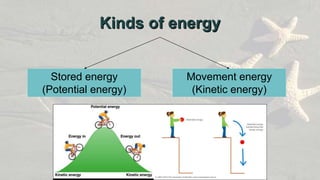
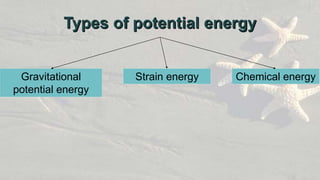
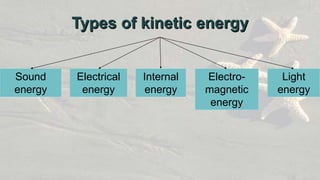
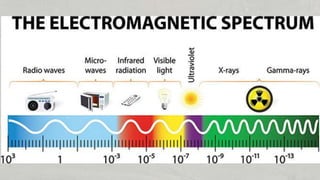
Energy exists in many forms including potential, kinetic, chemical, and electromagnetic. Potential energy is stored energy and includes gravitational potential energy from an object's position and strain energy stored through deformation. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion and includes sound, electrical, internal, electromagnetic, and light energy. Energy can change forms and is never lost or destroyed, though some is always wasted as heat. Common sources of energy include both renewable resources like sunlight and non-renewable resources like fossil fuels.