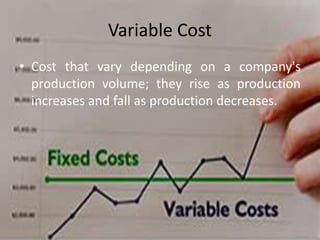
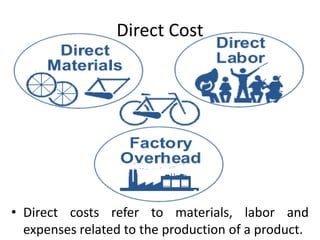
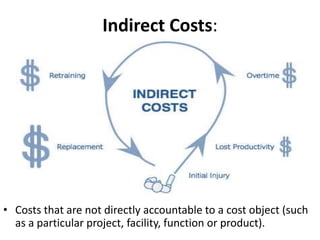
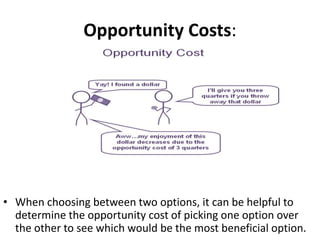
The document presents a comprehensive overview of Project Cost Management (PCM), focusing on its importance in keeping projects within budget through various processes such as cost estimation, budget determination, and cost control. It also outlines different types of costs—sunk, fixed, variable, direct, indirect, and opportunity costs—along with their definitions. The presentation aims to enhance participants' understanding and skills in managing project costs effectively.