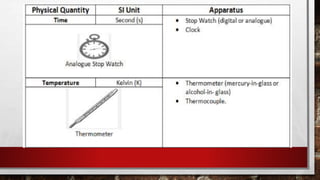
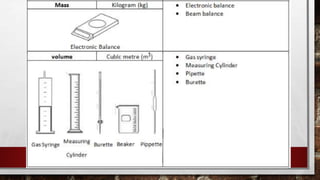
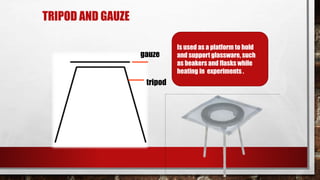
This document provides information about lab safety rules, common safety symbols seen in laboratories, and descriptions of various laboratory tools and equipment. It lists 10 lab safety rules but does not specify them. It also describes safety symbols for substances that are explosive, flammable, corrosive, toxic, radioactive, pose environmental dangers, or are oxidizing, gases under pressure, or health hazards. Finally, it provides the names, uses, and simple diagrams of common lab tools including test tubes, beakers, conical flasks, Bunsen burners, tripods and gauzes, clamps and stands, funnels and filter paper, round-bottom and flat-bottom flasks, separating funnels, and delivery tubes.