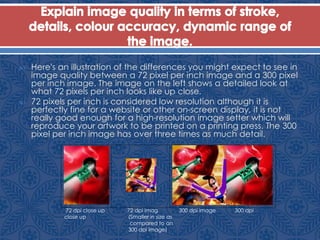
Image quality is determined by factors like sharpness, noise, dynamic range, tone reproduction, contrast, color accuracy and distortion. Sharpness refers to detail while noise is random pixel variations. Dynamic range is the light levels an image can capture. Tone reproduction is the relationship between scene luminance and brightness. Contrast affects loss of detail. Color accuracy and distortion can also impact quality. Software filters like blurring the background can improve an image's quality by making the subject stand out more, though they cannot add new detail. Frequency modulation screening randomly distributes dots to simulate gray levels and keeps dots the same size, varying frequency. It eliminates moiré effects seen with traditional screening. Higher resolution images, like 300 ppi versus 72













![Advantages
The screening of four colors are no longer made with four
different angles as with the traditional screen therefore it
eliminates screening moiré.
FM screening does not create rosette patterns.
Halftone dot sizes can be as fine as 10 micrometres, which
gives at the product a quality comparable to that of
photographic prints.[citation needed]
The effects of misregistration is not completely eliminated, but
the effect is certainly less apparent than in the traditional
screening, this feature is very favorable for printing on rotary
machines where the misregistration is very common due to
effects such as web growth.
The use of FM screening allowed Archant, a UK regional
publisher, to switch to fonts with "tiny holes"; such an "eco-font"
permitted a reduction in ink without turning fine text grainy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap27-140502020143-phpapp01/85/Chap27-15-320.jpg)