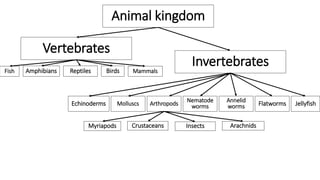
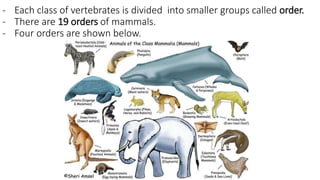
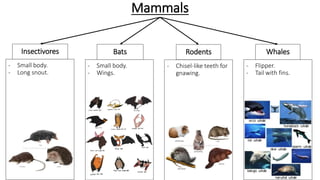
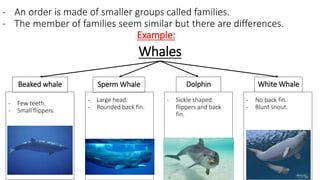
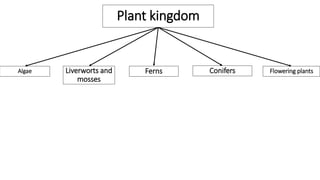
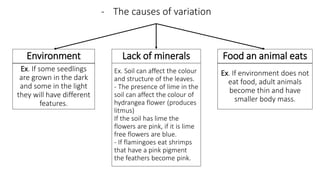
This document discusses classification and variation in biology. It covers the kingdoms of animals and plants, describing some of the major phyla and classes within each. For animals, it describes vertebrates like mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish. For plants it discusses algae, mosses, ferns, conifers and flowering plants. It also discusses the concept of variation, both between and within species, giving examples of how environment and food can cause variation.