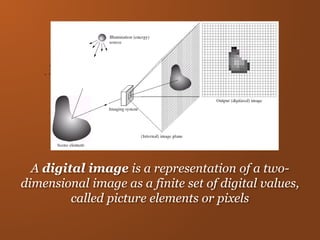
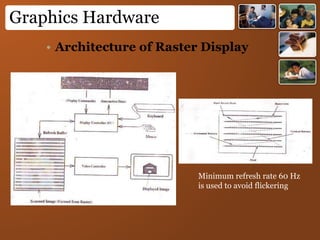
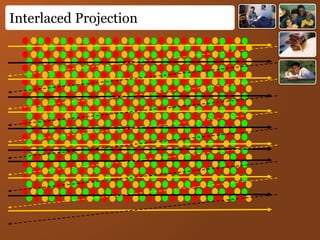
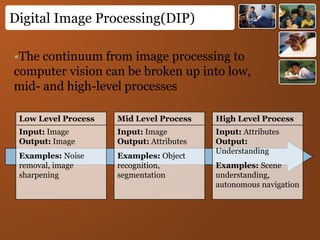
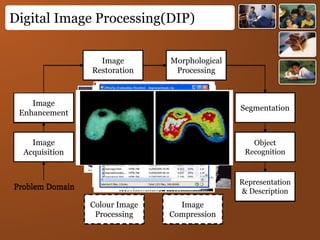
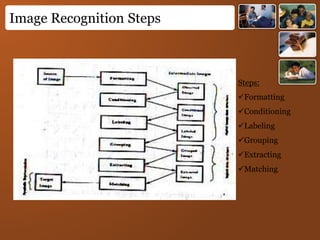
Digital images represent real-world scenes using a grid of pixels, each with a value representing color or intensity. Common file formats like JPEG and PNG use lossy and lossless compression respectively. Images can be manipulated by changing individual pixel values, while graphics are defined by editable primitives. Digital image processing techniques are used to enhance, analyze and understand image content.