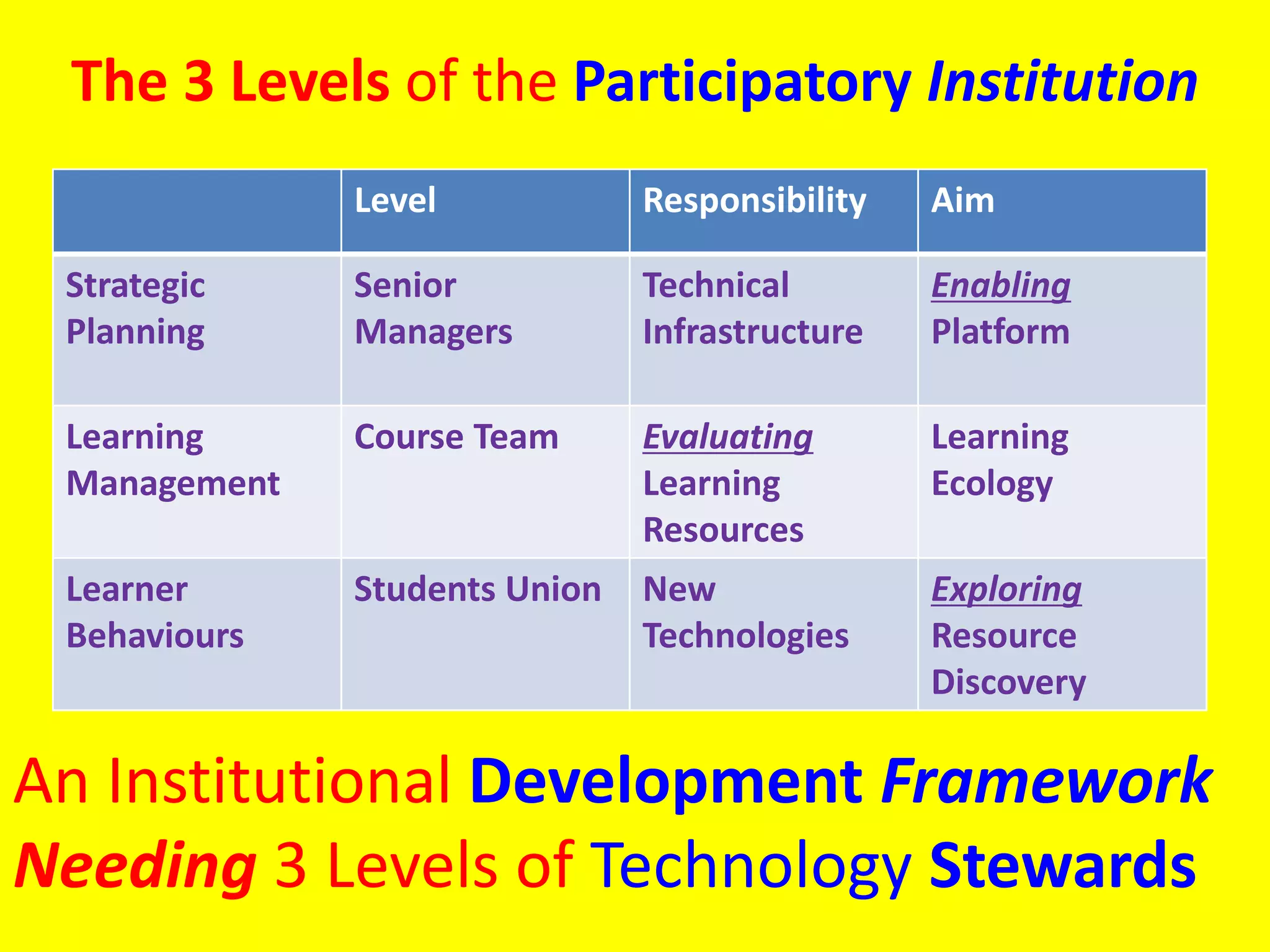
The document discusses modern teaching and learning methodologies, emphasizing the evolution from pedagogy to heutagogy, which advocates for self-determined learning. It highlights the role of technology and social media in education and the necessity for adaptive teaching methods that incorporate learner involvement and collaboration. Additionally, it proposes new learning infrastructures that prioritize engagement and innovative design over traditional educational frameworks.